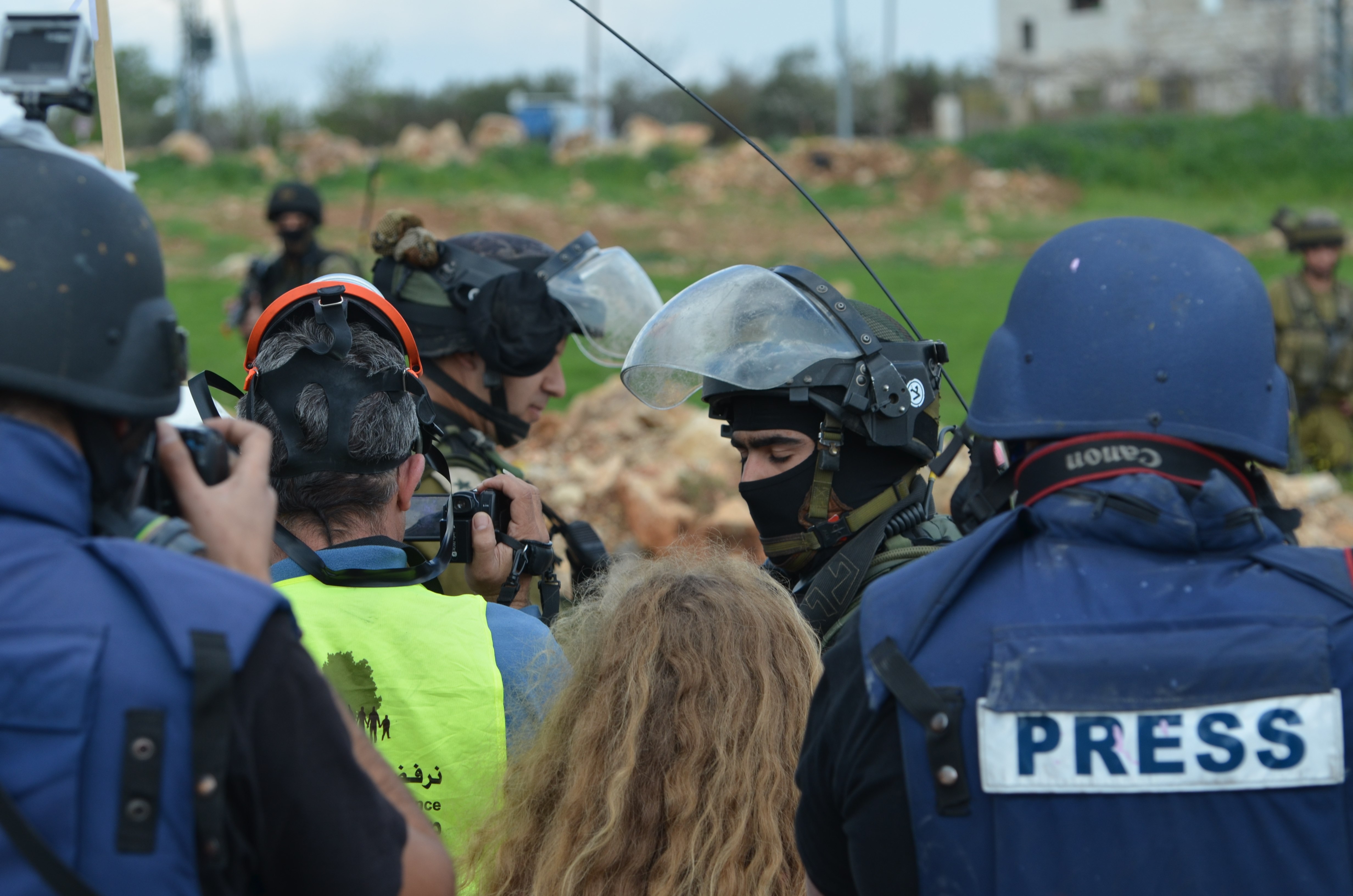
Braving threats from Al Shabaab as well as disapproval from their own, often patriarchal communities, six pioneering women have set up their own news agency in Somalia
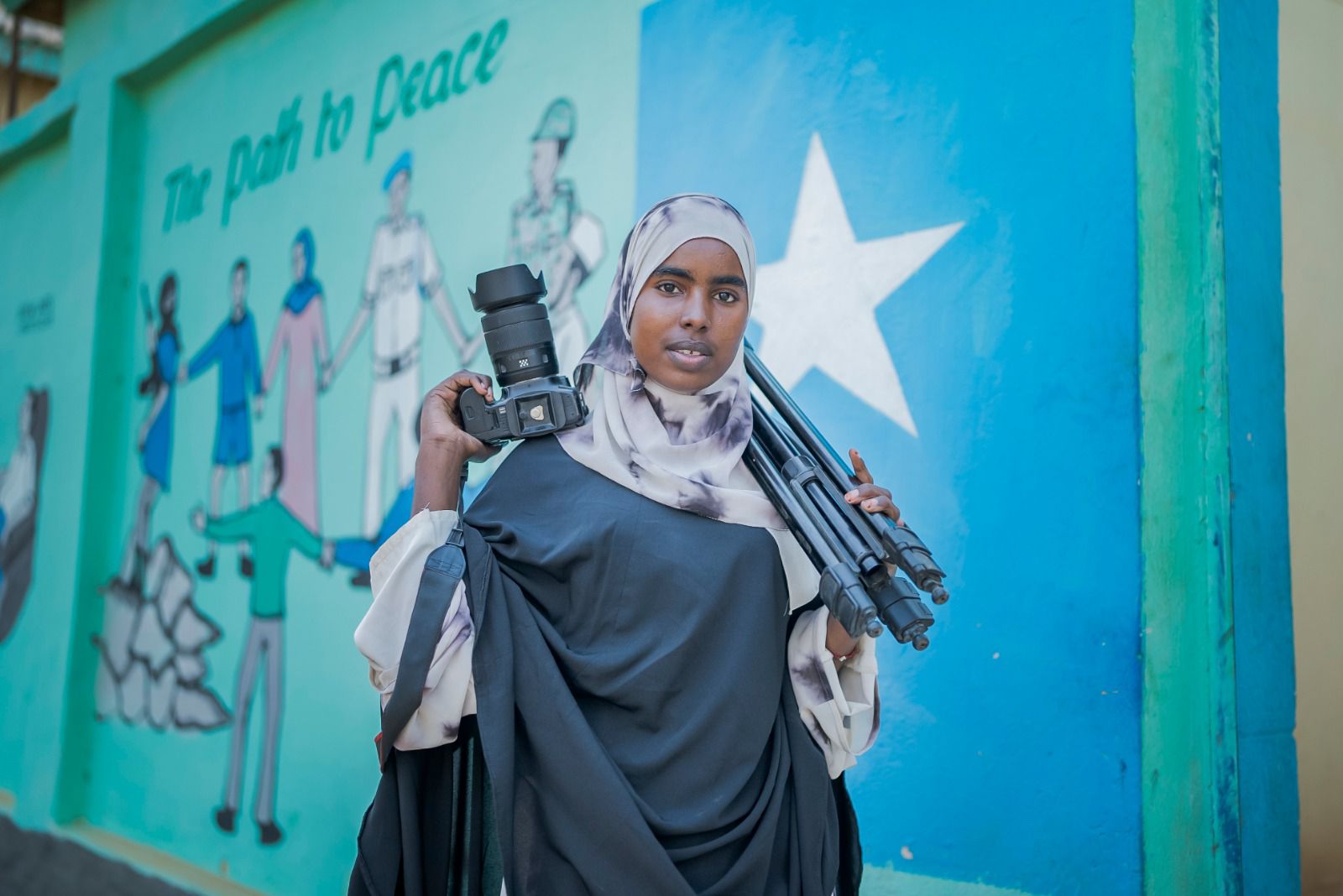
Twenty-year-old Shukri Mohamed Abdi was born at the peak of the civil war in the south-West city of Baidoa, and recalls a childhood marked by frequent moves to escape violence. She first trained to be a nurse but, seeing first-hand the effects of war on ordinary people, she decided to become a journalist.
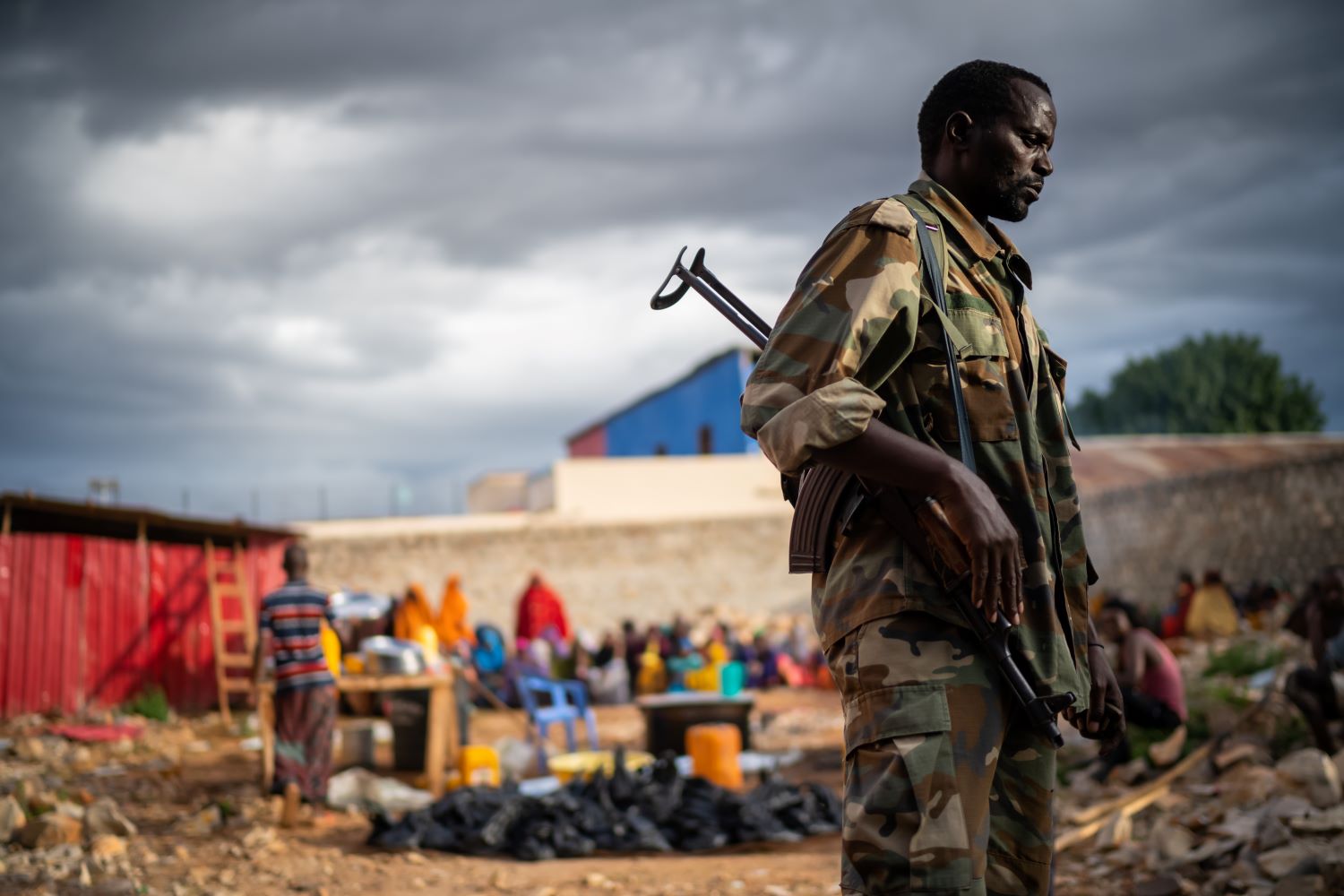
When she did just that, however, becoming a radio journalist at a local station in Baidoa, she was mocked and bullied every time she was on her news beat as a radio journalist - not just by the men she worked with, but by her audience as well. Eventually the bullying turned to intimidation and threats against her life - she believes from the militant Islamist group Al Shabaab - and she had to flee to the capital, Mogadishu, in order to continue working as a journalist despite her parents' insistence that it was too dangerous and not a suitable profession for a woman.

First as a nurse and later as a journalist, she says, “I had seen people bleeding and dying on the streets but eventually working as a journalist here was too big a risk and so I fled to Mogadishu for my own safety.”
‘Bright and clear’
These days, Shukri is one of a crew of six all-female journalists working for Bilan media which was launched earlier this year with backing from UNDP-Somalia, a United Nations organisation. “Bilan” is Somali for “bright and clear”. The news outlet aims to broadcast issues affecting ordinary people, children and women, and give a voice to subjects that are not always seen as important in the male-dominated industry.
In Somalia’s patriarchal society, to be a woman in a position of influence is often frowned upon. Bilan, therefore, is a novel medium that broadcasts important national and local issues far removed from the country’s obsession with politics and conflict news - those which affect the everyday lives of ordinary people, including women and children.
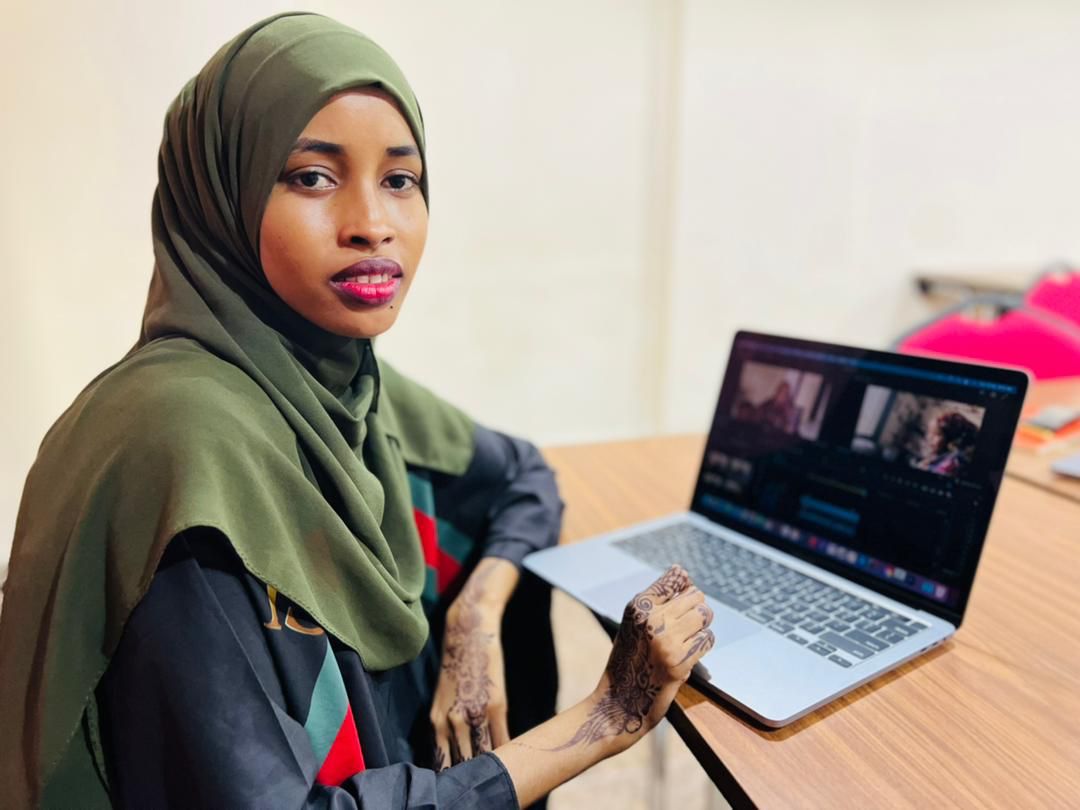

Keen Hassan, 26, whose family fled to Kenya when she was a child, came back to Somalia from Dadaab, where she took basic media training with NGOs like NRC and FilmAid. “In Kenya I was not allowed to work so I returned home to Kismayu.” She tried her luck with several media outlets in Kismayu but could not get a job - she believes because of her gender. She decided to move to Mogadishu.
“I did briefly work at the regional state TV station, Jubaland TV, as a reporter where I used to file soft stories as things like politics were kept for the men,” she explains. “We are an easy target for the police and the Islamist group as female journalists.”
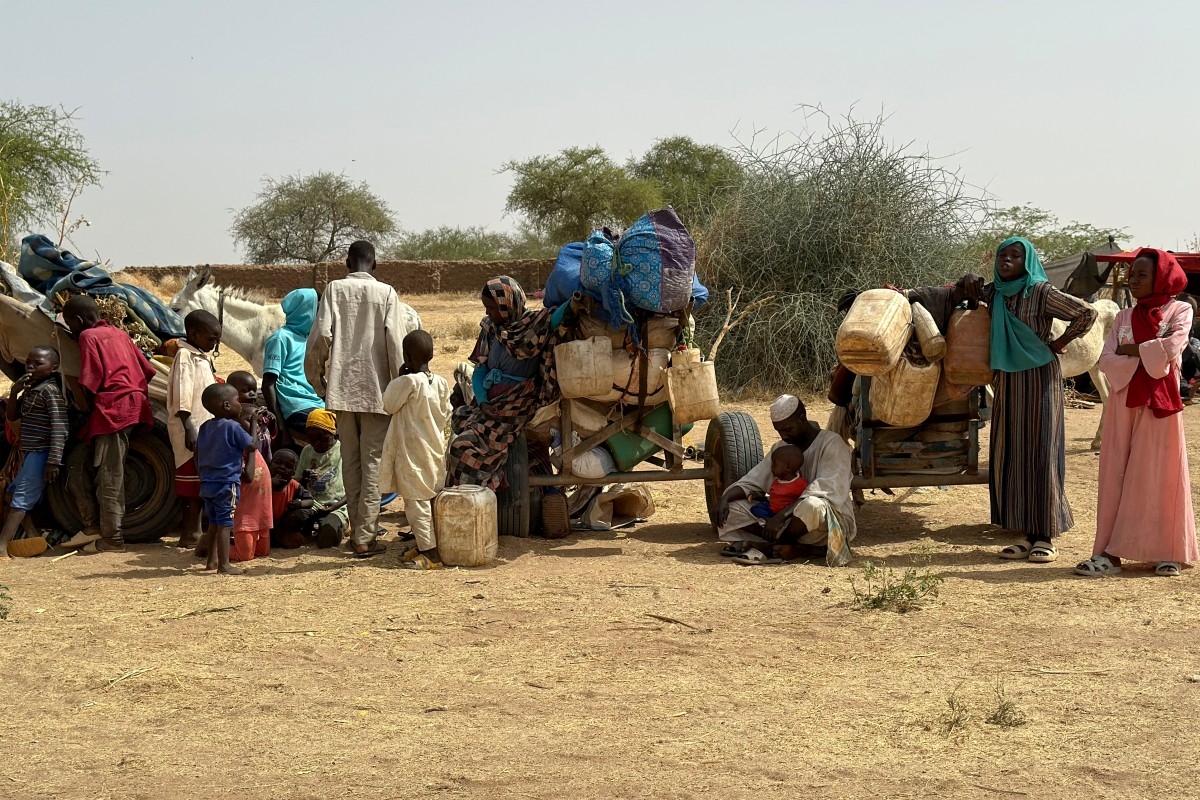
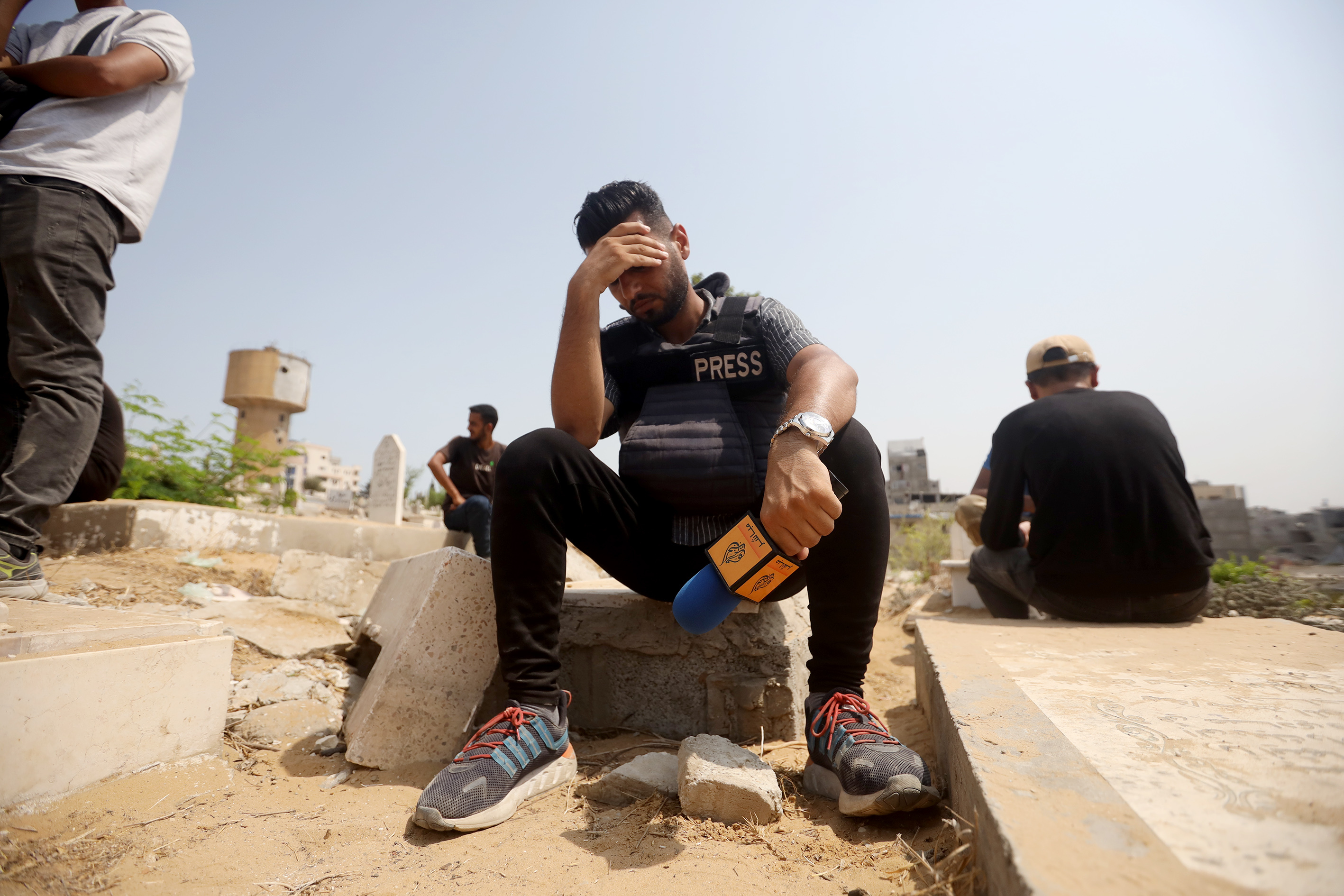
Female journalists are often marginalised and harassed in newsrooms by their colleagues while their families frequently believe journalism is not a suitable profession for a woman. All journalists are at risk from Al Shabaab, but women even more so. Indeed female journalists have been assassinated by the group, including Radio Mogadishu reporter Sagal Salad Osman, 30, who was shot and killed in 2015. The previous year, another female journalist working for Radio Mogadishu died in a car bomb explosion. Sometimes they are abused in the streets by police and are frequently denied promotions and training opportunities at work.

Facing violence and sexual harassment
According to a report published last year by the National Union of Somali Journalists (NUSOJ), female journalists revealed they faced sexual and gender-based violence which impacts negatively on their professional development.
In a country which is already one of the world’s most dangerous places to be a journalist, attacks on women contribute to the worsening media freedom climate in the country. These attacks result in women leaving the profession and also forces those still practising the profession to stay away from important political and security news stories for their own safety. In newsrooms, they frequently also face sexual harassment from colleagues.
“Several of these cases were not reported by the survivors and their colleagues because of the stigma associated with GBV (gender-based violence) as well as the fear of backlash from the perpetrator and/or the media organisation,” the NUSOJ report noted.
During 2021, NUSOJ documented 16 cases of women working in journalism who came forward and spoke confidentially of personal incidences of sexual harassment or GBV. Upon their request their names were not disclosed in the report.
The abuse and violence experienced by women journalists unfortunately feeds into a broader culture of gender inequality and gender-based violence in Somalia. This significantly impacts female journalists, professionally, emotionally and personally.
News organisations deemed independent or critical of the government have also faced similar attacks from the authorities and had their operations shut down, property destroyed and their professional equipment confiscated. Amnesty International has accused Somalia’s government of creating teams of online monitors who troll journalists and report them to Facebook’s standard enforcers in order to disable their accounts and silence critical media voices. This has forced journalists and media organisations to self-censor, with several media houses reluctant to cover political events or to consider press releases that denounce the authorities.
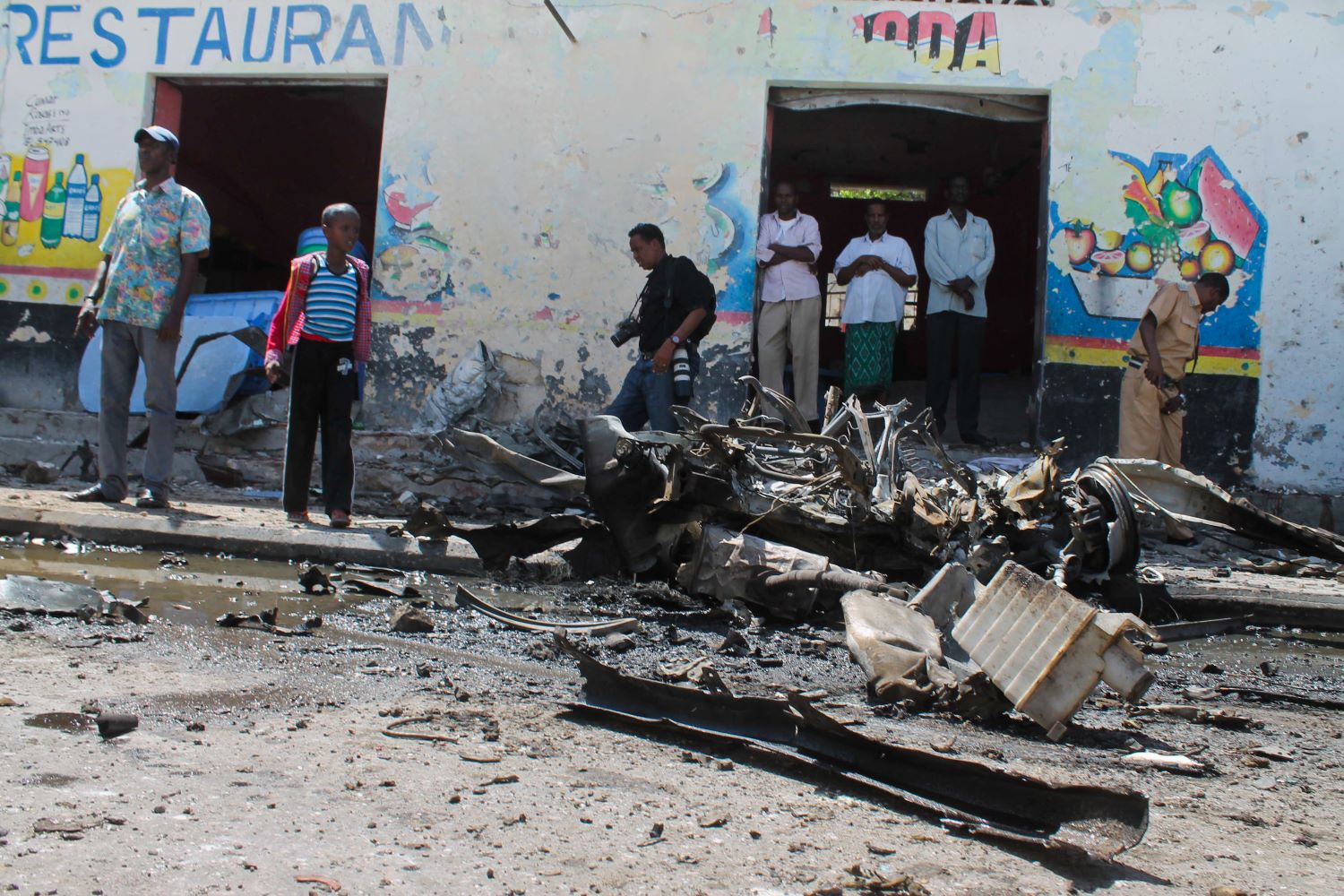

In 2021, two journalists were killed, there were four attacks against media houses, and 34 members of the media industry arrested.
Somalia’s penal code came into force in 1964 is still current law. It contains numerous offences which serve to curb media freedom and the right to freedom of expression. It uses vaguely worded provisions about the publication of false news. It also criminalises defamation, “offending the honour or prestige of the head of state, insult to public officers, insult to political, administrative or judicial bodies, false accusation and false evidence and offence against authorities”.
As a women-only media house we are going to bring taboo subjects into the open. Our sisters, mothers and grandmothers will talk to us about issues they never dare speak about with men
Fathi Mohamed Ahmed, Bilan's Deputy Editor
These provisions have been criticised as so broad and vague that they could be susceptible to widely exaggerated interpretations by both authorities and those subject to the law. Journalists, in particular, are often victims of the provision in Penal Code relating to “abusive exercise of a profession”.

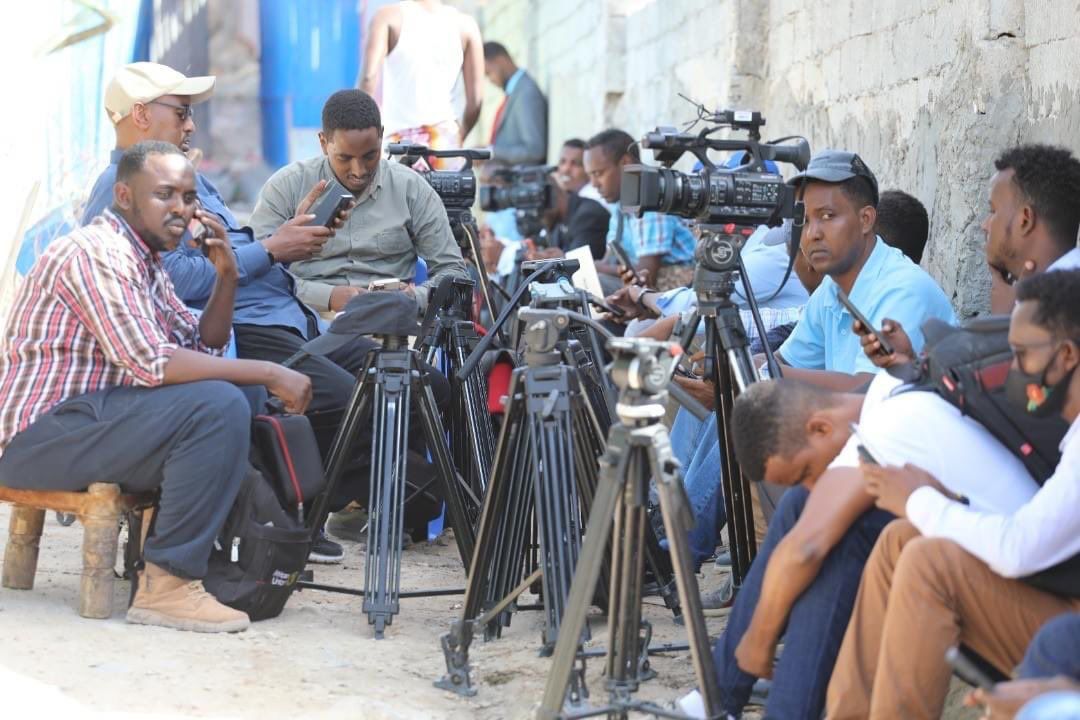
Covering the stories that other outlets won’t
The six-strong team at Bilan is composed of five journalists and an editor and will be producing both hard news and in-depth features for TV, radio and online.
The media unit which is funded by the United Nations Development Programme has full editorial independence and the journalists plan to cover diverse topics that affect women, domestic abuse, childcare and equal political representation.
The women working at Bilan say they will be able to access stories that other news agencies can’t - or won’t.

“As a women-only media house we are going to be able to bring taboo subjects into the open,” explains Fathi Mohamed Ahmed, Bilan's Deputy Editor. “Our sisters, mothers and grandmothers will talk to us about issues they never dare speak about with men.”
The abuse of female journalists in Somalia is one of these issues.
The NUSOJ report also highlighted a rise in attacks against women journalists, against a backdrop of gender-based violence in the country. This comes barely a month after the killing of female politician Amina Mohamed Abdi, an opposition leader and vocal critic of the government on March 23 this year in the Somali city of Beledweyne.

A major threat to journalists' safety comes from the Al-Shabab armed group, which claimed the two killings of journalists in 2021, while federal government authorities are mostly responsible for the arrest of journalists despite assurances given by the federal government to respect and protect media freedom have never materialised.
Concerns are growing over rising insecurity in this Horn of Africa nation as it surges closer to a much-delayed presidential election. Al-Shabab militants have warned that they will target politicians contesting the elections which are more than a year overdue.
The terrorist group seeks to establish an Islamic state in Somalia and overthrow the federal government in Mogadishu.
Treated as second-class citizens no more
Female Somali journalists who have for long been treated as second class citizens now have a medium through which they can report stories that have largely been ignored and where voices of nearly half the population have been stifled.
The media unit will pitch their programmes to international media outlets. The UNDP will also provide a six-month training and mentoring programme with established female journalists for exchange of ideas and mutual support. The six-month internship opportunity will be given to the best final year women journalism students from two universities in Mogadishu.
“We hope this will be a game changer for the Somali media scene, opening up new opportunities for women journalists and shining a light on new subjects that have been ignored, particularly those that are important for women,” says Jocelyn Mason, UNDP’s Resident Representative in Mogadishu.
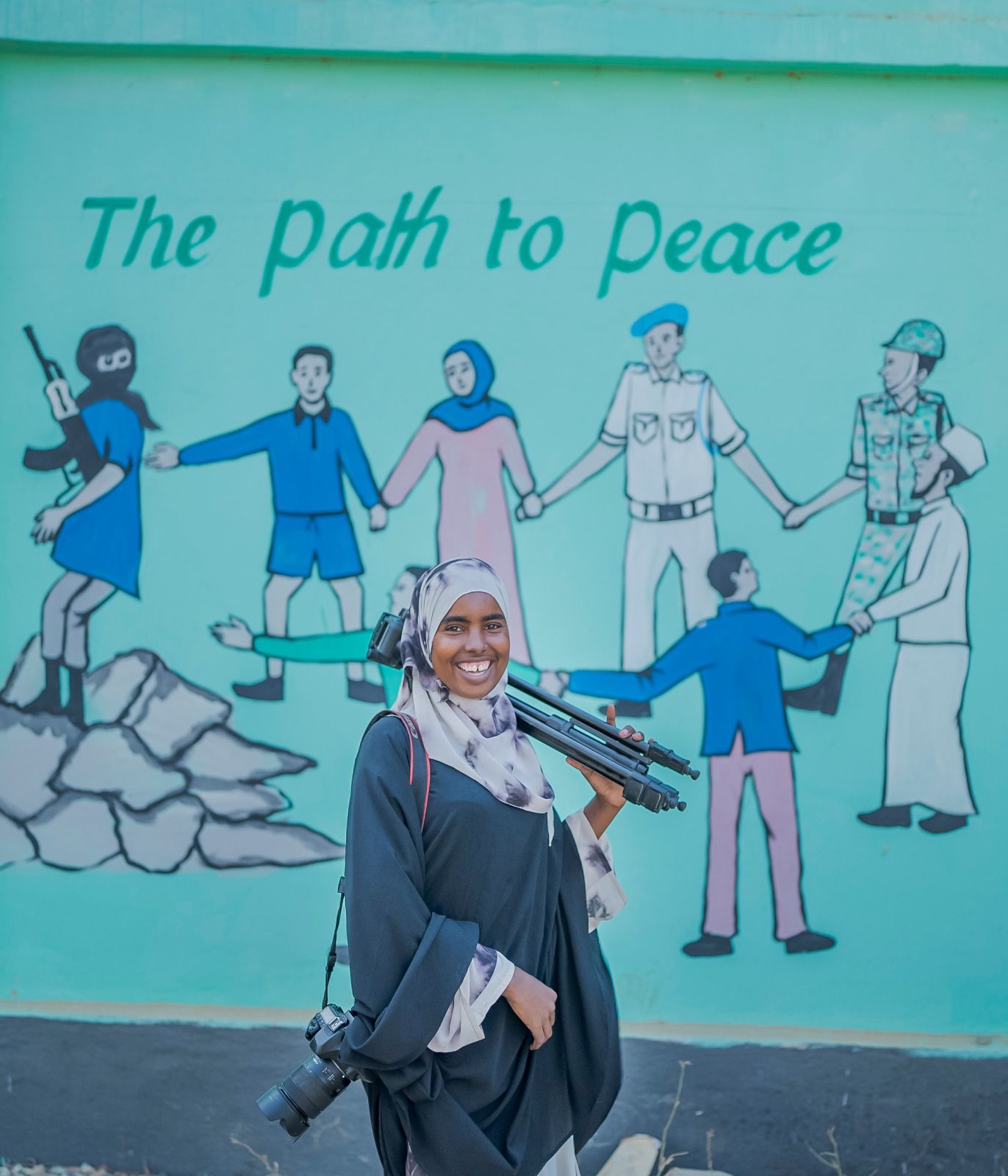

‘For the first time, we have a space where we feel safe, physically and mentally,” Bilan’s Chief Editor, Nasrin Mohamed Ibrahim, wrote in an opinion piece. “Never before have Somali female journalists been given the freedom, opportunity and power to decide what stories they want to tell and how they want to tell them.”
For Shukri, who is the youngest member of the team, it is a new experience having being taught mobile journalism. Now she no longer has to carry heavy cameras and gadgets for every story - something that can hinder her safety. She has had a hard time convincing her family in Baidoa that she should move to work for Bilan in Mogadishu, however.
“I plan to highlight the problems that affect women in my region where there’s also poor political representation,” she says.
For Keen, Bilan is a moment for women to re-set the narrative in their societies. "To stop violence against women, we appeal to the world to support us so that we can tell our stories the way we want to.
"We are not scared of anything. We will tell our stories."