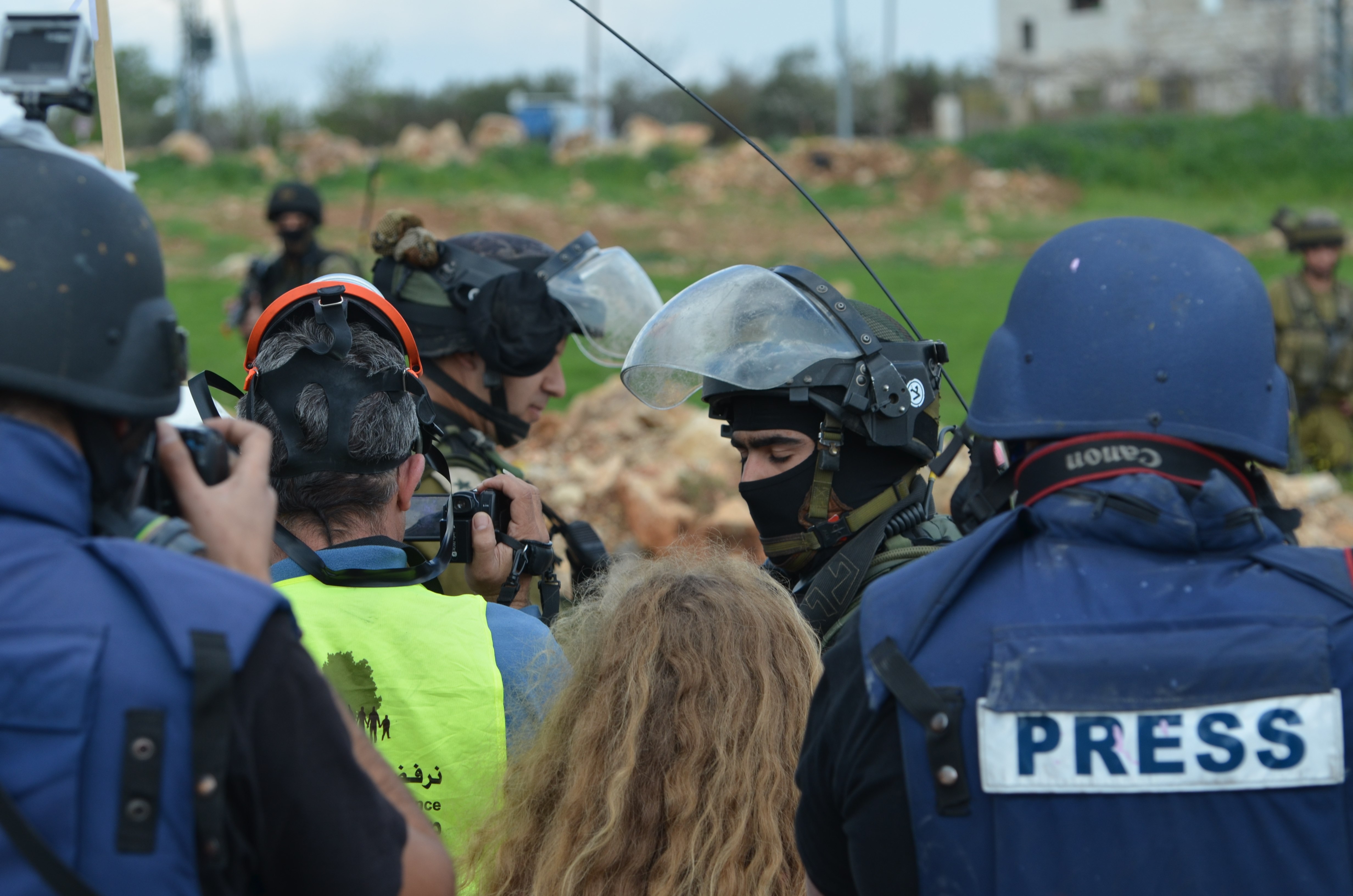
As political and commercial elites continue their stranglehold on mainstream media in Colombia, some independent minnows are starting to emerge. We examine how
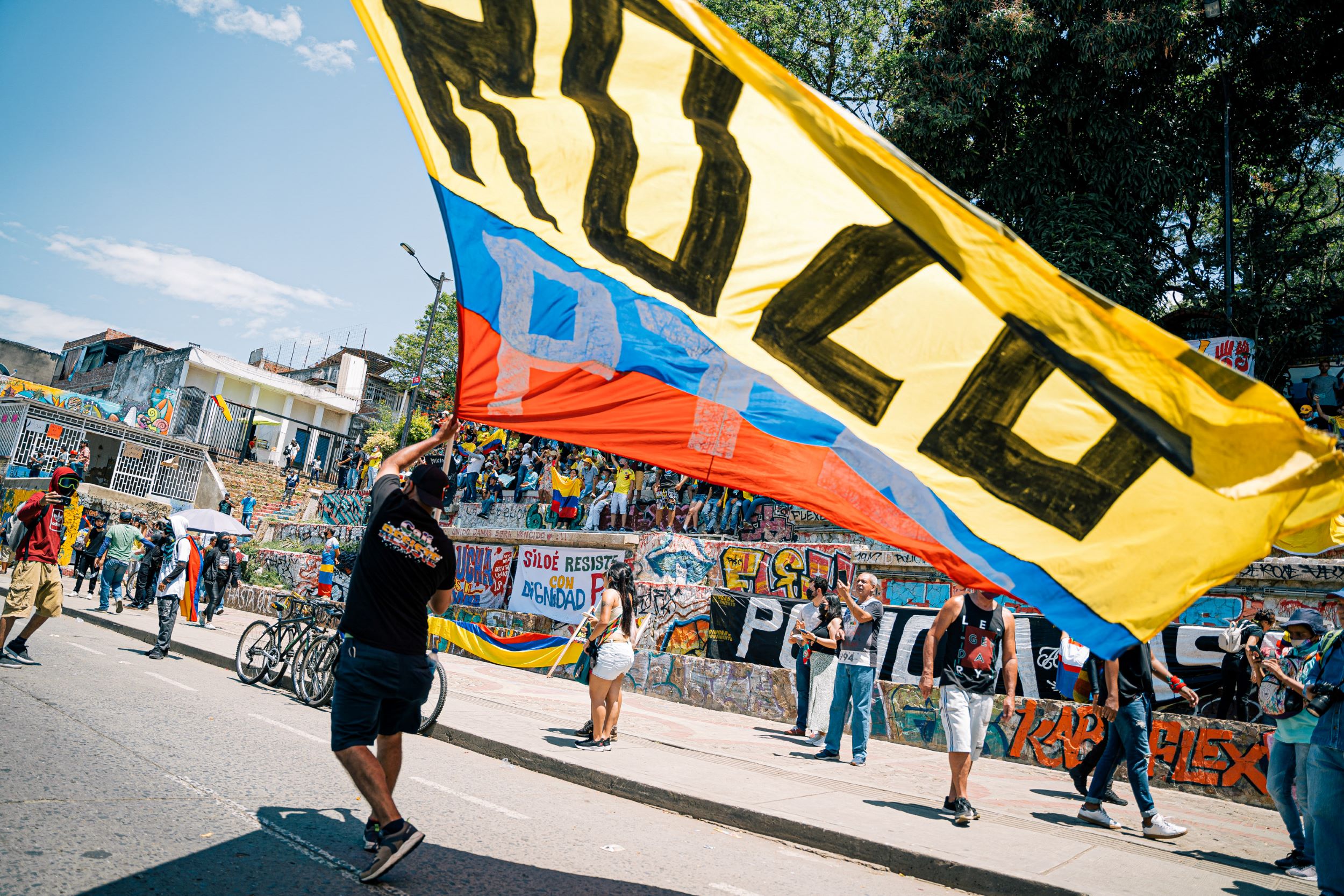
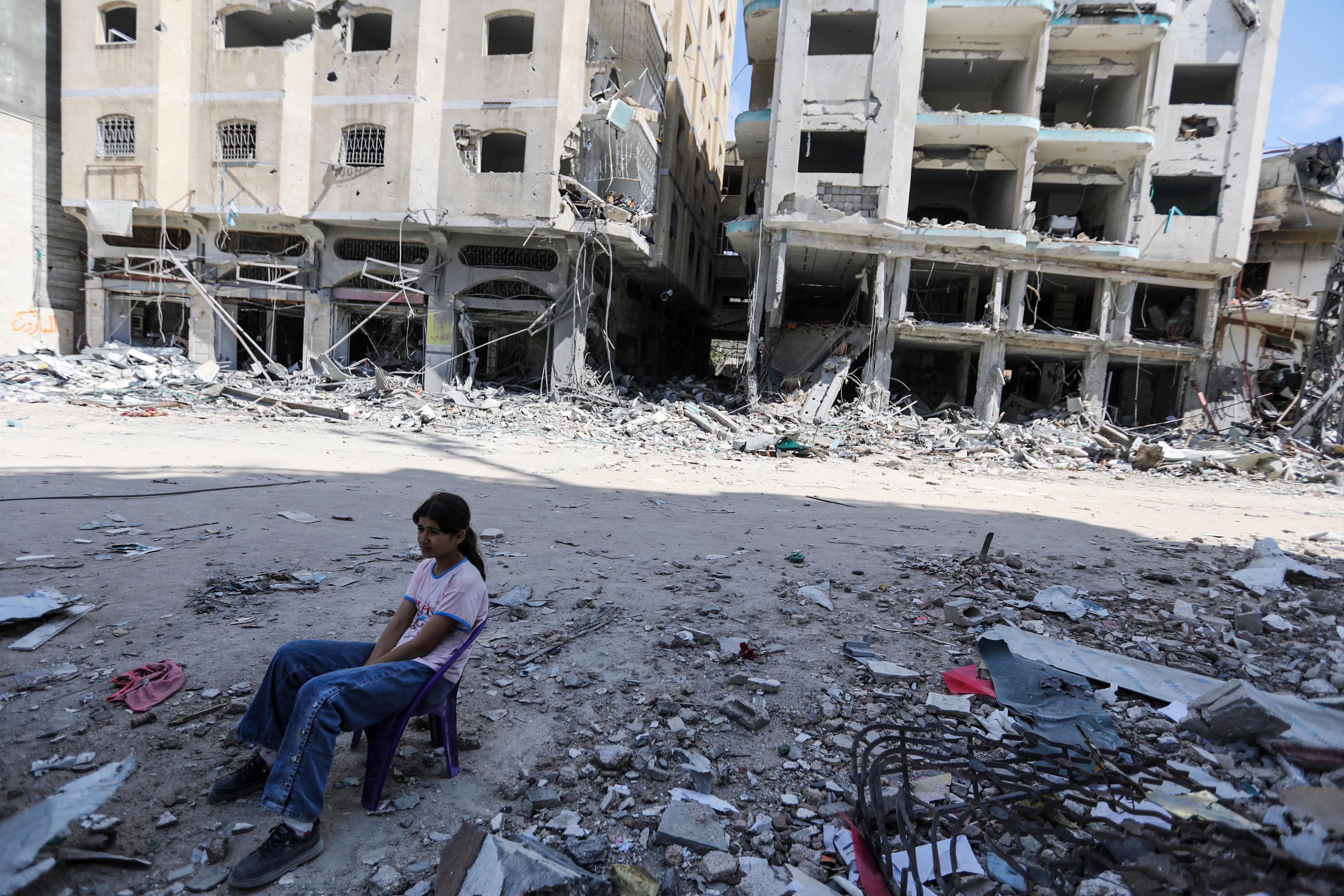
In 2021, amid a burgeoning social crisis caused by the pandemic and decades of war and deep social inequalities, some of the biggest protests in decades flared up on the streets of major cities of Colombia. Rapidly the protests became deadly. People were protesting about - among other things - ex-President Duque’s right-wing economic policies that proposed to tax food and first-necessity items, placing yet more financial burden on an already struggling population.
Across different social media platforms, videos of police and armed men in civilian clothes shooting at protestors went viral.
The mainstream media in Colombia soon began publishing reports about “vandals”, referring to protestors clashing with police and barricading the streets. As the protests continued, this narrative was quickly ramped up. The media reports suggested the protests were being infiltrated by different illegal armed groups. “Terrorist”, “vandals”, “infiltrated by guerrillas” were the terms used in reference to the protesters.
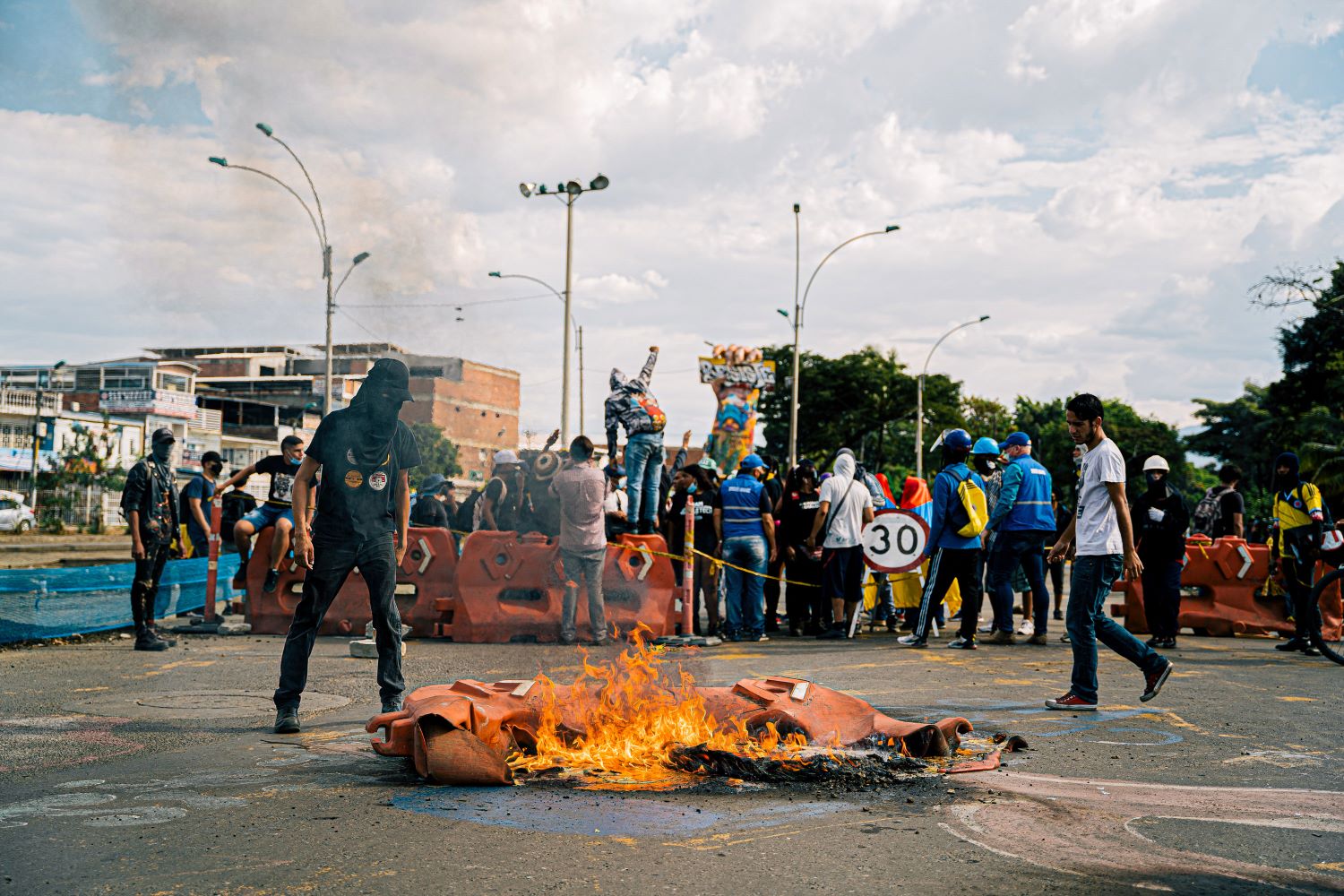
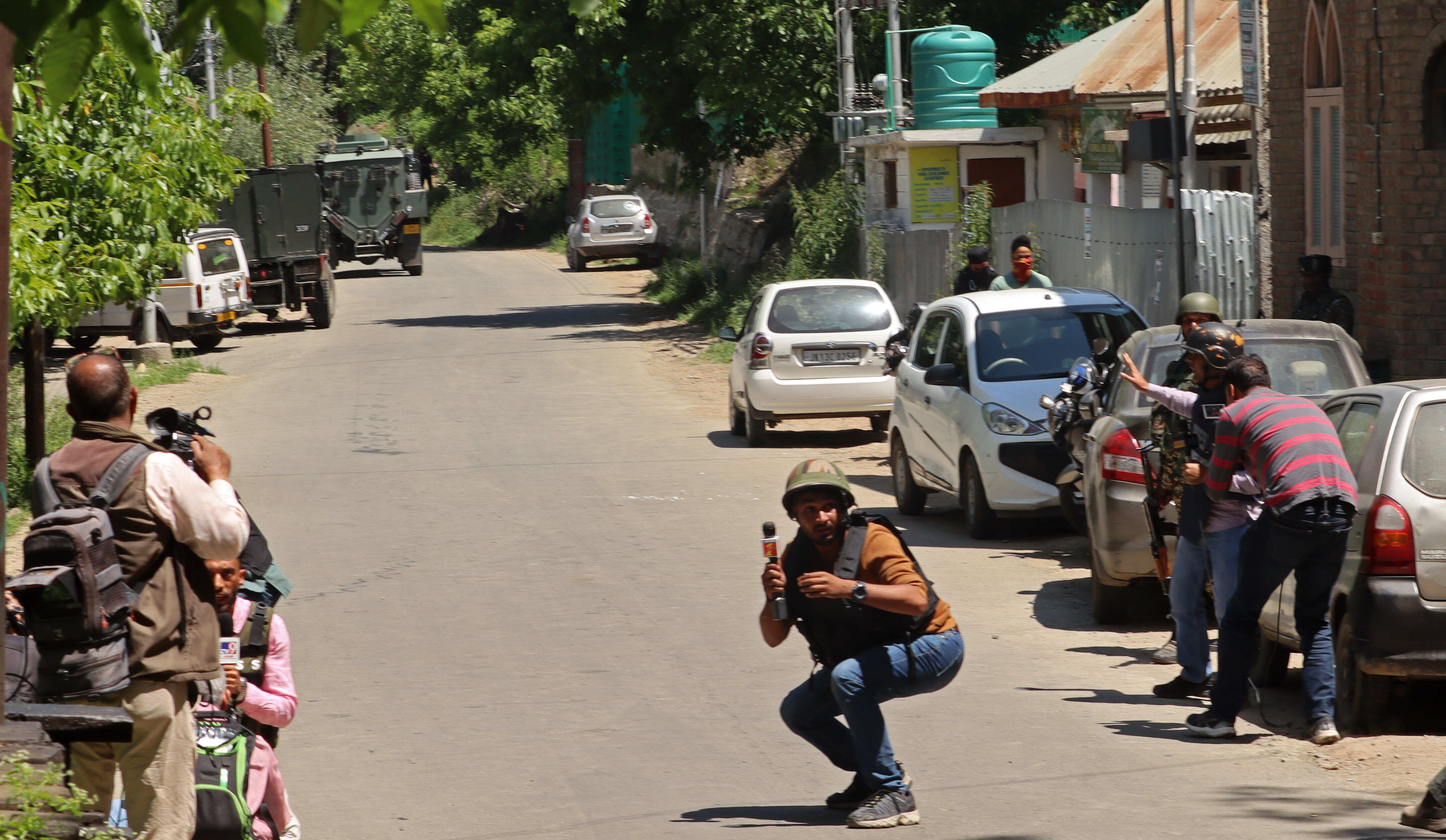
In a country immersed in armed conflicts since its foundation, more than 200 years ago, the protests became rapidly political. The war, which to a large extent had mostly taken place in the countryside, almost unseen and under-reported, was suddenly being seen live on Facebook, Instagram and Twitter. And the reality of the conflict - rather than the mainstream dismissal of it as caused by “vandals” - was being reported from the ground almost solely by independent journalists.
One of the main sources for independent and any interested international media was a police brutality watchdog, NGO Temblores, which was gathering data and information about civilians who had been killed, injured, tortured or “disappeared” - presumably by the state security forces.
A tale of two headlines
During the protests, two headline stories were published one day apart: one by Semana Magazine, a mainstream media outlet, and the other by Rolling Stone in Spanish, very much considered an alternative media source.
Semana’s story stated: “Colombia under threat: During the worst social and economic crisis in recent history, the country faces an unseen wave of urban terrorism camouflaged in legitimate protest. Democracy and institutions are in danger. What is the way out?”
Rolling Stone in Spanish, headlined: “Colombia resists: The voice of a generation.”
Maicol Cordoba, a 24-year-old freelance photographer, was the author of the picture that made it to the Rolling Stone in Spanish cover. He remembers that he published the picture in his Instagram account. He was contacted by the magazine for his picture of the protests in the south-eastern city of Popayan to arrange a rate.
Cordoba recalls his feelings during the social unrest: “In those moments I did not care so much about the price of the picture as to have it in the magazine; that it would give us - me, the photographer, and the people - a voice that could help us get out the information. Because after days (of the protests) in Cali, the situation was bad, and social media had begun to censor us. There were no lives getting out, no news from Cali (the epicentre of the protests).
“Those two covers show the white and black. And are an example of the great polarisation of Colombia,” says Ricardo Duran, editor in chief of Rolling Stone in Spanish, who took the decision to produce a special edition of the magazine during the crisis.
“Those two perspectives: of a Colombia that needs to manifest, that needs to talk, that needs to make demands, that needs changes. And the other Colombia that stigmatises any protest because it needs to defend the status quo, by any means, and can count on enormous capital to defend it.”
The protests marked a turning point for independent media voices - with others also re-publishing user-generated content from social media platforms posted by people on the streets.
The Colombian independent media group Cuestión Publica and The New York Times, among others, used such content to analyse and investigate events where violations of human rights by state security forces during the protests may have occurred. The monopoly over information seemed to be beginning to shift in Colombia.
Who owns the media in Colombia?
In Colombia, TV continues to be the main source of information. There are two main, hegemonic TV media outlets: RCN News and Caracol News. Both organisations are part of major economic conglomerates with ties to economic and political elites in Colombia.
RCN News is owned by Ardila Lula Organization, part of the Ardila Lule family. The family also owns RCN radio which covers a large number of radio stations, RCN entertainment production companies, which make soap operas and movies, as well as some soft drinks industries, sugar plantations, beer producers and even football teams.
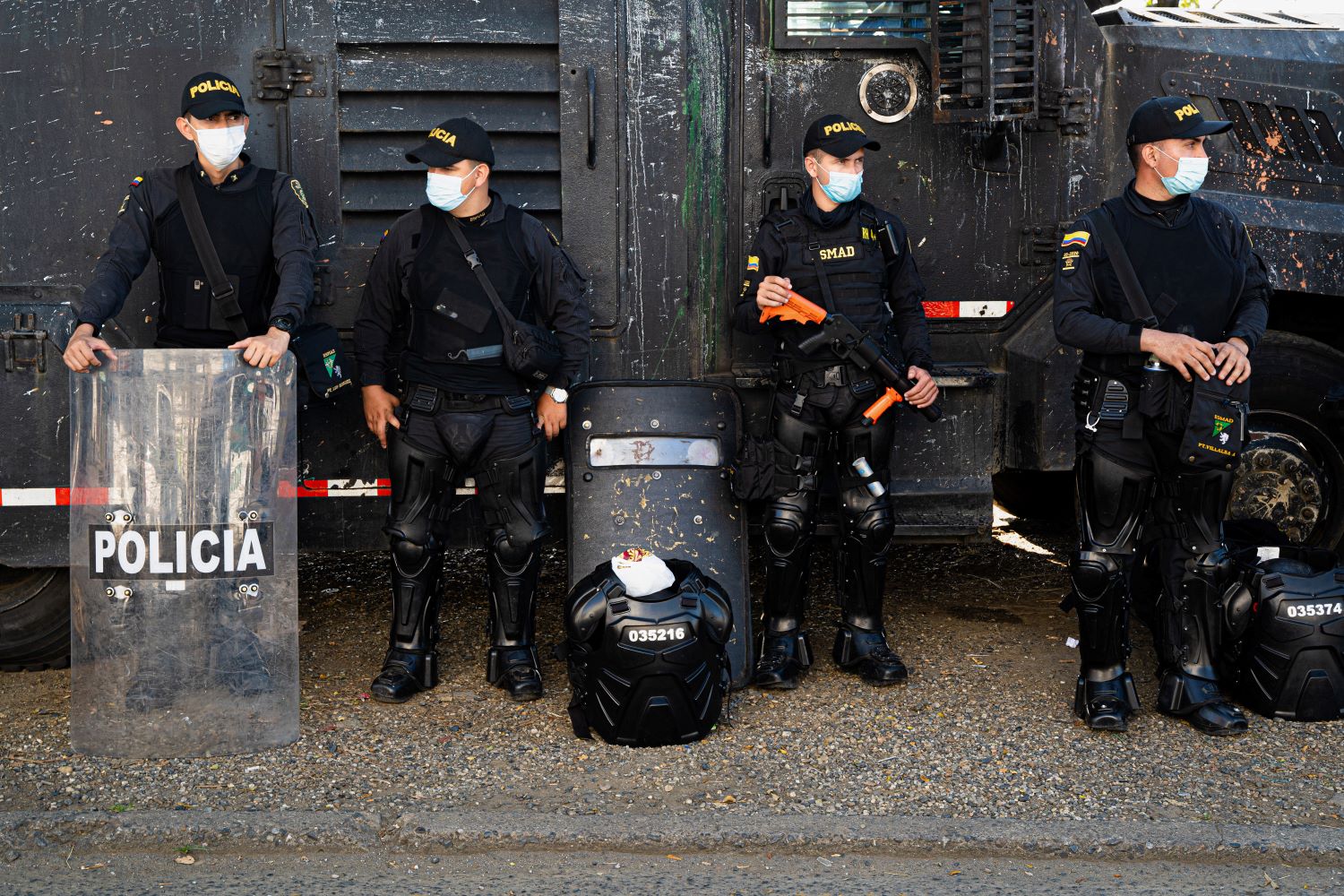

Caracol is owned by another of the richest families in Colombia, the Santodomingo family, represented by Valorem company which also counts Blu Radio, El Espectador newspaper - the second-most widely read newspaper in Colombia - movie theatre companies, energy companies, wood groups, retail supermarkets and other investment firms and transportation companies, among its stable.
El Tiempo - the most widely read newspaper in Colombia - was founded in 1919 and was owned for many decades by the Santos family. They are credited as having put two presidents in power in Colombia and are very much part of the political and economic elite.
The Santos family sold the company briefly to Grupo Planeta from Spain. The richest man in Colombia, Luis Carlos Sarmiento Angulo then acquired El Tiempo and its sub media companies. Carlos Sarmiento also owns banks and other companies including private pension funds that manage the pensions of millions of Colombians.
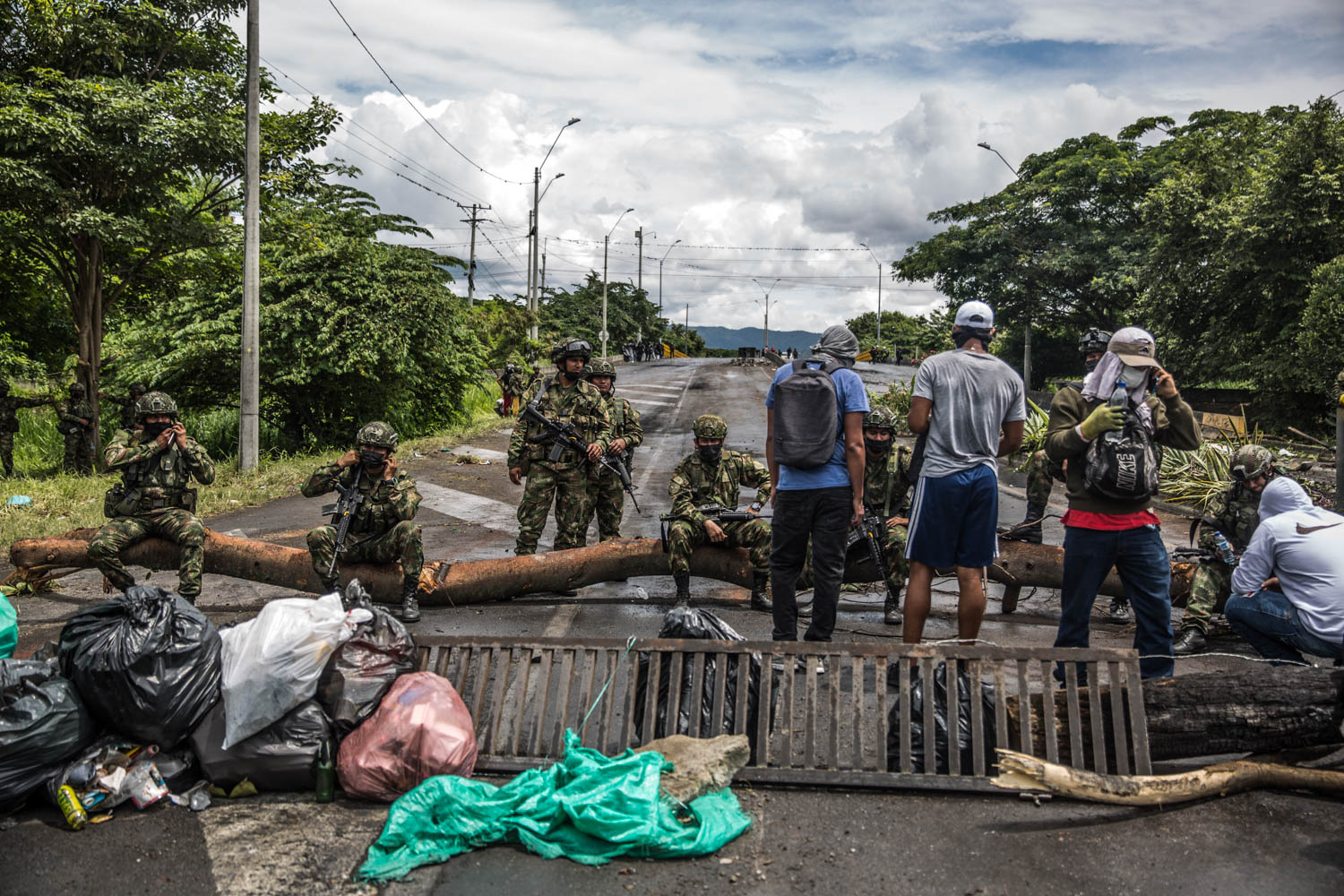

Another family of bankers, the Gilinsky family, one of the five richest families in Colombia, acquired Semana Magazine (print and digital) in 2020. Once a beacon of high quality journalism in Latin America and a respected weekly investigative, long form and feature magazine, it has now become a vehement political actor in defence of the economic and political ideology of the right.
These sorts of acquisitions have been made under a banner of a “rescue” for the media outlets during the ongoing economic crisis. However, it is clear where the interests of these media owners lie.
In August 2022, Gustavo Petro, who is often described as an economist and former guerilla fighter, became the first leftist president in the history of Colombia. One of his primary missions was to reform the tax system, including introducing a new tax on soft drinks and processed food. The government says this is a public health focus to fight obesity and diabetes.
The owners of RCN - one of the main media companies - are also the owners of sugar cane plantations and soft drink companies. RCN and other main media were swift to report about the possible increase in inflation as a result of the new tax. Some journalists even argued that sugary drinks are part of the working-class diet and should not be taxed.
Independent media - filling the ‘credibility gap’
In 2020, while the Gilinsky family was busy acquiring Semana Magazine and with the COVID-19 pandemic raging away in the background, Jose Guarnizo and 30 other journalists left the magazine just days before the implementation of the lockdown in Colombia. The Spanish newspaper, El País, published a piece about this, entitled: “The decline of the Colombian magazine Semana”.
Guarnizo did not falter; along with several other journalists, he created the digital platform Voragine which now employs 12 people. As described by Guarnizo, Voragine is a media outlet for investigative journalism focused on human rights violations and corruption cases using long-form features and in-depth chronicles.
Like other rising independent outlets in Colombia, Voragine has committed to refusing any state or government funding. “We have to be independent in order to talk about any issues we cover: human rights and corruption. We owe nothing to any politician or any political ideology,” states Guarnizo.
Today in Colombia there are many independent media outlets but among the most active are 20 independent media outlets gathered in the Liga Contra el Silencio (League Against Silence). Many of these outlets are less than 10 years old and each one has a different focus and financing methods.
These independent outlets have largely emerged to fill a “credibility gap” as the public’s trust in the mainstream media has fallen. According to a 2019 survey by Gabo Foundation, 84 percent of respondents said they have no faith in the media.
For Laura Sofia Mejia, general director of Baudo Agencia Pública, the measure of media influence is not clicks on articles but rather the impact on communities where the stories are taking place. Baudo focuses on environmental issues and conflict reporting and employs 11 people.
“Measuring the impact of the coverage is more about, for example, how are other organisations interested in supporting the communities?” says Mejia.
Duran adds: “Rolling Stone in Spanish is 100 percent independent media, and we try to provide a counter power against the traditional political powers. This has cost us in commercial terms, and it is uncomfortable for some readers. Nevertheless, we have always felt that this is our duty.”
The economic aspect of independent media in Colombia is the main concern, not only so that they can continue their operations, but also to ensure their independence from big political and economic powers in the country.
Different models of financing are used by independent media in Colombia.
Reader subscriptions, advertisement, grants and awards are the most common ways of financing independent media in Colombia.
Mutante is a digital platform that, according to its website, focuses on creating “conversations'' about specific topics: LGBTQI+, human rights, environmental issues and social inequalities. Its financing model includes subscriptions, grants, awards and sponsored content. The sponsored content is produced by a civil society organisation aligned with Mutante’s vision, according to its website, with editorial independence from their sponsor.
“At Baudo we take a position on human rights, linked with rigorous investigation and committed investigation,” says Mejia. “Even though we have a position, it does not affect our professionalism. That means equilibrium of sources, investigation on site and responsibilities that are not abandoned. Some people might call us activists, said in a contemptuous way. But I think journalism that promises to be objective but is financed by a big mining company is much worse.”
Reporting the war
In times of war it can be difficult to differentiate information from propaganda. This was the case earlier this year during one of the many massacres that have occurred in Colombia since the peace accords with the FARC-EP guerrilla back in 2016. The peace accord ended a 60-year conflict between Marxist guerilla groups and state security forces, as well as illegal paramilitary forces allied with state security forces and other leftist guerrillas. Between 1985 and 2016, more than 400,000 people were killed, 121,768 disappeared, 50,770 were kidnapped and 8 million internally displaced according to the Truth Commission’s final report.
On March 28, 2022, 11 people were killed by Colombian military personnel conducting a military operation in the village of Altos del Remanso, in the southern province of Putumayo.
Jose Guarnizo travelled to the area after the massacre occurred. He teamed up with colleagues from El Espectador and Cambio who were working on the ground there. They joined efforts to investigate and gather a vast array of testimonies from witnesses and inhabitants of the village. They gathered official statements, interviews with prosecutors and military reports.
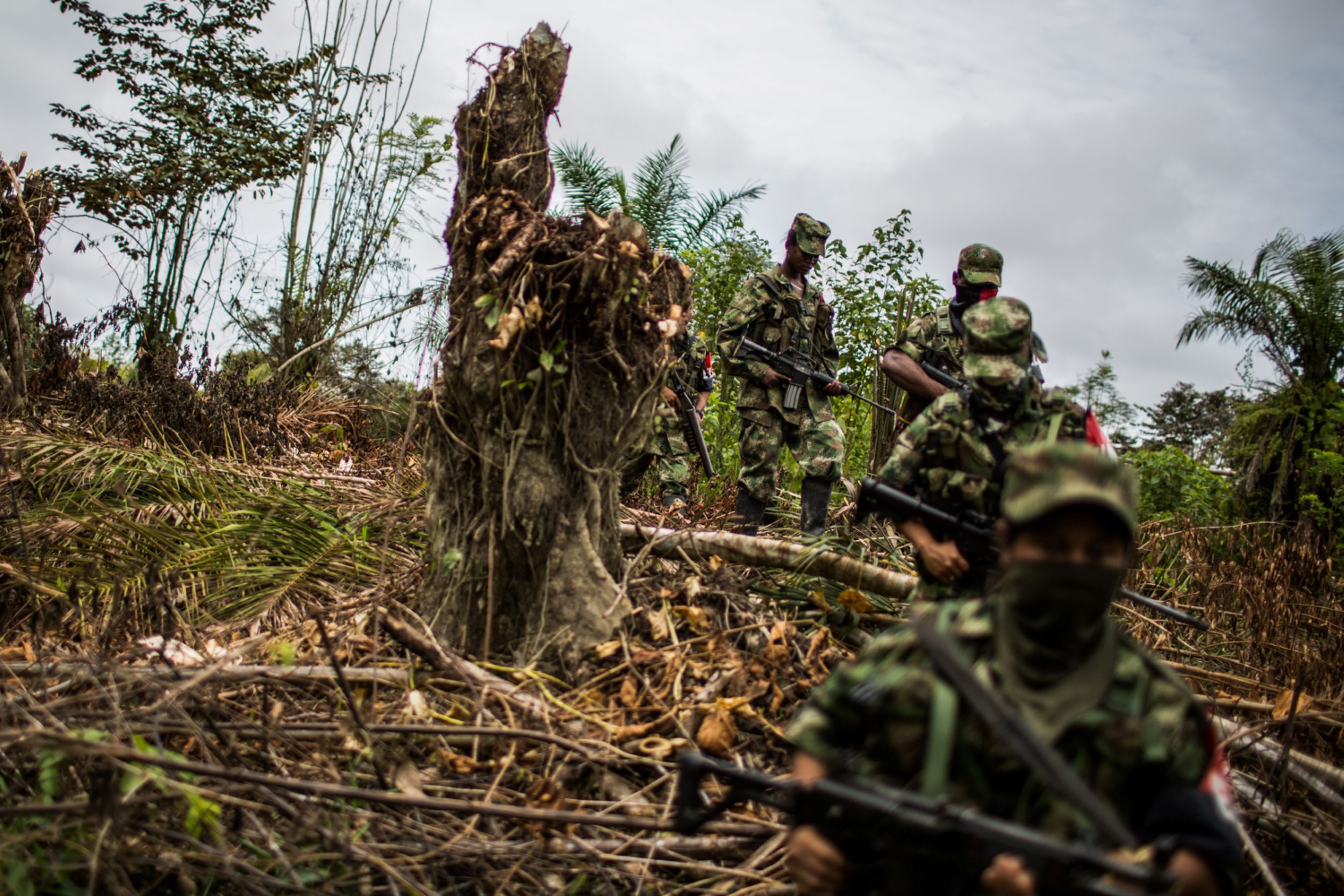

Three different pieces came from this collaborative effort, each one published in El Espectador, Voragine and Cambio; and each of which carried different story lines, sources and focus. All three stories concluded among many other facts that unarmed civilians were killed during the operation.
However, in one of the first pieces published after the massacre, the magazine Semana wrote: “The Army defends itself and reveals proof of the operation against FARC dissidents in civilian clothes, in Putumayo”. The piece did not quote even one person living in the village or who witnessed the massacre. Video and photographic material were provided by the Army, the main sources were military intelligence and official statements from the Army. There was no mention of unarmed civilians being killed, nor any mention of the possibility of any wrongdoing during the military operation.
Almost a month after the killings and in the midst of a congressional indictment of the then Minister of Defence, Semana published a new “exclusive” piece entitled: “The unknown story of the military operation that unleashed a controversy in the country.” The piece once again used as its main sources military intelligence “classified information”, military reports and a single mention of a report by the Ombudsman Office.
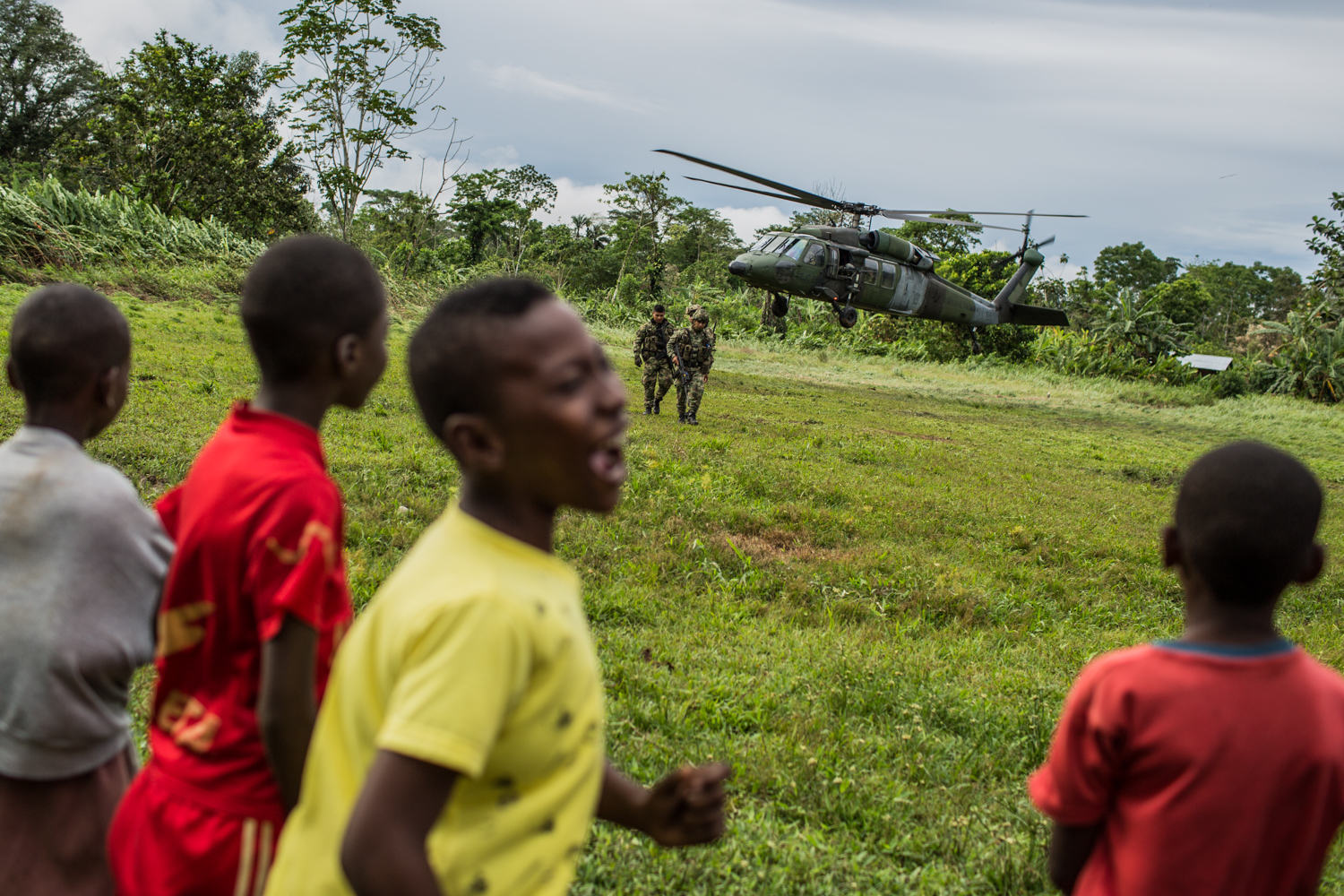

The official version of the incident by ex-President Duque and the Minister of Defence referred to what happened as “a successful military operation against units of FARC dissident factions operating in that area of the country”. The Minister of Defence, Diego Molano, declared on Twitter: “It was not against innocent Indigenous people, but ‘narco cocaleros’ (coca leaf farmers and drug traffickers). It was not a party, but against criminals that attacked our soldiers. Let’s defend Colombians.” Meanwhile, the now-ex-President Duque also took to Twitter to declare: “11 members of the dissident factions have been neutralised.”
The role of the media
The final report of The Truth Commission, an institution created to investigate crimes as well as the fate of many of the victims of the conflict - established as part of the peace accord between the FARC-EP and the Colombian government - was published in June this year.
Franciso de Roux, head of the Truth Commission, said at the end of his speech which questioned the responsibilities of Colombian society for the war: “What was the role of the opinion makers and the media? How did we dare to allow it to happen, and to let it continue?”
In Colombia, using the excuse of “objectivity”, some media have avoided a conversation about the political role they have held during the armed conflict. Mainstream media in Colombia, particularly, have economic interests at stake. But those economic interests are also political interests that have influenced the armed conflict in Colombia.

The fact is that both independent and mainstream media have economic issues to consider - under differing circumstances and with different financial models at play. Without financing, no media outlet can operate.
Furthermore, independent media have also become employers of journalists at a time when more and more newsrooms are reducing staff. The working conditions of journalists, both freelance and staff, in Colombia should be a main concern of all media companies - independent, big or small. These working conditions affect the quality of the journalism that is produced.
It is crucial to identify to what extent economic necessities or interests represent a political bias in order to give the public a clear idea of who is providing them with information about the conflict and current political affairs.
How to continue financing with models that reaffirm their economic independence is another challenge to the continuation of independent media.
In a country with deep social inequalities the access to information varies enormously. In remote and isolated places in Colombia - frequently the battleground for conflict - the only information the public receives is from the mainstream media through TV.
The challenge of how to reach this segment of the Colombian population, which has been marginalised socially and politically and left at the margins, is another major issue for independent media outlets to navigate.
Plurality in the media landscape is crucial in a country that has taken its first steps of transition to a leftist government and that has been immersed in a decades-long war. Is imperative for journalism to be able to hold the powers that be accountable.
In the times of fake news and during a crescent of distrust in the media, the ideological sphere surrounding the media, whether it is recognised or not, should not divert from the social responsibility of journalism to deliver factual information to the public.