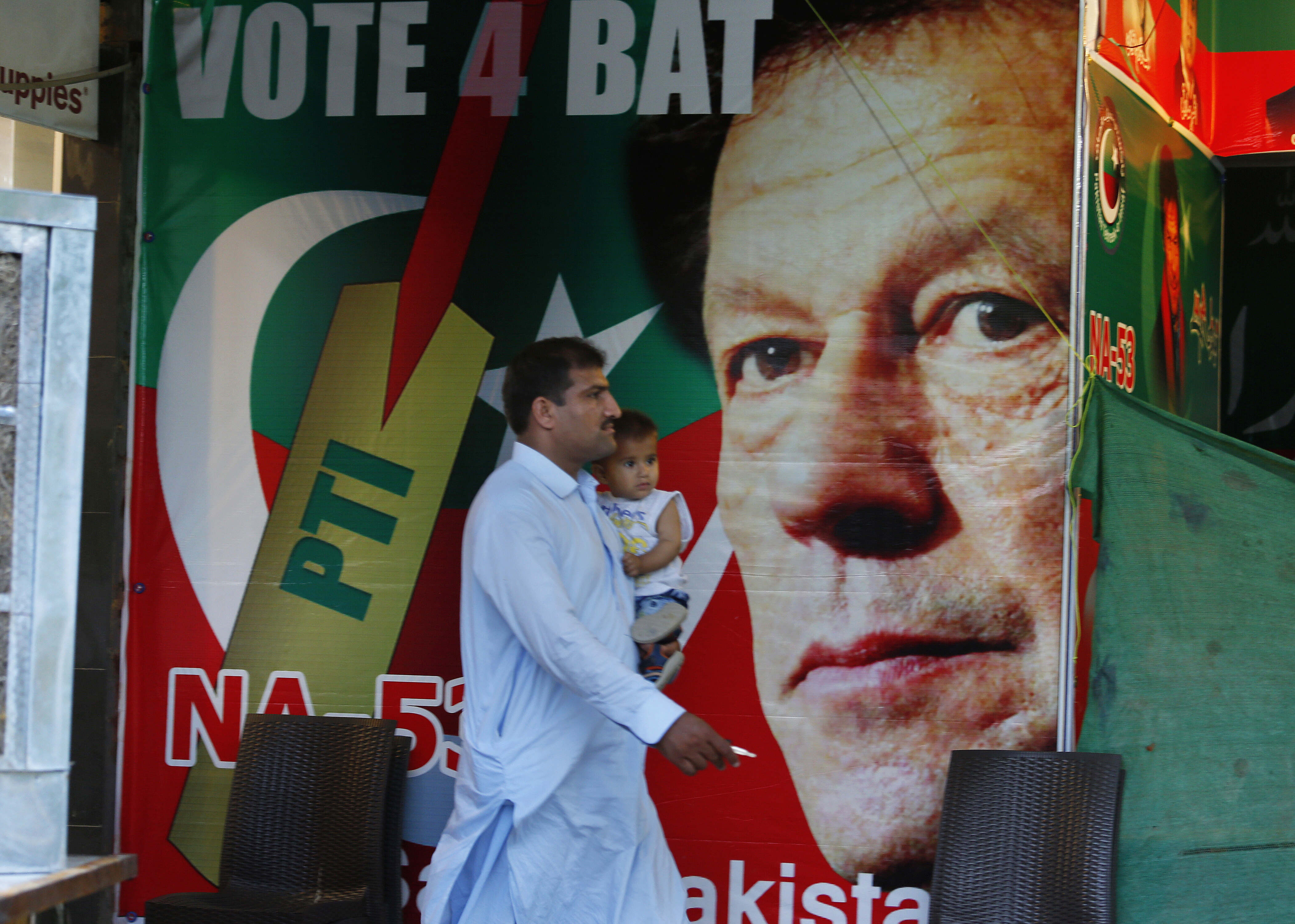
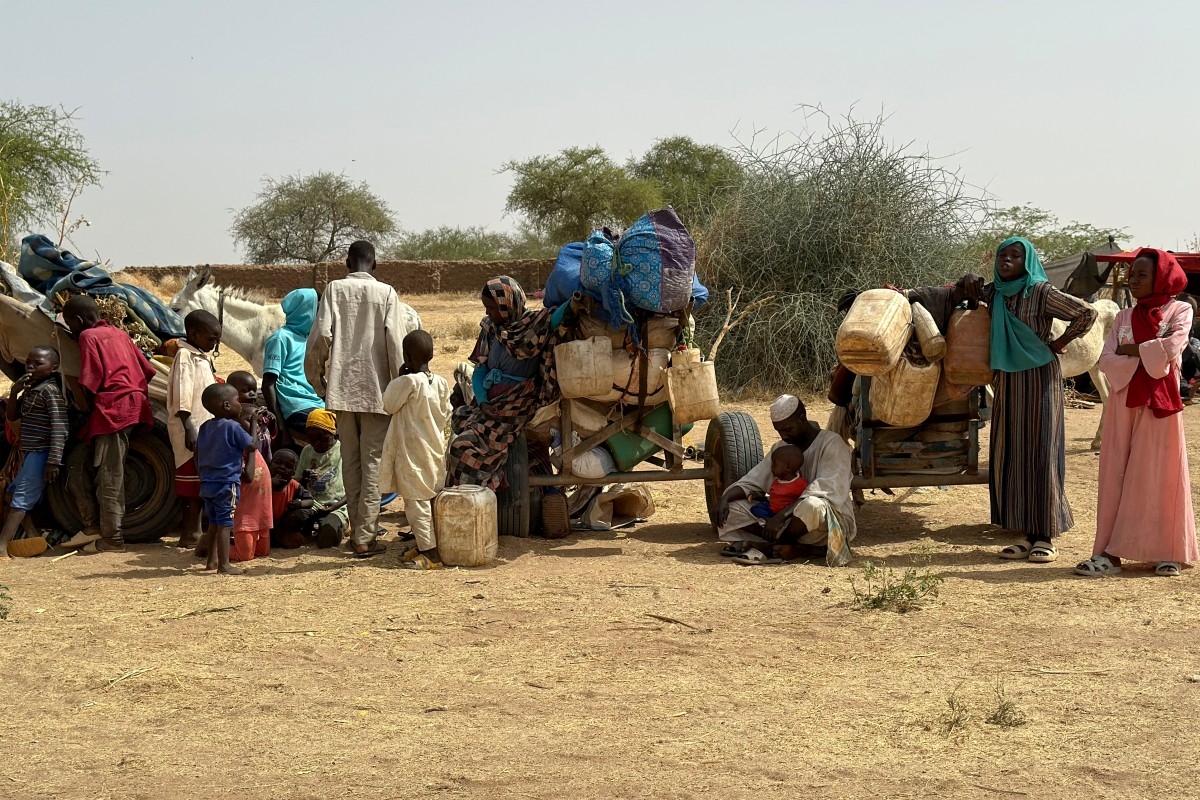
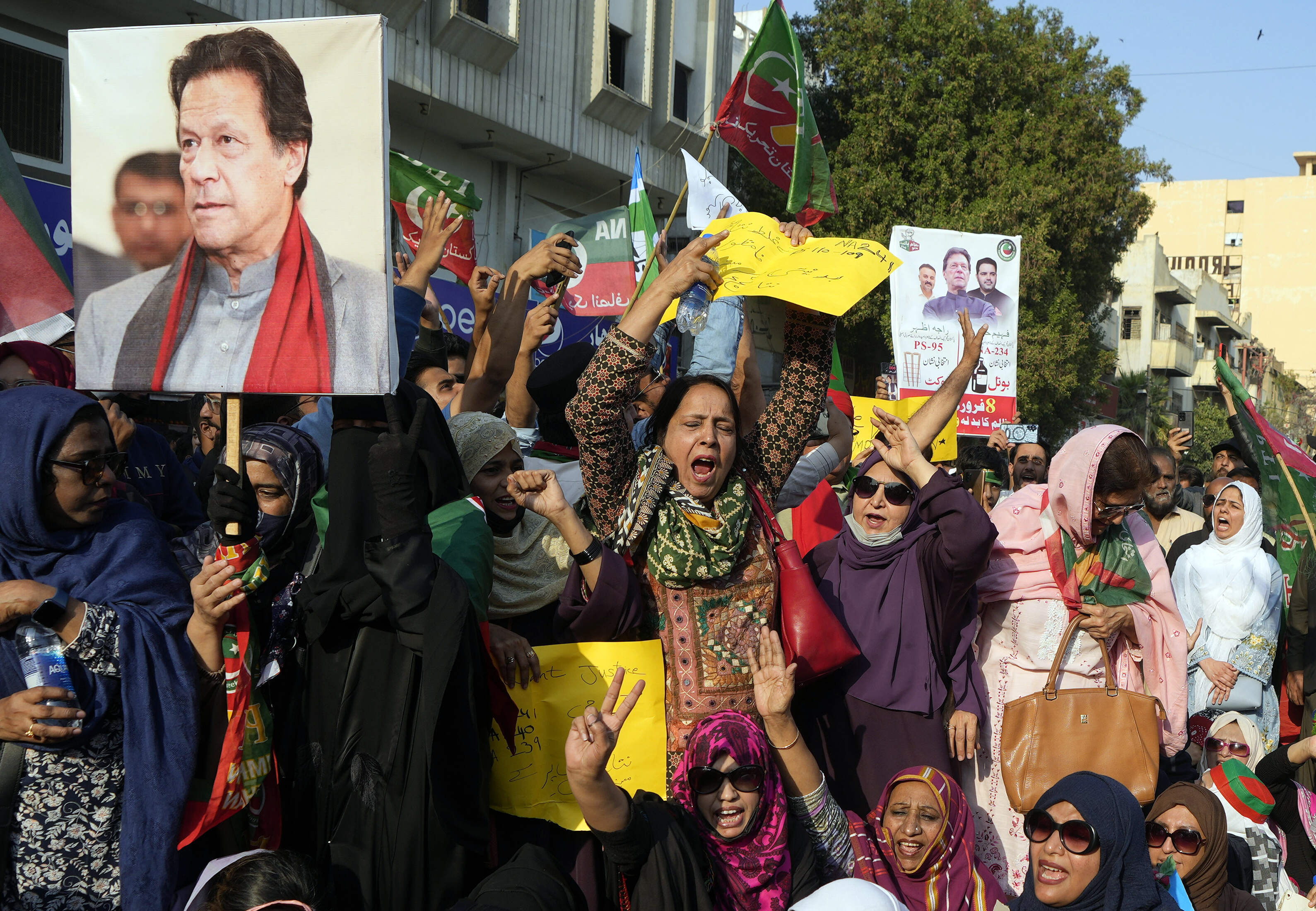
As the chapters of Pakistan's 2024 elections unfolded, transforming the streets into a vivid canvas of political symbols—ranging from tiger-stuffed toys perched atop campaign vehicles representing the Pakistan Muslim League (PMLN) to arrow logos painted on walls referring to the Pakistan Peoples Party (PPP)—the notable absence of posters featuring the popular former Prime Minister, Imran Khan, and the scarcity of flags representing his party, Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaf (PTI), left a striking gap in the narrative.
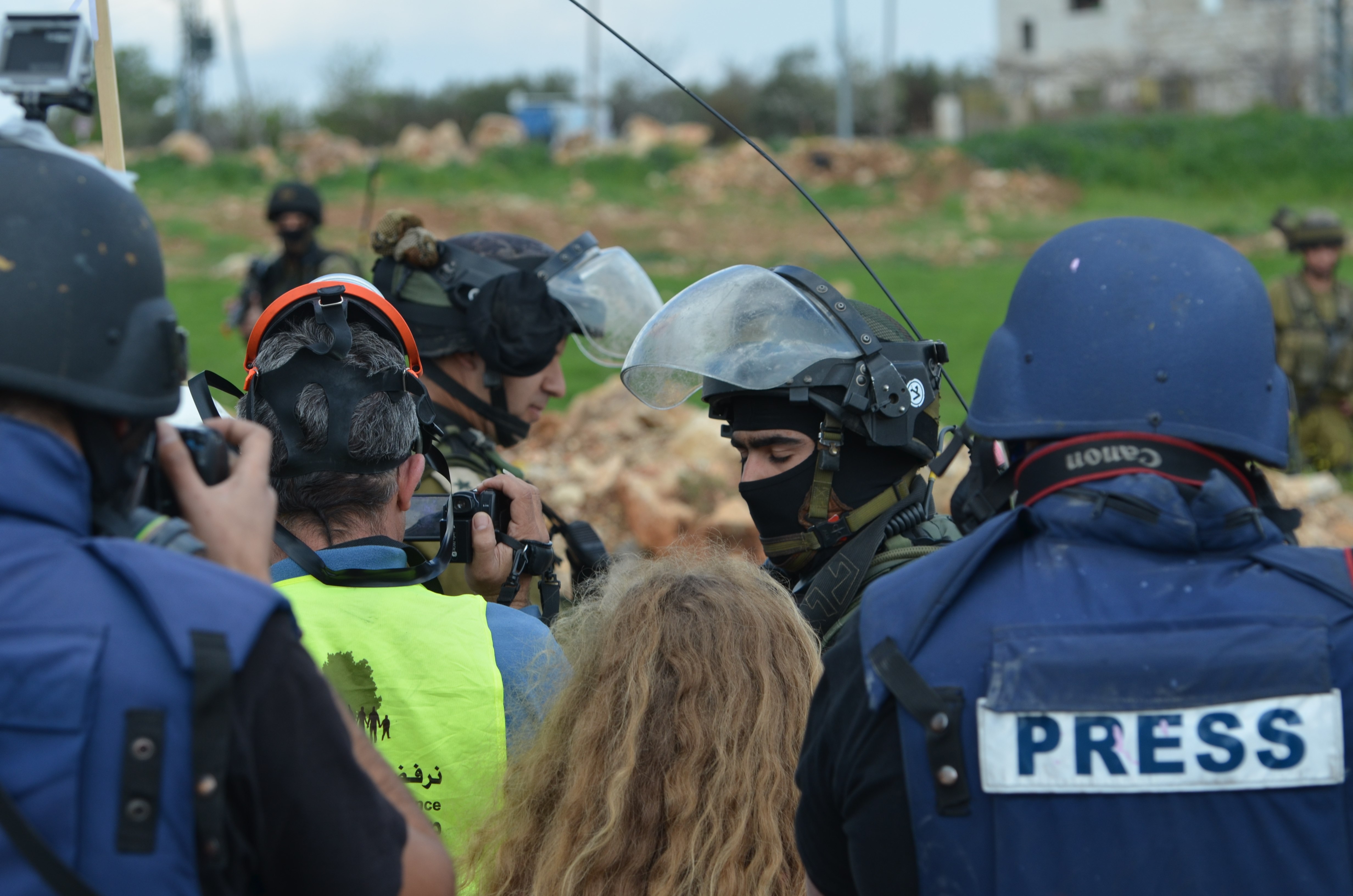
This absence, evident not only in public spaces like lamp posts and billboards but also on national television screens, showed a deliberate control influenced by media censorship.
numerous Pakistani journalists revealed that they had received instructions from an official within the country's influential military to enforce this almost comprehensive ban on the political party's coverage leading up to the elections
Understanding Media Censorship in Pakistan
The first signs of these restrictions emerged on March 6, 2023, after Khan's strong speech against the military. The imposition of restrictions heightened notably as riots broke out following his arrest on May 9th, 2023. In a complicated relationship with Pakistan's military, Khan finds himself banned, with the military's influence contributing significantly to the decision. No longer holding the leadership position of his party, he continues to be a significantly popular political figure in Pakistan, even while in prison and barred from contesting elections.
After his arrest, a shroud of silence enveloped the Pakistani media. But, as the election campaign season progressed, these restrictions intensified. Media channels were explicitly prohibited from showcasing the flags of PTI and airing any of their prior campaigns. Affiliated candidates had independent status, while the media consciously avoided acknowledging their connections with Imran Khan's party. In an exclusive report by Al Jazeera, numerous Pakistani journalists revealed that they had received instructions from an official within the country's influential military to enforce this almost comprehensive ban on the political party's coverage leading up to the elections.
In the Spotlight: Case Studies of Media Censorship in Pakistan
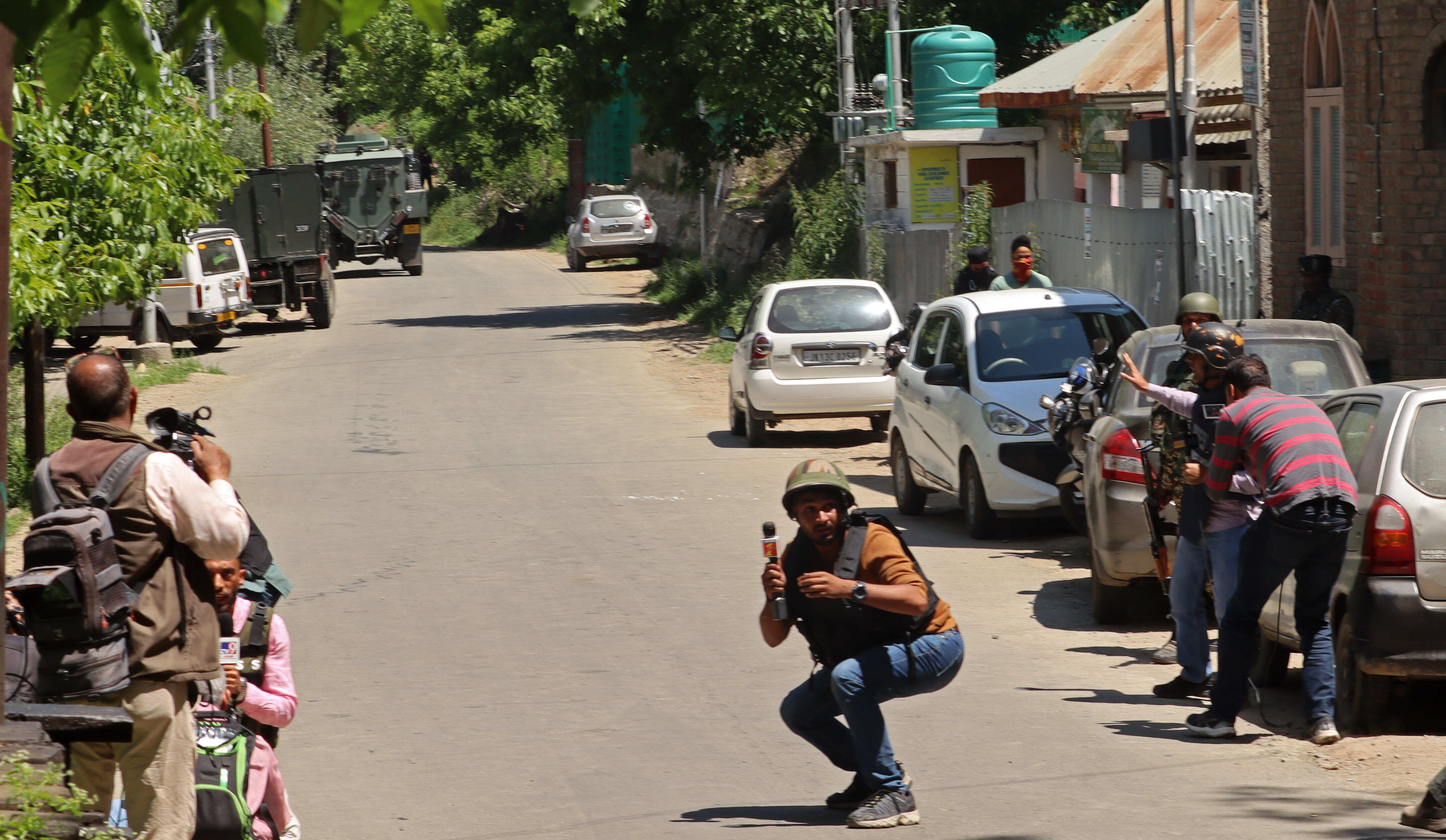
On the day of the elections, February 8, 2024, a journalist on the national Pakistani channel, Express News, posed the question, "So who will win, the tiger or the arrow?" Hinting at a conscious decision to favour or acknowledge only these two parties (PMLN and PPP), the journalist intentionally avoided independent candidates associated with Khan, who are leading in the final results.
This reliance on other platforms indicates a perceived lack of space for critical discourse domestically, highlighting the importance of a robust and open media environment for a thriving democracy and the free exchange of ideas.
Such a controlled media environment during election campaigns limits the public's access to diverse viewpoints, hinders informed decision-making, and undermines the principles of fair and transparent elections. Such restrictions can skew the narrative in favour of one party, suppressing dissenting voices and raising questions about the authenticity of the electoral process. A vibrant and independent media is essential for fostering a democratic society, and any attempts to curtail its influence can have far-reaching consequences for the democratic values that elections aim to uphold.

However, on the same day, during a broadcast on another prominent news channel, ARY News, notable journalists, Iqrar Ul Hassan and Waseem Badami, made mention of 'PTI' and 'Imran Khan' while discussing the election results. They specifically discussed individual candidates associated with the party, including well-known figures like Zain Qureshi, the son of PTI's senior vice president, Shah Mahmood Qureshi. These candidates were impossible to ignore due to their widely recognised identities. Additionally, the journalists analysed the constituencies in electoral success, drawing comparisons to Imran Khan and his party's victories in the 2018 elections. A notable incident occurred in July 2023 when ARY News faced severe criticism for blurring Khan's photo during the live telecast of the International Monetary Fund (IMF) meeting.
As the ban on mentioning Khan's name or displaying his picture grew more pervasive in Pakistani media, local journalists turned to international publications to express their opinions and reactions. For example, back in June 2023, Hamid Mir, a Pakistani TV news anchor and author, wrote an opinion piece for The Guardian titled "I literally cannot say Imran Khan’s name on Pakistani TV—this madness has to end," where he mentioned the challenges of even openly criticising him on air. Pakistani journalists have also contributed to Al Jazeera's podcast platform "The Take" and written opinion pieces to openly express their views on Khan during the current situation. This reliance on other platforms indicates a perceived lack of space for critical discourse domestically, highlighting the importance of a robust and open media environment for a thriving democracy and the free exchange of ideas.
When Pakistani media avoided covering PTI and Imran Khan but prominently featured PMLN leader, Nawaz Sharif, suggesting an increasing likelihood of him forming the next government, it created the perception of biased coverage. On Feb 11, Kamran Khan, President and Editor-in-Chief of Dunya Media Group, expressed concern in a tweet featuring a screenshot of "The News" newspaper that carried the headline, "Public's Decision for Nawaz's Vision. Nawaz Sharif, the PM."
Tweet: "Just 48 hours before the election, Nawaz Sharif's PMLN spent hundreds of millions of rupees to enact this paid ad of deceit, lies, and outright deception on the front pages of almost every major newspaper in Pakistan. The Election Commission of Pakistan allowed this to happen, as it allowed Shahbaz Sharif's TV interview on the election eve. The bottom line is that nothing worked. The PTI was not allowed a single rupee worth of TV newspaper ad, not any public or corner meeting, nor an election symbol, yet they defeated the state's blue-eyed thugs all across Pakistan."
Ultimately, despite attempts at media manipulation, Nawaz Sharif secured fewer seats than the candidates individually supporting Khan.
Another piece published on Feb 1 by Dawn News, titled "The Return of Nawaz," suggested that the tide had been gradually turning in his favour for months, anticipating a swift acceleration in the coming weeks.
Similar Censorship Cases in Turkiye and Russia
In a different political landscape, with the upcoming 2024 presidential elections on the horizon in Russia, President Vladimir Putin has also implemented new media restrictions. These regulations aim to limit coverage of Central Election Commission sessions solely to registered media outlets, potentially excluding freelancers or independent journalists. The amendments also explicitly prohibit media reporting on the commission's activities at military bases or in regions under martial law without prior clearance from regional and military authorities. Similar to Pakistan's situation, this will marginalise independent voices and suppress alternative perspectives. It will reinforce the government's narrative and hinder the public's access to unbiased information, potentially impeding transparency and independent scrutiny of electoral processes.

Ultimately, despite attempts at media manipulation, Nawaz Sharif secured fewer seats than the candidates individually supporting Khan.
Another illustrative example showcasing the intricate relations between the media and the military can be observed in Turkey. On July 15, 2016, elements within the Turkish military attempted to overthrow the democratically elected government led by President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan, and seize control of crucial institutions, including media outlets. Soldiers took control of television stations, such as CNN Turk, forcefully shutting down live broadcasts. However, their efforts were ultimately stopped, as the government managed to regain control. After suppressing the coup attempt, the government initiated a broad crackdown on media outlets critical of President Erdoğan and his party, as part of its response to what it considered a threat to the country's stability. Numerous journalists were arrested, newspapers were shut down, and broadcasters were taken off the air. This crackdown created a restrictive environment, limiting the media's ability to scrutinise government actions and hold authorities thoroughly accountable.
Laws related to national security, blasphemy, and other sensitive topics can be manipulated to restrict media content.
As a result, media insiders and observers argue that the news narrative in Turkey is often shaped to favour Erdoğan and his government. A Reuters special report, titled "Insiders reveal how Erdogan tamed Turkey’s newsrooms," vividly illustrates this transformation of Turkey's once-vibrant media, now dominated by a tightly controlled chain of government-approved headlines, front pages, and topics for TV debate.
Unveiling the Mechanisms: How Media Censorship Operates in Pakistan
So, how does such censorship operate in Pakistan? Is it systematic, following established mechanisms, or is it imposed arbitrarily?
Understanding the mechanisms through which censorship operates in Pakistan requires a nuanced perspective that considers legal frameworks, regulatory bodies, arbitrary enforcement, internet controls, national security justifications, military influence, and self-censorship.
In some cases, censorship operates within a legal framework established by the government. Laws may be enacted to regulate media content, restrict specific topics, or curb certain forms of expression. The Pakistan Electronic Crimes Act (PECA) has been criticised for its potential use in curbing freedom of expression. Laws related to national security, blasphemy, and other sensitive topics can be manipulated to restrict media content.
Regulatory bodies also play a crucial role in overseeing and implementing censorship policies. The Pakistan Electronic Media Regulatory Authority (PEMRA) is responsible for regulating electronic media in the country. Authorities may use regulatory measures to control media narratives by issuing directives to outlets or even revoking licenses. While PEMRA didn't officially issue any statement restricting coverage of a specific party during the election season, it did issue a ban on airing Khan’s speeches on March 5, 2023. It warned that violators would have their licenses cancelled. On the same day, ARY News had its license suspended for airing a speech by Khan, as reported by the Committee to Protect Journalists (CPJ).
In the same report, CPJ's Asia program coordinator, Beh Lih Yi, described this as:
"Pakistan’s ban on satellite television channels broadcasting former Prime Minister Imran Khan’s speeches and the suspension of ARY News’ license are the government’s latest attacks on press freedom and the right to information. Authorities must immediately reverse these blatant acts of censorship and allow the media to report on key political developments in the country freely."
Authorities may use regulatory measures to control media narratives by issuing directives to outlets or even revoking licenses.

However, censorship in Pakistan can sometimes be arbitrary, with authorities selectively targeting media outlets or journalists based on their coverage or perceived biases. Journalists critical of the government may face harassment, threats, or legal action, leading to self-censorship within the media industry. For example, in May 2021, Hamid Mir, a prominent journalist and Pakistani talk show host of the "Capital Talk" news program, on the Geo News network, was suspended after critical comments on the military.
The military can control media censorship too, either directly or indirectly, influencing narratives considered sensitive or against national interests. However, this involvement raises concerns about the autonomy of media outlets and their ability to operate independently.
Censorship in Pakistan can sometimes be arbitrary, with authorities selectively targeting media outlets or journalists based on their coverage or perceived biases.
Moreover, Pakistan's government can control access to information on the internet, particularly on social media platforms. This can involve blocking websites or platforms, limiting internet speeds, or monitoring online activities. On Feb 8, the day of the elections, the government temporarily suspended mobile phone services.
In the current scenario, it appears that the ban on PTI and Imran Khan in Pakistan appears to be a complex mixture of systemic measures and arbitrary decisions, reflecting a blend of structured regulations and ad-hoc implementation.
Charting the Way Forward: Responses to Media Censorship
In response to this censorship, PTI adopted innovative approaches to challenge restrictions. Notably, the party utilised artificial intelligence (AI) to produce audio clips featuring Khan's synthesised voice, generated from text he had written in prison and approved by his lawyers. This AI-generated message was broadcast during a virtual rally and also when declaring victory after the final results. In addition, PTI creatively embraced online platforms such as YouTube and TikTok for virtual rallies to connect with the audience and navigate the limitations imposed on traditional campaigning.
Yet, censorship directed at such influential political figures can have far-reaching consequences for society. It may lead to lower political engagement and voter turnout. Nevertheless, despite such challenges, voter turnout remained at almost 48 percent in these elections, representing only a decrease of 3 percent compared to the previous general elections.
In addition, censorship can contribute to a decline in public trust in media outlets, as the public may perceive restrictions as an attempt to manipulate information. This erosion of trust can have long-term consequences for the credibility of media organisations. Supporters of the censored party may perceive the restrictions as unfair, leading to heightened polarisation and the potential for social unrest.
Meanwhile, journalists, afraid of facing consequences, might choose to censor themselves to stay within the rules. This self-censorship can hinder investigative journalism, restricting the public's access to important information about political figures and events.
Lastly, and most importantly, such censorship has the potential to shape international perceptions of Pakistan's commitment to democratic values and freedom of the press. It could impact diplomatic relations and Pakistan's standing in the international community.