Across the world, media organisations are guilty of misrepresenting the stories of refugees and other vulnerable minorities, stirring up panic and outrage within their respective countries. We look at some examples.
Discrimination and hate speech in media do not only hurt the feelings of the individuals or communities they target. They can also contribute to crimes committed against them and stoke the flames of armed conflict, or incite or justify the commission of crimes against ethnic or national groups, as well as encouraging violence against specific demographics such as women, children, refugees, minorities or political opposition figures.
In Sweden, a study - entitled “Social Media Mechanisms for Right-Wing Political Violence in the 21st Century” - showed a correlation between tweets and Facebook posts concerning refugees and the number of attacks against them in a particular period. According to the study, the greater the number of tweets and posts featuring the word ‘refugee’ (flykting), the more arson attacks were committed by “extremists” against refugee accommodation.
The study explained that social media algorithms help to produce “echo chambers”, that is, that individuals are exposed more to content that matches their personal preferences than to any other. In other words, these algorithms provide increased opportunities for individuals with racist inclinations to view media content depicting immigrants and refugees as a danger to society, creating a “justification” for violence against them.
The first graph shows the number of tweets containing the word “refugee” against the number of attacks against refugee housing in Sweden between March and September 2016. The second shows the correlation between the number of Facebook posts including the word “refugee” and the number of attacks in the same period.
Another study on digital hate speech in Bulgaria, conducted by the Sofia Development Association, tracked the reactions of the public, the media and politicians to the different stages of the refugee and migrant crisis.
This study found a link between people’s attitudes to refugees and migrants and the extent to which hate speech circulated in digital media. The study found that “the opinions of Bulgarian citizens are influenced and shaped mainly by the media”, and that, as a result, “a large part of the population perceives refugees as a national security threat”.
A 2016 report by the Bulgarian Helsinki committee likewise stated that television was the medium that the public saw as most responsible for spreading hate speech, while the internet came in second place.

The media and moral panic theory
Moral panic is defined as a moment in “a situation in which public fears and state interventions greatly exceed the objective threat posed to society by a particular individual or group”, says Maha Omar, journalist and academic.
"The idea of moral panic has been used to understand many social problems, including drug gangs, schoolyard violence, child abuse and mistreatment of immigrants and refugees.
"Any observer of the current climate surrounding refugees in the West can easily grasp the essence of the ideological discourse used by populists worldwide.
"This discourse creates a wide space in which lies about migrants will be accepted, and is based on moral panic. Moral panic accounts for “panicked” majority reactions in a given society towards cultural groups like refugees or immigrants: this majority sees that the migrant minority threatens the central values of society and the economic privileges that citizens enjoy.
"Political campaigns then base their rhetoric on this discourse by giving ever more space to fake news and conspiracy theories."
Discrimination in the media: Some case studies
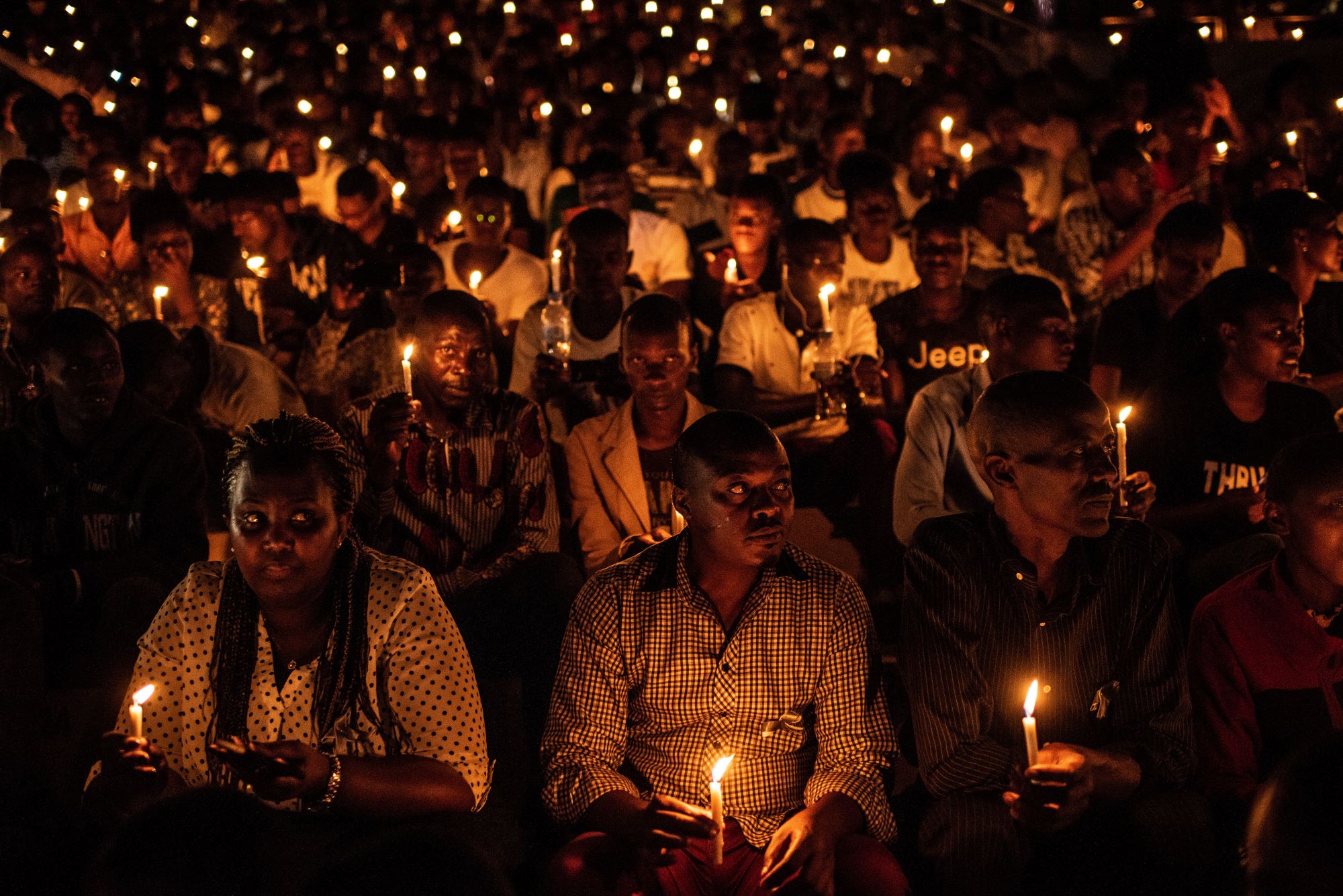

The Rwandan Civil War
Discussions of discrimination in the media always reference the Rwandan Civil War. It is an important case study both because of the barbarity of the crimes committed and also because the trials that followed it concluded that the media was responsible.
The Rwandan broadcaster, RTLM, played an important part in fomenting conflict between the Hutu and Tutsi ethnic groups in 1994, calling for the killing of Tutsis and describing them as “cockroaches” in its coverage of events.
In cases of this kind, hate speech is a crime punishable by law. The International Criminal Tribunal for Rwanda sentenced the RTLM’s co-founder, Ferdinand Nahimana, and its executive chairman, Jean Bosco Barayagwiza, to life imprisonment for promoting hatred against the Tutsis through its broadcasts.
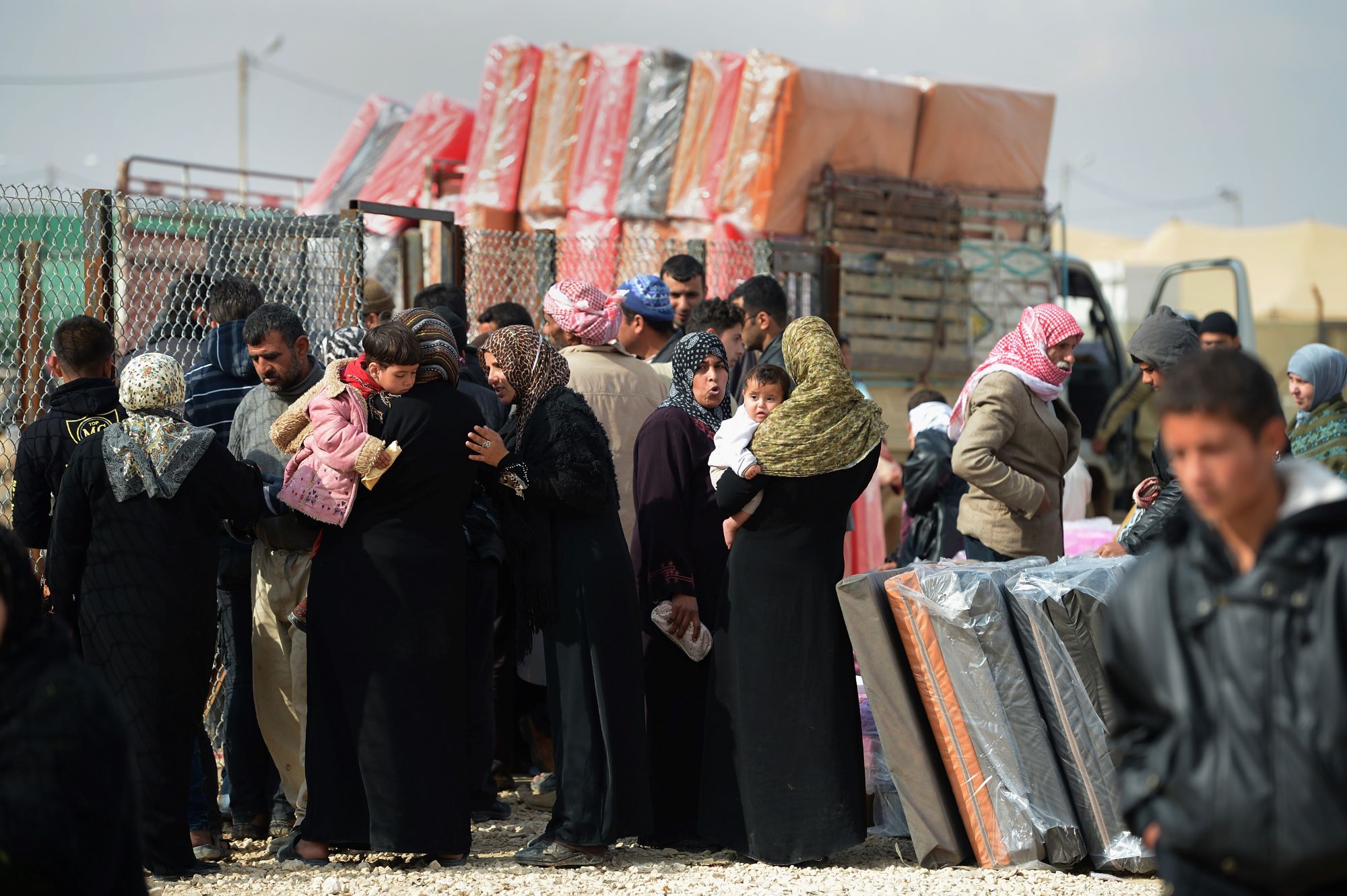

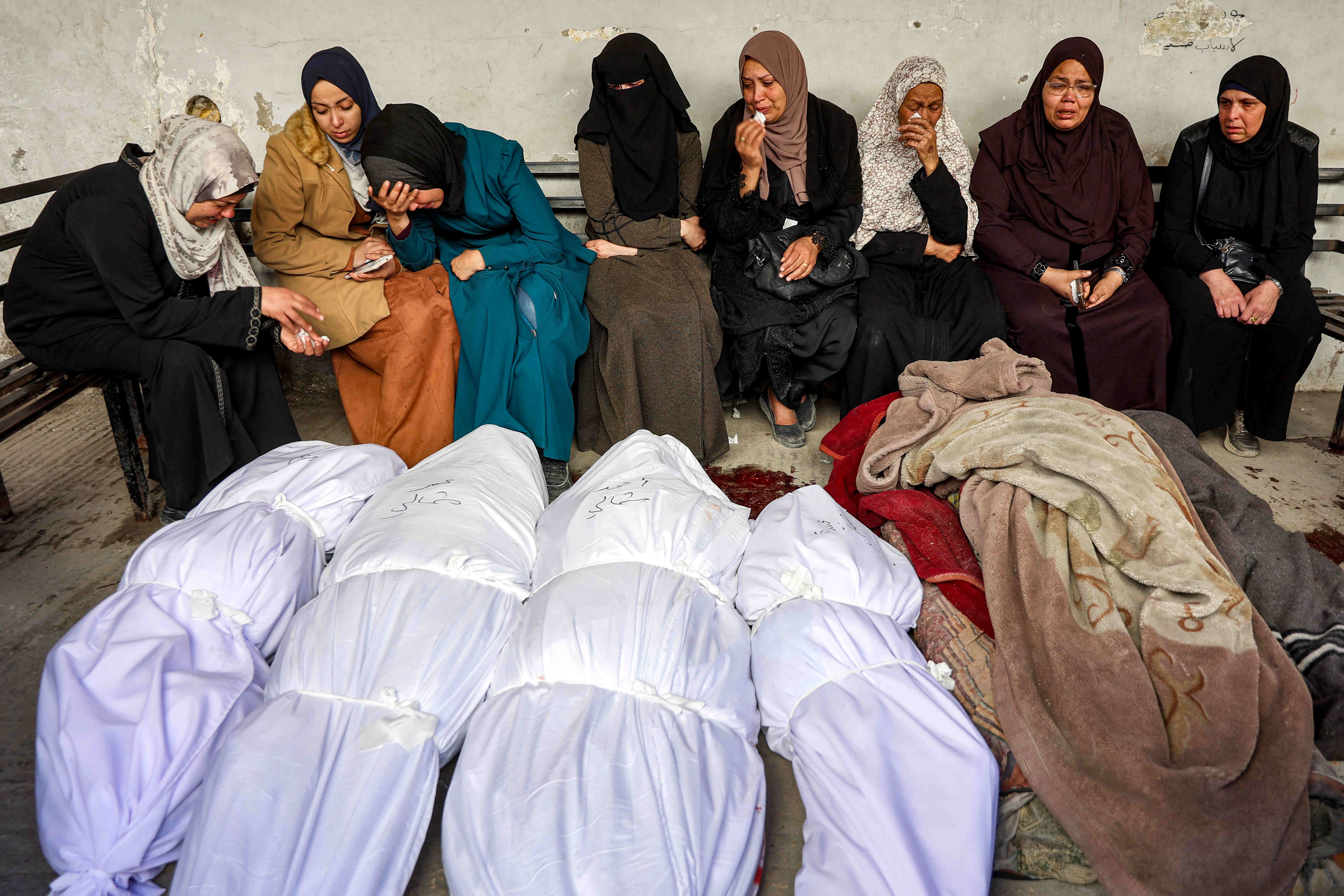
Syrian refugees in Lebanon and Jordan
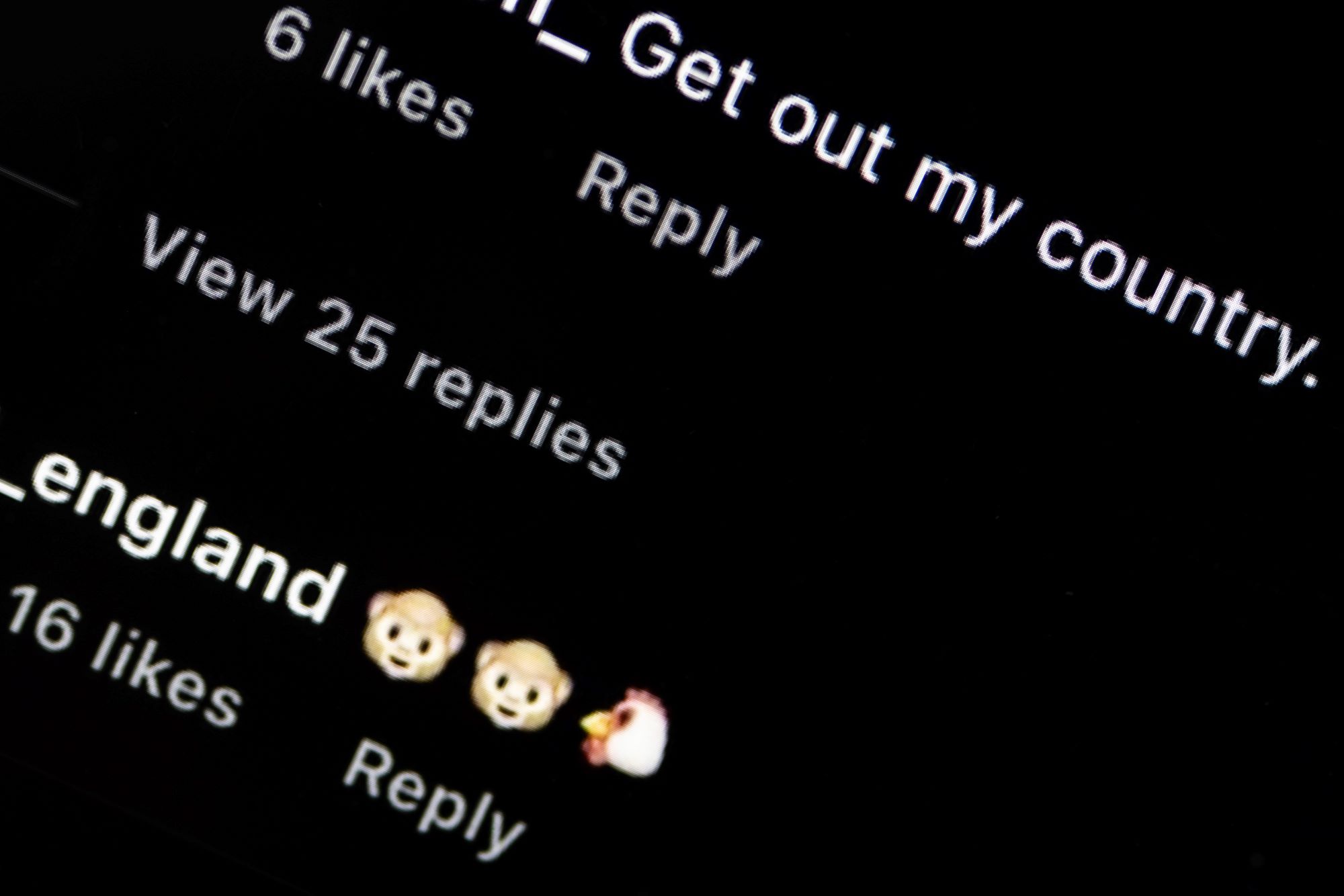
Both the Lebanese and Jordanian media have produced biased coverage of Syrian refugee issues. This has contributed to negative societal attitudes towards them which have in turn produced opposition to their presence.
In Lebanon this is more clearly noticeable because racist speech on social media has developed into incidents of physical violence against refugees. Politicians have played a part in exacerbating this tendency, with some of them promoting racist speech: the Lebanese Foreign Minister [name him], has tweeted [when?] equating refugees with delinquents [let’s link to the tweets].
A piece published by the Lebanese news outlet MTV titled “Cancer afflicting Lebanon... And two reasons it is spreading”, September 5, 2018. Here, MTV quotes a doctor who considers Syrian refugees to be a major factor in rising cancer rates in Lebanon. The doctor gives no evidence for these claims, but the channel nonetheless treats them as scientific truths without any attempt to verify them. MTV has since removed the piece from its website.
The Jordanian newspaper Al Rai, meanwhile, published a story on its website titled “Sewage Overflows Because of Syrian Refugees”. The newspaper later amended the title to “Population Pressure and Misuse Lead to Sewage Overflow”, but kept the government official’s statement about Syrian refugees in the introduction to the story used on social media, without citing a source and without attempting to verify this claim. The story was published in a tweet, and received a great deal of criticism.

Iraq
Iraqi Media House has produced a report titled “The Hate Dictionary” (in Arabic) documenting examples of hate speech in Iraqi media and on social media. The report tracks the most prominent words and expressions used in the media “which call for murder, violence, retribution, contempt [or contain] discrimination or swearing”.
There are many other cases of discrimination in Arab media. Examples include incitement against the Egyptian Rabea protests during the Egyptian army’s takeover and sectarian discrimination between Sunnis and Shi’a in Iraq.
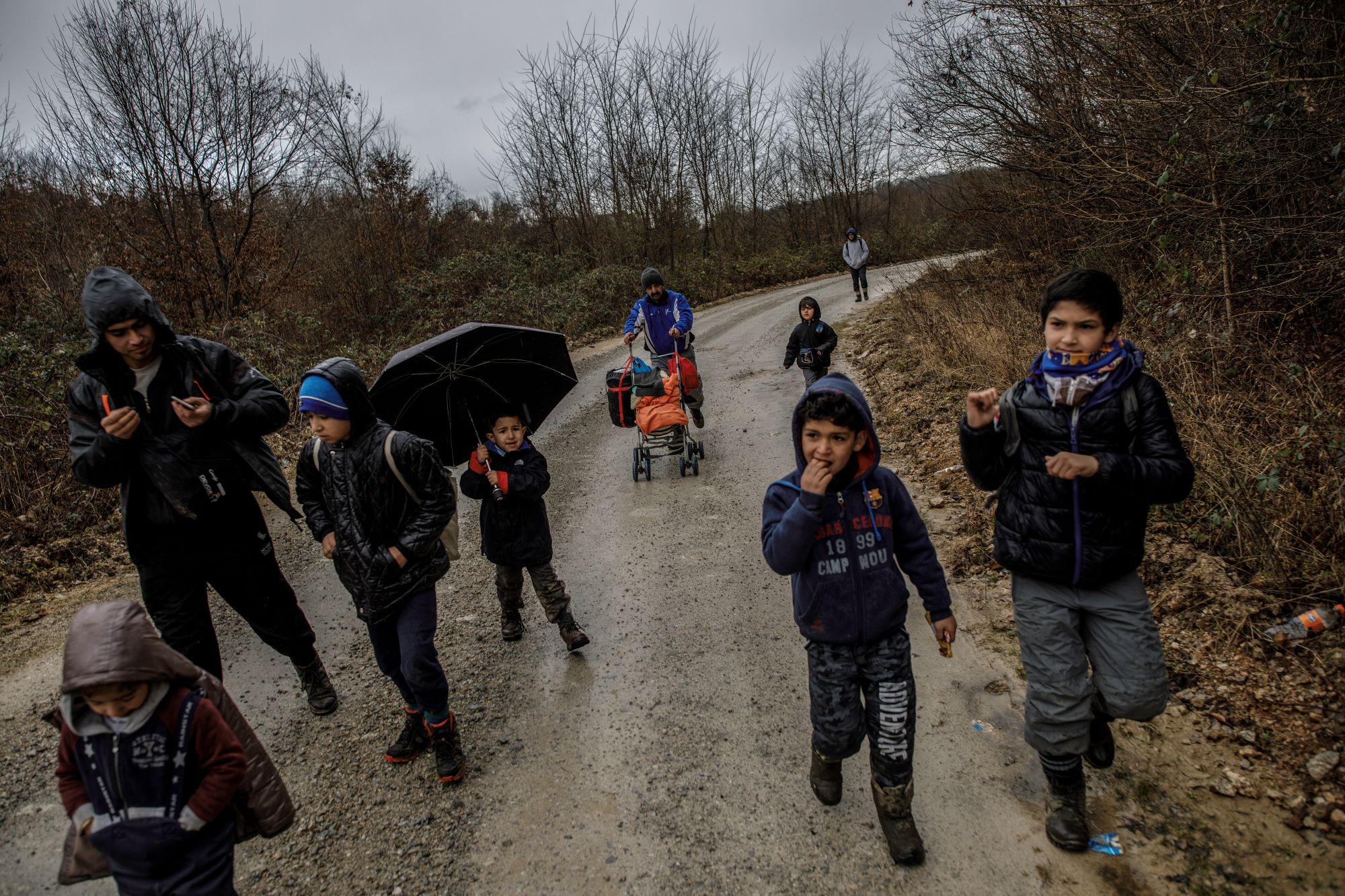

Migrants and refugees in Western media
The situation is no better in much of the European media, particularly in countries with migrant and refugee populations. The conservative right has gone from strength to electoral strength in Europe by promising anti-immigration and anti-refugee policies, thereby exploiting xenophobia spread by the media.
Even media outlets that show professionalism in their coverage as a whole are sometimes discriminatory in their crime coverage. There is often more focus on crimes whose perpetrator is an immigrant or refugee and less interest in those committed by citizens. Hate speech appears clearly in the Western media through its use of hostile language against refugees.
In this Daily Express front page story, for example, the paper calls for the army to intervene to stop a “migrant invasion”.
Edward Bulwer-Lytton once declared that "the pen is mightier than the sword". In recent news narratives we can see how true that can be, and how hate speech perpetuated by the media doesn't merely hurt feelings, it can actively legitimise hatred violence towards vulnerable communities.
An earlier version of this article appeared in the AJMI publication, Avoiding Discrimination and Hate Speech in Media