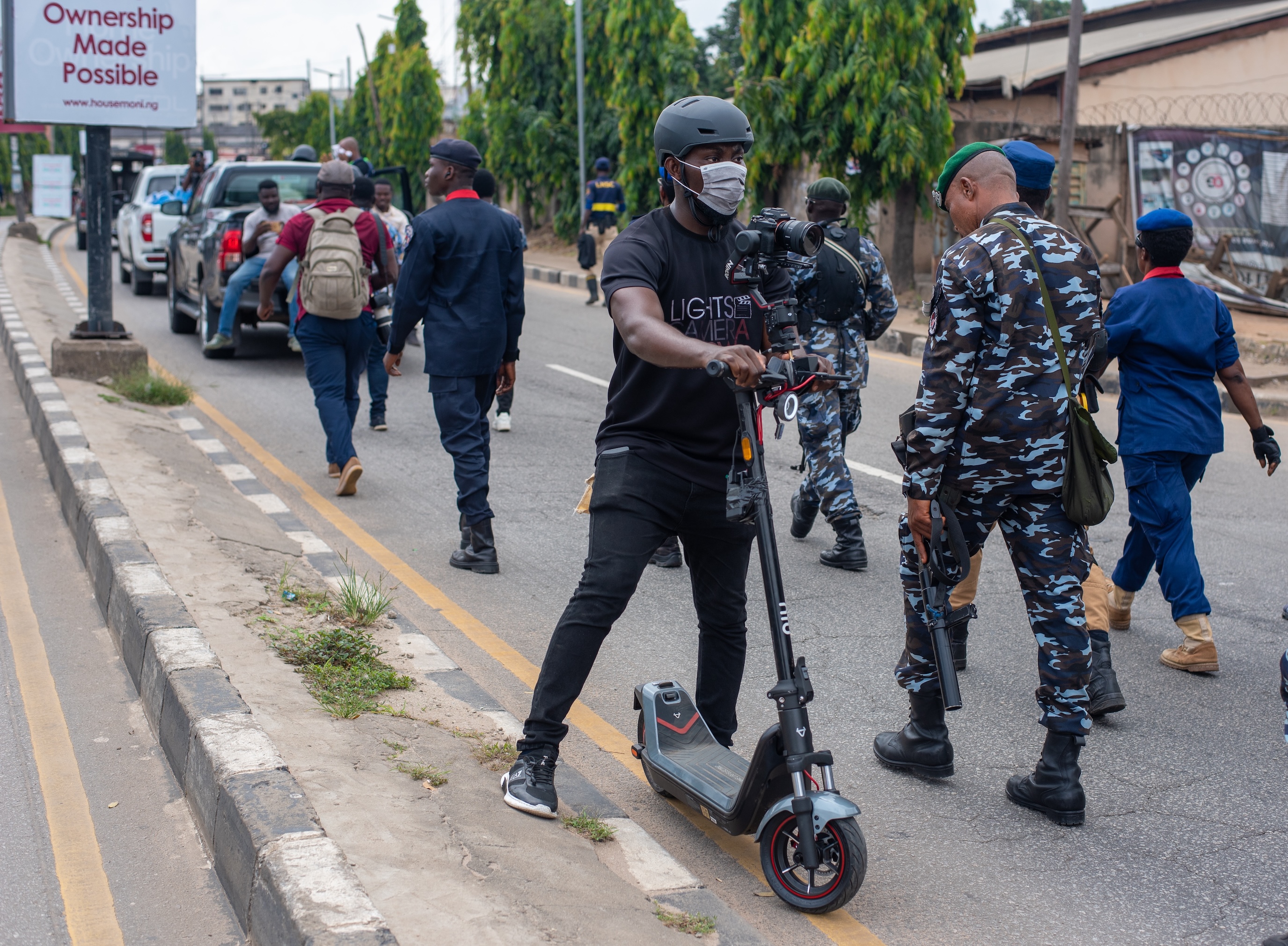Imprisoned, exiled and forced to base themselves overseas, independent journalists in Vietnam are punished harshly if they publish the ‘wrong’ sort of content. Some, such as Luật Khoa tạp chí, are fighting back
“If Vietnam makes it to the UN Human Rights Council, we will have to eulogise the State and the Party. If not, we shut up,” says Thu, a journalist working for a state-affiliated media group in Hanoi.
Thu, who does not want to give her real name for fear of reprisals, is citing the message from her editor-in-chief who had received instructions last October during his weekly meeting with his ultimate boss, the Central Propaganda Department in Vietnam.
For Thu and her colleagues, this is “as usual as daily meals”.
Back in 2017, a similar top-down order had been issued. Phạm Sanh Châu, former Vietnamese Ambassador to UNESCO, became one of the rare candidates in Asia and the first from Vietnam to compete for the post of General Secretary of UNESCO. Thu and her colleagues were instructed by the same editor-in-chief to ensure glowing publicity for the candidate.
Then, when he was not elected to the post, they were instructed not to mention it.
At the behest of the Central Propaganda Department, which operates a cumbersome propaganda apparatus in the country of almost 100 million people, Vietnamese outlets publish news in unison. They were silent together on Phạm Sanh Châu's failure in 2017 and sang the Party’s praises in unison over its “protection and promotion of human rights”, when Vietnam won a seat at the Human Rights Council in 2022.
Vietnam uncensored?
Vietnam’s press has not always been so strictly controlled - indeed, part of Vietnam was briefly acquainted with freedom of speech.
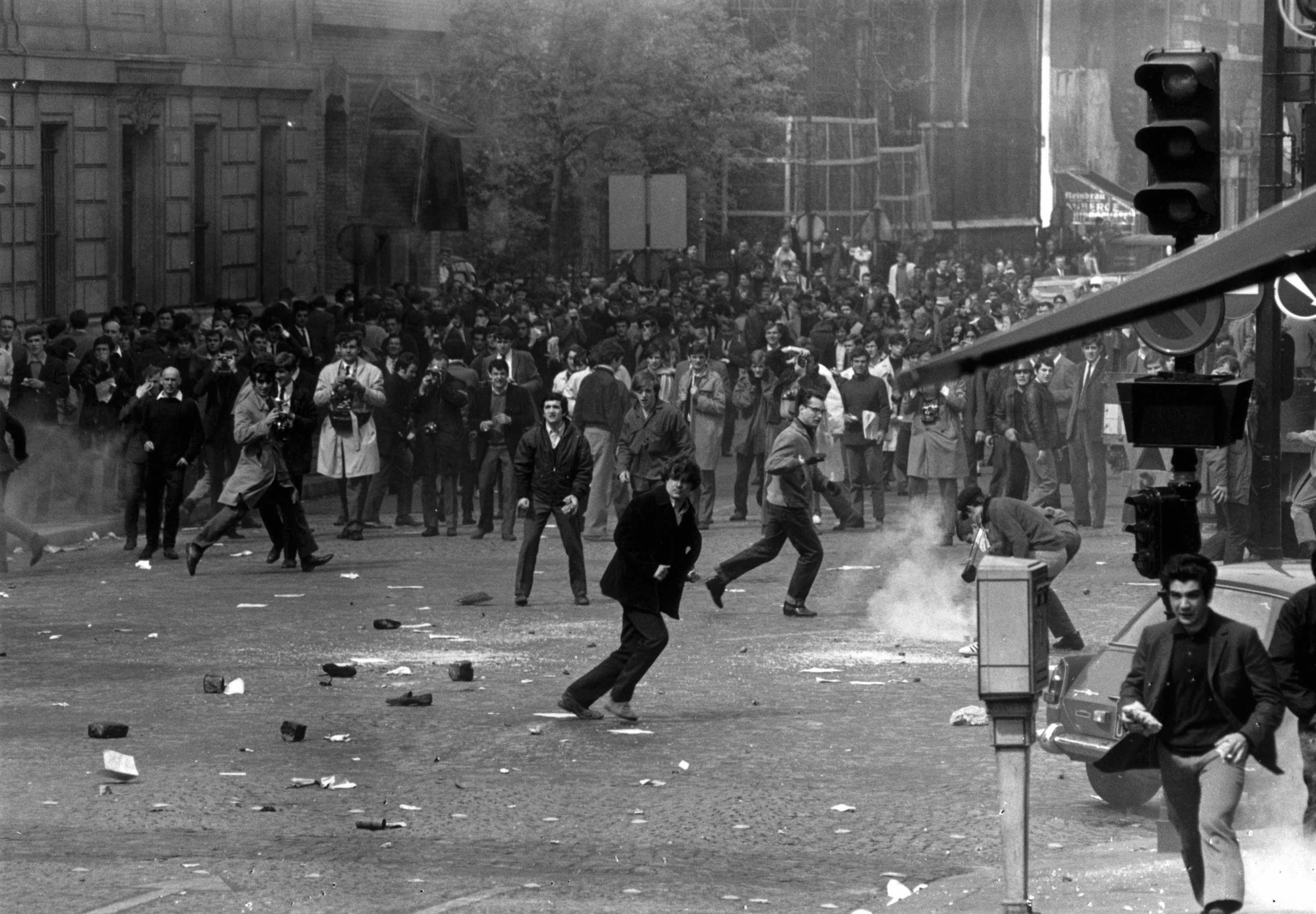
From 1945 to 1975, and particularly between 1954 and 1975, Vietnamese press was subjected to two distinct political regimes. In the Democratic Republic of Vietnam (DRV), non-communist media outlets were quickly eradicated, while the press in the Republic of Vietnam continued to operate in a pluralistic environment. The political journalism scene in Saigon was characterised by diversity and unrest, particularly following the arrival of more than 1 million northerners who migrated to the city after 1954.
The Nhân Văn - Giai Phẩm affair (1955 - 1958) exemplified the Communist Party's efforts to regulate the press in the North. Nhân Văn and Giai Phẩm (Humanism and Beautiful Work) were dissident literary periodicals which led movements calling for freedom of speech and sought to openly critique what they saw as abuses by the Communist Party before they were banned. Those who joined the movements were imprisoned or sent for “re-education”. In the southern region of the country, the CPV utilised revolutionary media to counter non-communist and anti-communist news outlets.
After the reunification of the country - or the Fall of Saigon in 1975 - numerous attempts to push for bottom-up democratisation of the press failed. With the capture of Saigon by the Communist Party of Vietnam (CPV) in 1975, the presence of a dynamic and diverse press came to an end, as media organisations and journalists who did not conform to communist ideology were forced to cease operations. The CPV has since then de-legitimised dissent of all kinds in both outlets and social media. Numerous independent journalists had to flee Saigon for survival.
These days, Vietnam does not celebrate World Press Freedom day on May 3. Instead, the country has its own day to extol its own journalism. June 21 is not just Vietnam’s Press day. More precisely, it is “Vietnamese Revolutionary Press Day” (báo chí cách mạng).
The press is perceived as a tool for class struggle and social control; established, developed, and directed by the CPV to uphold the Party's pivotal and historically predetermined leadership role. A state-recognised journalist is thus required to uphold the revolutionary ideals of the CPV.
Despite this tight control, autonomous outlets operated by Vietnamese people at home and abroad, be it officially registered or unregistered, have emerged, despite frequently being dismissed by the CPV as “illegal”.
Founded in 2014 by Vietnamese activists and operating entirely online, Luật Khoa tạp chí (LKTC), for example, is part of a broader project called Legal Initiatives for Vietnam (LIV). Its primary goals are to disseminate legal knowledge for Vietnamese citizens and to become a platform for uncensored news about Vietnam.
Newsrooms on the edge
The multimedia LIV, now legally registered in Taiwan, is not easily accessible to those based in Vietnam. Nor is its English version: The Vietnamese. None of the three founders, Phạm Đoan Trang, Trịnh Hữu Long and Trần Quỳnh Vi, studied journalism in college. They just happened to embark themselves on this journalistic journey: with a view to promoting legal literacy in Vietnam, which many activists for democracy considered as the starting point of bottom-up democratisation.
On September 12, 2019, Trang was awarded the Prize for Impact by Reporters Without Borders’ Press Freedom Awards in Berlin. Nonetheless, Trang, who worked for 13 years for state media before pursuing independent journalism, was unable to travel to receive her award in person.
At the time of publication of this article, Trang has been in jail for almost three years for “propagandising against the Socialist Republic of Vietnam” under Article 88 of the 1999 Penal Code, which simply penalises any writer/dissident and sentences them to up to 20 years imprisonment. She had published articles exposing wrongdoings in the Party.
Trần Quỳnh Vi, a lawyer and journalist based in the United States and one of Trang’s partners, is mainly in charge of the English version, The Vietnamese. Vi acknowledges her limitations in being not on the ground in Vietnam, yet has been able to be in touch with activists from afar on a daily basis. Being fluent in Vietnamese distinguishes her from the vast majority of American journalists.
“It would be very hard for privileged American journalists to portray how things are in Vietnam," says Vi.
She adds that the “inconvenient truth” is that journalists are far from equal when it comes to being able to carry out reporting duties. She is aware of her own privileges compared to Vietnamese colleagues, especially those based in Vietnam.
“Trang and I are both journalists. We write about pretty much the same issues on human rights. Yet, while I can write freely and never have to worry about being arrested, she is in jail".
From political activism to journalism
In 2011, Trang and Long took to the streets to protest against China after Chinese patrol boats attacked a Vietnamese oil survey off the coast of Vietnam. At the time, many peaceful protestors for patriotic causes were detained by the police.
“It was also a time when there was an unprecedented rise in cases of unjust detentions and imprisonment in Vietnam,” says Long.
The lack of laws against demonstrating in Vietnam (there are rules about registering protests before they take place, however) did not prevent the authorities from clamping down on those who chose to protest. “That there was no law on demonstration does not mean that we are not allowed to demonstrate,” says Long.
What struck Long, who was then working as a legal consultant for Vietnamese companies but is now based in Taiwan, was the lack of legal literacy among the Vietnamese public at large.

In fact, he says: “The Vietnamese Constitution acknowledges the right to demonstration. But most were unaware of that." For this reason, says Long, the general public was quick to cast blame on those who were being arrested for protesting. Unjustly detained people, thus, lost support from their families and friends while being denied the opportunity to obtain justice for themselves.
“Most people thought those detainees must have done something wrong to be arrested or imprisoned,” says Long. “The thought of protecting the rights of detainees never crossed their mind."
Under Article 7 of Resolution 38/2005/NĐ-CP on state measures to ensure public order, gatherings of more than a few people in public places must be registered in advance with the relevant People's Committee where the activities are due to take place. This regulation does not apply to activities organised by Party and State agencies, the Vietnam Fatherland Front and political-social organisations. In short, even a gathering of five people on the street would need permission from local authorities.
Trang and Long decided that they needed a platform to dissect and discuss legal issues for lay people in order to ensure that people know what their rights really are. They decided to launch LKTC online.
“People need to stop blindly obeying the law," says Long. “They need to question the law, and even resist the law when it is not in line with common sense or with our Constitution. When there is no law on it, it does not mean we are not entitled to this right.”
More importantly, Long emphasises his hope that his readers and the general public will develop the ability to differentiate between propaganda-oriented media that merely asks people to conform to the law, and independent media that actively contributes to the dissemination of rights, enabling people to question, doubt and even criticise the law.
One of the key issues that he aims to bring attention to is that while laws exist, law enforcement officers and judges are often lacking in independence. “Police and judges must be Communist Party members," he says.

Life on the ‘left side’
Saying no to censorship and self-censorship, the team is committed to covering what is left out by the Party-led media system.
The term "right side" (lề phải) has become a euphemism for Vietnam's official media outlets, as opposed to "outlawed media", particularly self-proclaimed journalism on social media platforms. As a result, independent journalists and “netizens” refer to themselves as the "left side" (lề trái), which tend to provide accounts that challenge official narratives when necessary.
In the eyes of the CPV, the LKTC is left-sided at least and reactionary at most.
The government has called the LKTC an illegal entity on mainstream media several times. As a result, it has become impossible to recruit staff and contributors based in Vietnam, despite offering an attractive salary package. It is also not possible to reach out to local authorities as well as ordinary people.
Since 2017, there has been a sharp decline in the number of LKTC readers. Such a shrinking in readership can be put down to numerous factors. However, according to Long, it is mostly due to the top-down blocking of their official website.
Attacks on LIV by major Party-backed news outlets has made collaboration with contributors and donors within the country even harder. For example, in a recent article published by a state-backed news outlet, LKTC is portrayed as a hostile force which always defames, distorts and misinterprets actions by state or Party organs in an attempt to “provoke gullible populations”.
LIV and LKTV have no way to counter such attacks. “We are not authorised to practise journalism in Vietnam, nor can we have our office in the country," says Long. “Even making donations to us would put readers at risk”.

Cyber laws
As a result, the editorial board has to come up with detailed and regularly updated instructions to help readers navigate the state-engineered “Bamboo wall”, a lighter version of China’s Great Firewall that blocks websites deemed as undesirable by the government. Each article has to be sent to both non-paying and paying readers via different channels. Currently, the LKTC is focusing its content on religious censorship in Vietnam, a topic that has remained more or less a taboo, and which is nowhere to be seen on the mainstream media.
The LKTC was launched at the same time that the Ministry of Public Security opened its Department for Cyber-Security, which possesses the ability to access data held by internet hosting and content providers, conduct cyber-attacks against news websites, obtain personal data, track and monitor bloggers and close down blogs and personal page.
The safety of its readers remains a concern for the team. “Readers might face legal consequences if they install a VPN to read the LKTC," says Long. Writers and contributors are therefore allowed to use pen names if they have security or privacy concerns.
Paying their staff members and contributors in Vietnam poses another challenge, however. “The government can track down every transaction,” says Vi.
Another primary mission of LKTC is to highlight and correct censored history, particularly the state’s version of the short-lived Republic of Vietnam (1955-1975), in order to show that freedom of press is not merely stuff of dreams - it has already existed before. In some ways, the team is not creating something brand new, but rather attempting to revive something that was once there.

For Vi, who was born in Vietnam and migrated to the US as a teenager, working as a journalist focusing on Vietnam and writing for a Vietnamese audience is a way to keep in touch with her own Vietnamese identity.
“Vietnam is still my own home country. And Vietnamese is still my mother tongue”, she says.
Hopes for a brighter future
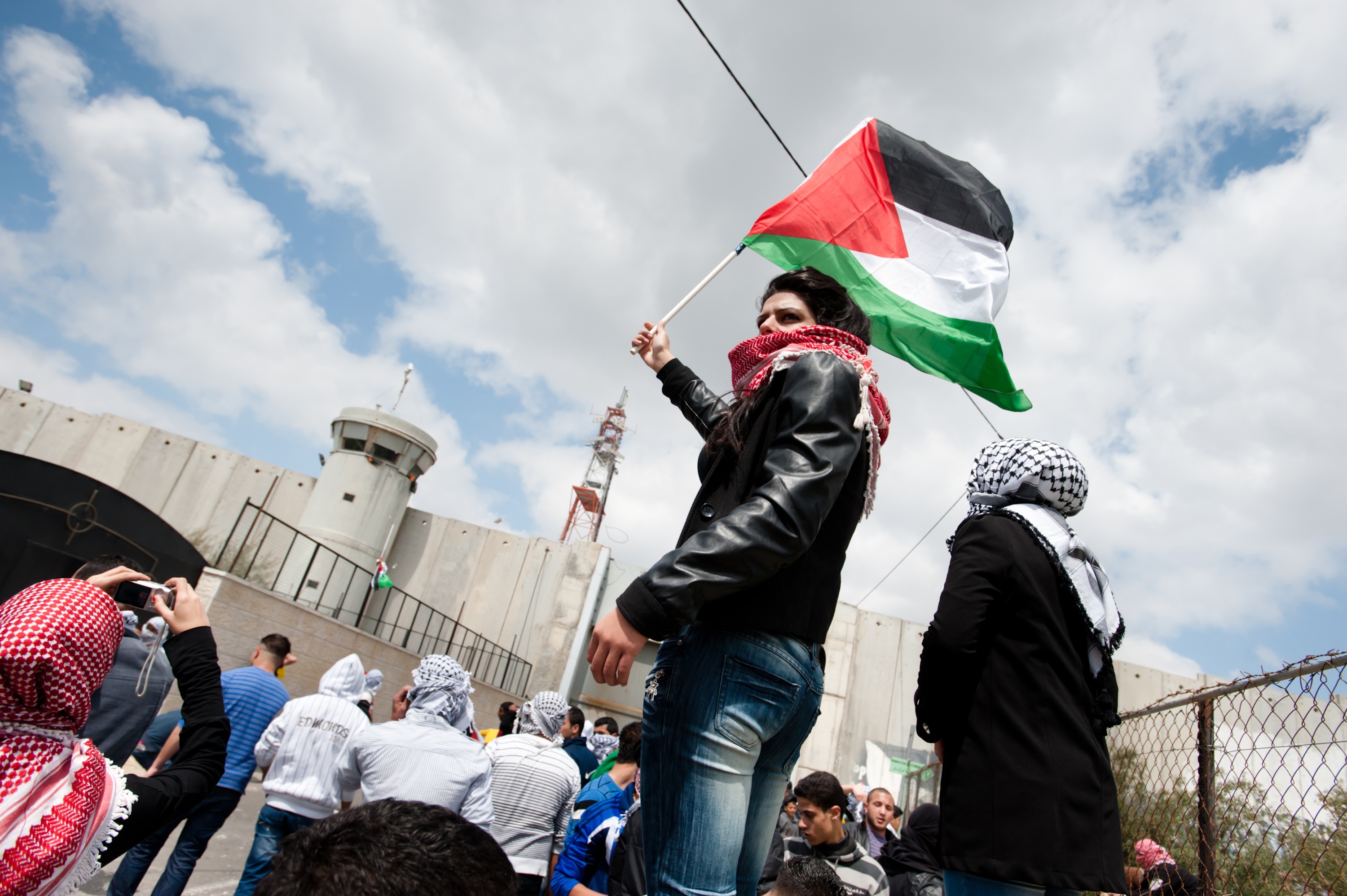
There has never been a more pressing need for independent journalism in Vietnam. The media in Vietnam is deemed to be in a "highly critical state", according to the World Press Freedom Index measured by Reporters Without Borders, with a ranking of 178 out of 180 countries. It has dropped four places in this index in just one year and Reporters Without Borders describes Vietnam as the third most prolific jailer of journalists.
“When Voice of Democracy Cambodia (the online news outlet) was just shut down in February this year, Western media said it was a severe attack on freedom of speech,” says Thu. “But Cambodian people at least had independent outlets on their soil. We do not have any in Vietnam”.
Despite enormous legal, financial and operational challenges, Long and Vi are confident that they are making a change. “Now, people are talking more and more about the right for detainees to remain silent, or the right for citizens to demonstrate," says Long.
Long says that private donations and paid subscriptions have been on the increase. Recently, his team received a donation of VND 50,000 (around $2) from a Vietnamese student with a heart-warming message: “I am only a student. I only have this much [to donate]. I hope your team will persevere in your work.”
It is messages like this that keep the team going in its fight to bring independent journalism back to Vietnam.