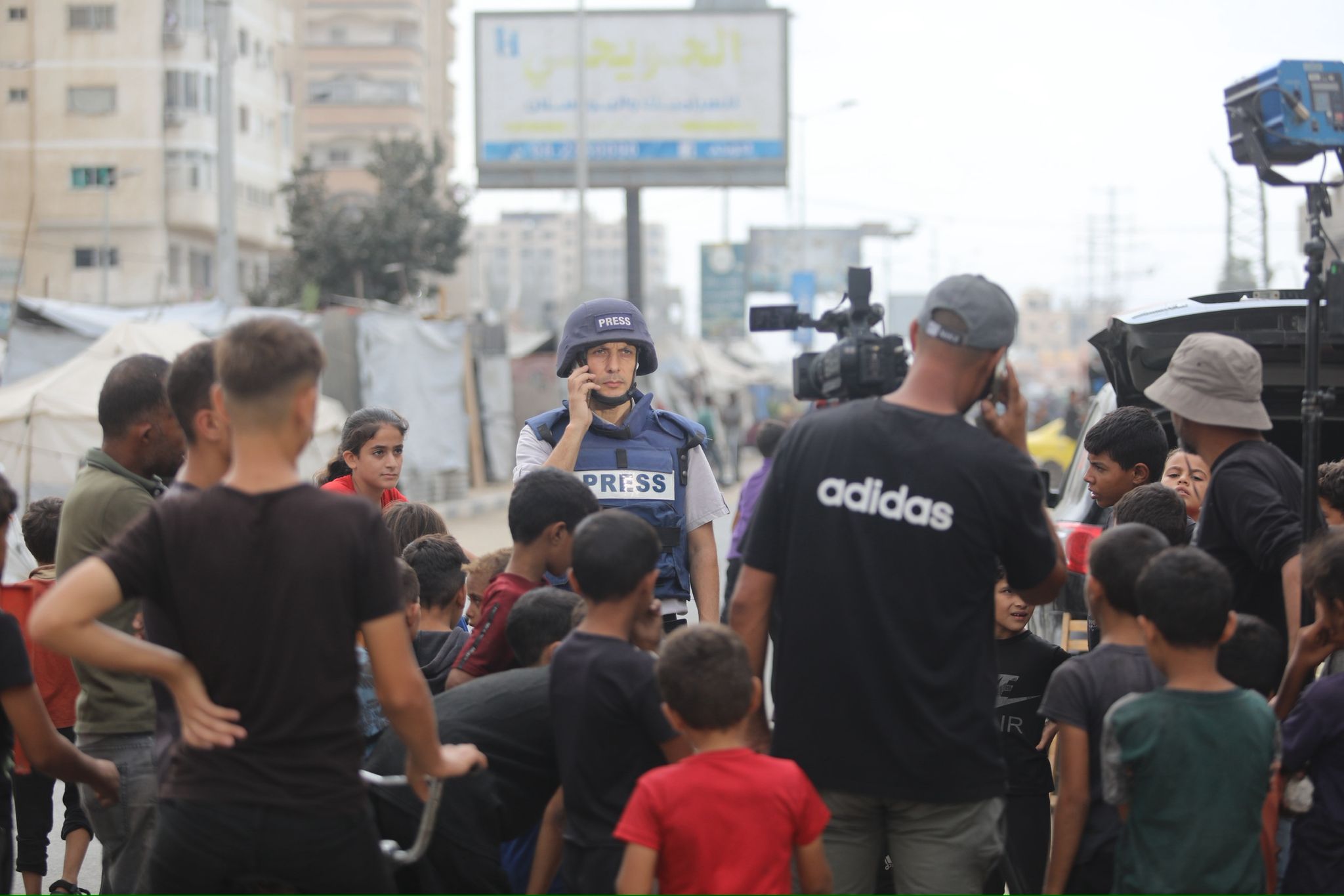
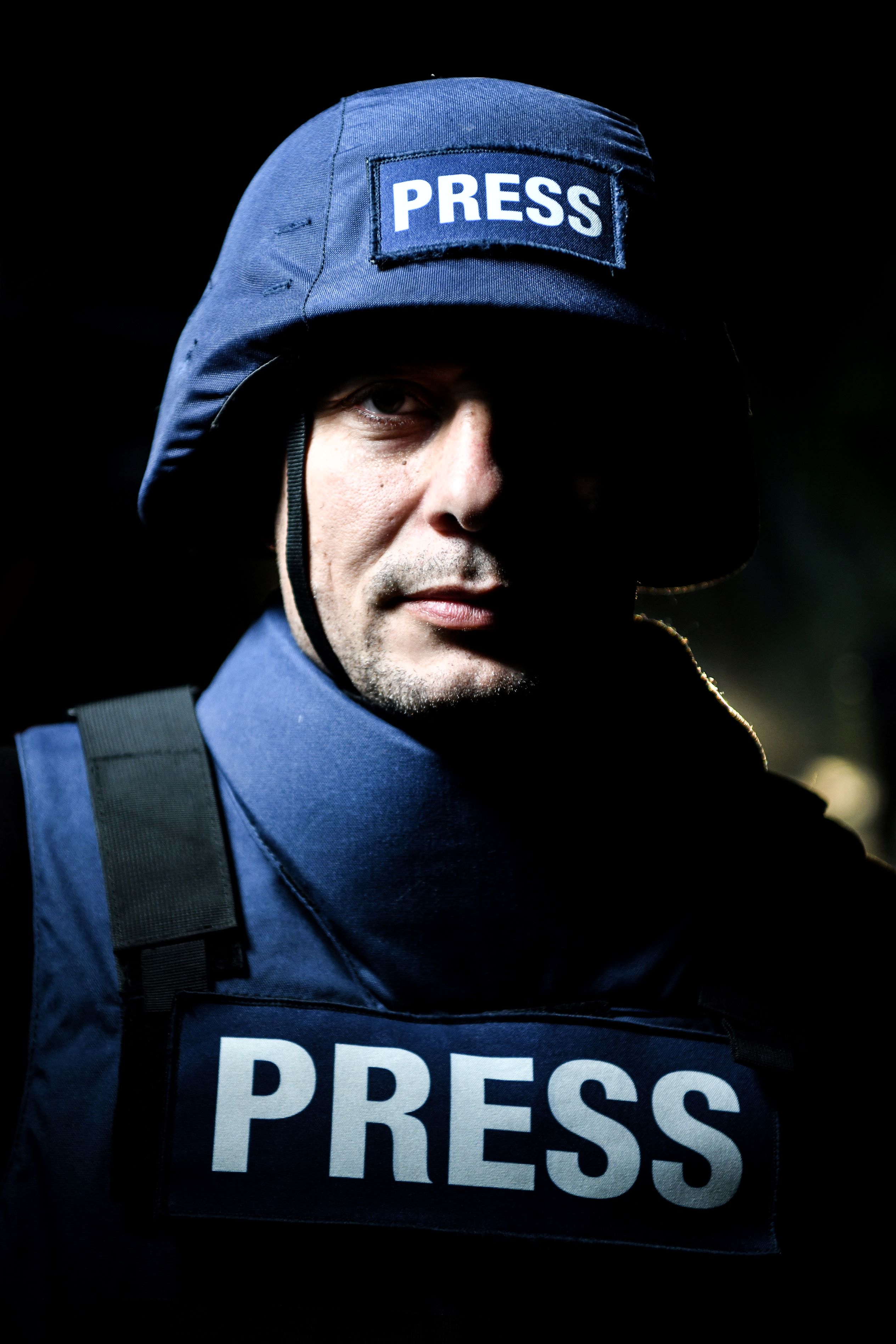
How to protect yourself following the news that sophisticated spyware has been used to hack the smartphones of journalists, activists and politicians around the world.
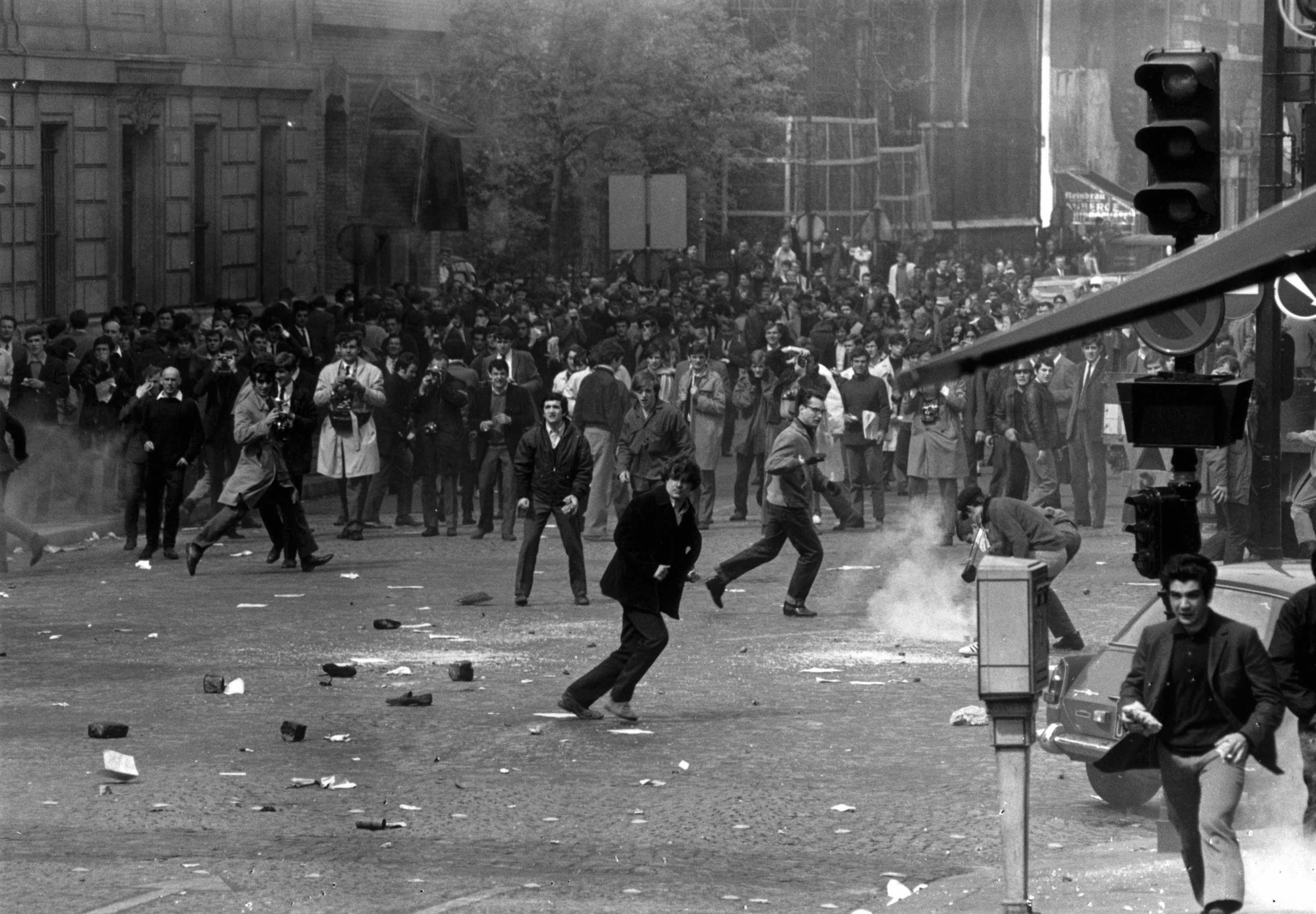
Revelations in July that “repressive” governments around the world had been using Israeli-manufactured spyware to monitor the smartphones of journalists and activists have caused understandable alarm among members of the media.
On July 18, a consortium of 17 media organisations calling itself the Pegasus Project revealed that specialist spyware known as “Pegasus” - manufactured by the Israeli surveillance company NSO Group - had been used to hack phones. The scale of the surveillance operations had been leaked first to Amnesty International and Forbidden Stories, a Paris-based media non-profit organisation, which carried out a forensic investigation of the data and passed it on to the media groups.
Around 50,000 phone numbers belonging to journalists, political activists and political figures were found to be on a list of numbers believed to be “of interest” to clients of NSO. According to a report by the Guardian, the list included numbers belonging to AFP, the Wall Street Journal, CNN, the New York Times, Al Jazeera, France 24, Radio Free Europe, Mediapart, El País, the Associated Press, Le Monde, Bloomberg, The Economist, Reuters and Voice of America.
Also on the list were some heads of state and prime ministers, members of Arab royal families, diplomats and politicians as well as activists and business executives. The Guardian reported that not all numbers on the list had been confirmed to have been hacked, however.
According to The Washington Post, a phone belonging to the fiancee of its murdered Saudi columnist Jamal Khashoggi had also been infected by the Pegasus malware just days after he was killed at the Saudi consulate in Istanbul in 2018.
Two years earlier, NSO had pledged to police abuses of its software, stating that it would “bring the company into alignment with the UN Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights”. In response to the Guardian’s report on the Pegasus issue, however, it denied what it called “false claims”.
What makes this scandal stand out are both the numbers of people involved and the revelation that this very sophisticated spyware has the ability to infect a phone with no action by the targeted person (known as “zero-click”)
NSO stated: “NSO Group firmly denies false claims made in your report. Many of which are uncorroborated theories that raise serious doubts about the reliability of your sources, as well as the basis of your story.”
Pegasus is a spyware that can turn Android or iOS phones into surveillance devices. References to it have surfaced in the past for being used by repressive governments to hack and spy on journalists and human rights activists.
In 2016, for example, the hacking of a UAE human rights defender was exposed by Citizen Lab and Lookout Security. They alerted Apple, which in turn quickly released an update to patch the vulnerabilities.
In 2019, WhatsApp filed a lawsuit against NSO over Pegasus spyware which had been used to compromise the accounts of more than 1,400 journalists, human rights activists and dissidents around the world by exploiting the App’s zero-day vulnerability (software weaknesses that have not yet been found or fixed by manufacturers).
What makes the most recent scandal stand out are both the numbers of people involved and the revelation that this very sophisticated spyware has the ability to infect a phone with no action by the targeted person (known as “zero-click”), to give complete access and control of a phone to the attacker.
Pegasus is not the first - or the only - such malware in existence, nor can we be sure that it is the most sophisticated.
Government agencies have long used software to monitor the activities of persons of interest. In the US, the NSA has used a spyware programme called Dropout Jeep to hack into Apple iPhones. Israel’s Cellebrite has been widely used by law enforcement, intelligence and private agencies in 150 different countries, while Candiru produced a spyware called “Sourgum” which is able to exploit vulnerabilities in Microsoft and Google products and is believed to have been used to monitor journalists and activists as well.

How to protect yourself from spyware
Some weapons-grade spyware is difficult to prevent from actively monitoring and stealing information once they have been installed in the phone; however, standard digital security practices can protect you from less sophisticated malware.
-
Always keep your device’s operating system and Apps up to date: Phone manufacturers continually fix bugs and security flaws that could potentially be exploited by hackers and spywares
-
Use a two-step-verification for your accounts whenever possible; these use apps such as Google Authenticator and are set up to send a code to a different device or to a platform that is not shared on all devices.
-
Use password manager apps instead of saving passwords on phone Notes, which are easy to access by hackers (unless you are using a code that only you can understand). Do not allow your device to save passwords.
-
Keep your phone organised; remove unfamiliar and unused Apps
-
Review your privacy settings frequently - these are frequently adjusted and changed by App owners and phone manufacturers. Disable access to photos, the microphone, camera, contacts and your location on all apps (only give temporary access when needed for in-app use).
-
Use complex and secure passwords for all devices, sites, and apps; use fingerprint and face-lock when available.
-
Avoid using public Wi-Fi. If necessary, use only trustworthy virtual private networks (VPNs) to secure online activities; non-secure Wi-Fi and VPNs can be used as an access point to infect your device. Make sure the VPN service you use has no government affiliation. Never use public Wi-Fi to communicate with sources you want to protect or to receive or download important documents.
-
Only download apps from official stores: Malware and spyware programmes sometimes hide within the software of some apps. (This will not prevent sophisticated malware such as Pegasus, however, as that has the ability to infect even iOS built-in apps).
-
Verify before clicking on links - check if the whole link is visible, if its sender is authentic and can be trusted.
-
Cover camera lenses on all devices (if the phone security gadget is not available, use stickers) to avoid recording your surrounding or compromising who you are with.
-
Turn your devices off at least once a day. Amnesty Security Lab found that many malware operations are temporarily halted when a device is restarted.

How to defend yourself against a Pegasus-level attack
Pegasus is a weapons-grade, click-less malware. Once inside the phone, it can harvest everything on it; all communications history (including deleted information), including calls, SMS, contacts, emails, photos and videos, GPS data, your calendar, web browsing history and chats.
It can take control of your device, activating the microphone and camera, recording calls and keystrokes and taking screenshots, without the victim noticing a thing.
Forensic analysis conducted on victims’ phones has identified several gateways and vectors (attack techniques) for Pegasus, not all of which are click-free. Here is how to counteract each one.
Zero-click attacks
These attacks exploit vulnerabilities in the programming software of your device. One way is through a simple WhatsApp call received on the device, after which the app crashes and the caller's name disappears from the history. Similarly, an iMessage (with no notification) can infect a device without any interaction from the victim. To protect your information from zero-click attack theft:
-
Disable, then uninstall, the spyware’s point of entry; iMessage, Mail, Apple Music or FaceTime.
-
Always keep apps and devices updated (actively check for updates).
-
Use a second phone not connected to the internet for sensitive information interviews, research, investigation and communications.
Man-in-the-middle attacks
Also known as “network injection attacks”, these are used to redirect the victim to a malicious website without the need for the user’s interaction; by infesting the device via software vulnerabilities. This technique requires control of the local Wi-Fi network and it is quite difficult to know if you have been targeted. To avoid this kind of attack:
-
Avoid using public or non-secure, free Wi-Fi.
-
Use well-researched VPNs which have good privacy records, have no government affiliation and do not allow storing of browsing history.
-
Use VPNs that are located outside of the country you are in.
Spear-phishing attacks
Messages are sent to victims tailored to their interests in order to lure them to click on an attached link or document. Several journalists targeted by Pegasus (and Candiru) were found to have been attacked in this way in the forensic analysis investigation in July. These malicious links can arrive in the form of emails, SMS, social media messages or via WhatsApp and other messaging Apps. Once they are clicked on, the spyware is installed. To protect against this kind of attack:
-
Don’t click on a shortened link before confirming the whole-length link. Use URL expander such as URL Expander or ExpandURL to see the entire link before clicking on it.
-
Always scrutinise the authenticity of the sender of the link or attachments before clicking and don’t click on anything from senders you don’t recognise.
-
On social media, even if the sender is someone you do recognise, ask them first if they were the actual senders. Even if the sender is an acquaintance, their account may have been hacked and used to send spear-phishing links.
-
If the link appears to be important, open it on a non-default browser. Apple and Android devices normally default to a set browser - Safari and Google respectively. So far, Pegasus is known to target default browsers. Alternatively, use a secondary device that does not contain important information.
The Amnesty International and Citizen Lab forensic investigation found targeted journalists had received spear-phishing links embedded in messages about bank accounts and credit card purchases, work and topics they reported on, an immediate security threat, notices from news organisations or embassies, and even messages of personal concern.
Physical attacks
Attackers can manually install spyware if the target’s phone can be physically obtained. To prevent this type of attack:
-
Limit physical access to your devices by third parties - do not let anyone you don’t know and trust use them.
-
Always secure your devices and any messaging apps you use with complex and unique passwords and use fingerprint and face-locking access wherever you can.
-
Try not to let your device out of your sight; in gatherings or public places, and especially in airports, during border crossings and at checkpoints (when the security personnel demand to check your laptops and phones).
-
Minimise your device’s locked-screen command ability to prevent access by third parties. To do this, you should disable functions and App access that connect to the internet from your locked-screen control centre (on the iPhone) or Quick Setup Menu (on the Samsung). These include QR Scanner, Wi-Fi and links to Windows.
-
Enable the remote-wipe feature feature on Find-my-iPhone/mobile/device in the device settings (Apple ID/ Samsung account/security settings in Huawei) and on your cloud account, to erase all information if you ever lose your device.

What to do if your device is infected
If your journalistic work or activism has put you on a government’s “person of interest” list, no firewall or end-to-end encryption can protect you from Pegasus’s zero click attack. If, despite taking precautions you suspect your device is infected:
-
Stop using your infected phone, especially for work-related communications. Start using a new phone to contact your sources without downloading your old phone’s backup from cloud (some malware can be nestled in App software or delivered through factory apps such as Apple Music and Photo stream, and may migrate to the new device from cloud).
-
Keep the infected device as evidence for analysis.
-
Keep the infected device away from your work environment so you don’t compromise your surroundings and sources.
-
If replacing the device is not possible, return the device to its factory settings. Doing this and regularly restarting your device can temporarily stop the spyware from running in the background.
-
Remove unknown devices connected to social media accounts and messaging apps. This can be done in your security settings.
-
Disconnect (log out) from all online account apps on the infected device (email, WhatsApp, Signal, Twitter, Line, Facebook, etc), keeping track of the used passwords on those accounts. Reset passwords on all accounts from your new device using password manager apps and never re-use old passwords.
-
Consult a digital security expert to assist in re-establishing a secure digital profile. If you are a freelance journalist or do not have access to tech support, contact the Access Now Helpline.
-
Contact Pegasus Project IT experts to check if your number is among the 50,000 leaked by sending your phone number to Share@amnesty.tech to be checked, and for technical assistance in using their Mobile Verification Toolkit which is used to check if a device has been infected with Pegasus.
The damage to journalism
The Pegasus leak raised serious concerns among rights advocates and journalists about the dangers of surveillance technology, the future of press freedom, freedom of expression, journalists’ safety and the right to privacy.
Repressive governments won’t be barred from exploiting sophisticated weapons-grade spywares against its people under the guise of “national security”.
Without proper regulation of the sale, transfer and use of such surveillance technologies, and without checks and balances that hold governments and companies accountable for misusing such technology, basic human rights such as freedom of expression, privacy rights, press freedom will all be in danger.
Several of the journalists targeted by Pegasus said they were worried about being trusted by sources in the future
The UN High Commissioner for Human Rights, Michelle Bachelet, said when the Pegasus Project revelations became public: "Use of surveillance software has been linked to arrest, intimidation and even killings of journalists and human rights defenders. Reports of surveillance also have the invidious effect of making people censor themselves through fear.
"One key step to effectively prevent abuse of surveillance technology is for States to require by law that the companies involved meet their human rights responsibilities, are much more transparent in relation to the design and use of their products, and put in place more effective accountability mechanisms".
Several of the journalists targeted by Pegasus told The Wire that they were worried about being trusted by sources in the future. One was reported as saying that “public knowledge of his targeting could dissuade sources from getting in contact with him in the future”.
Bachelet and Amnesty international have called for a Moratorium on “cyber weapon” usage and sales, but until that happens we might have to go back to low-tech journalism and leave our devices behind on assignments.
Useful resources
The Access Now digital security helpline can diagnose your problems and provide helpful technical advice in nine languages.
The Digital First Aid Kit gives advice about a device that is behaving suspiciously, as does Surveillance Self-Defence.