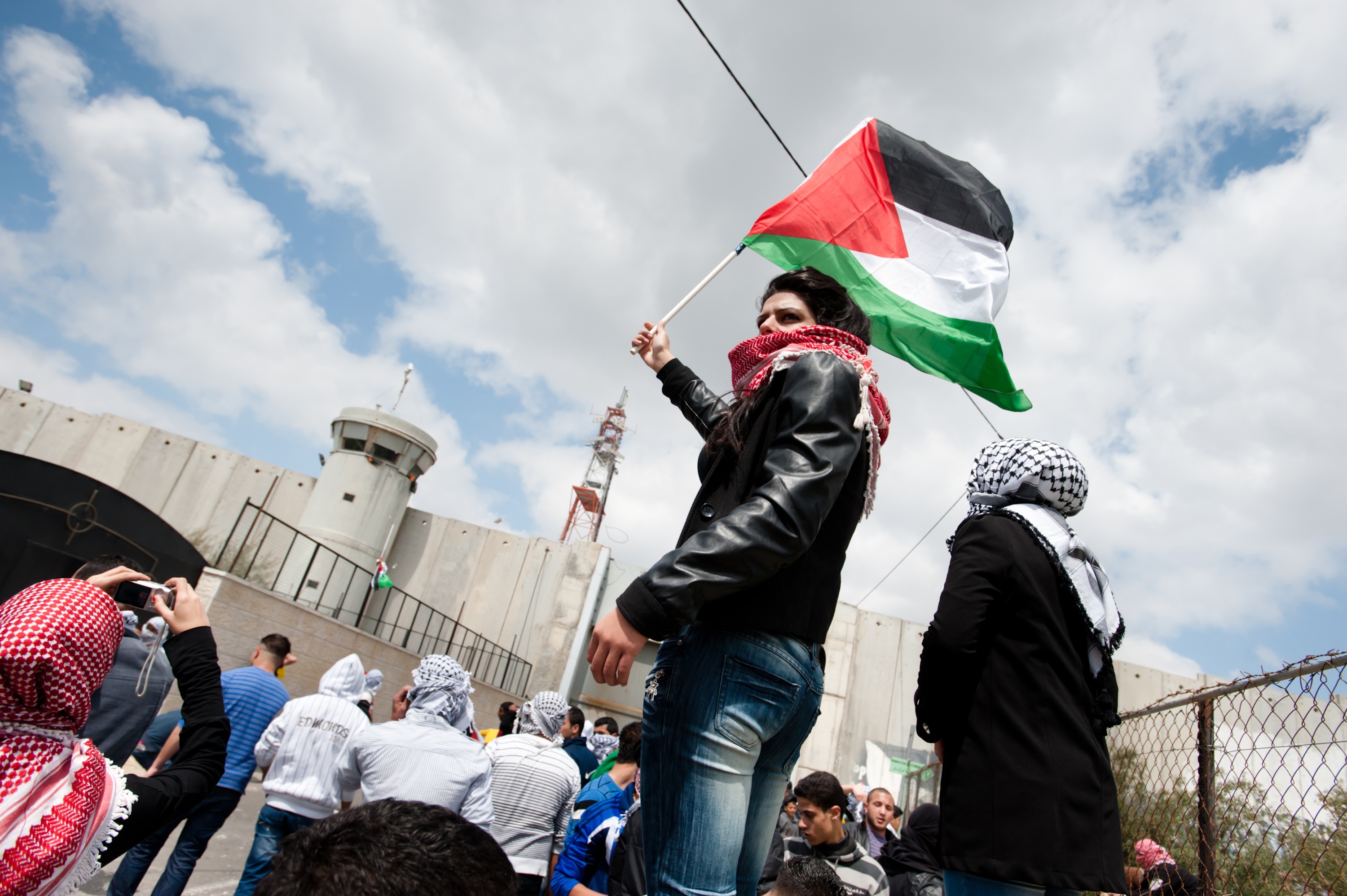
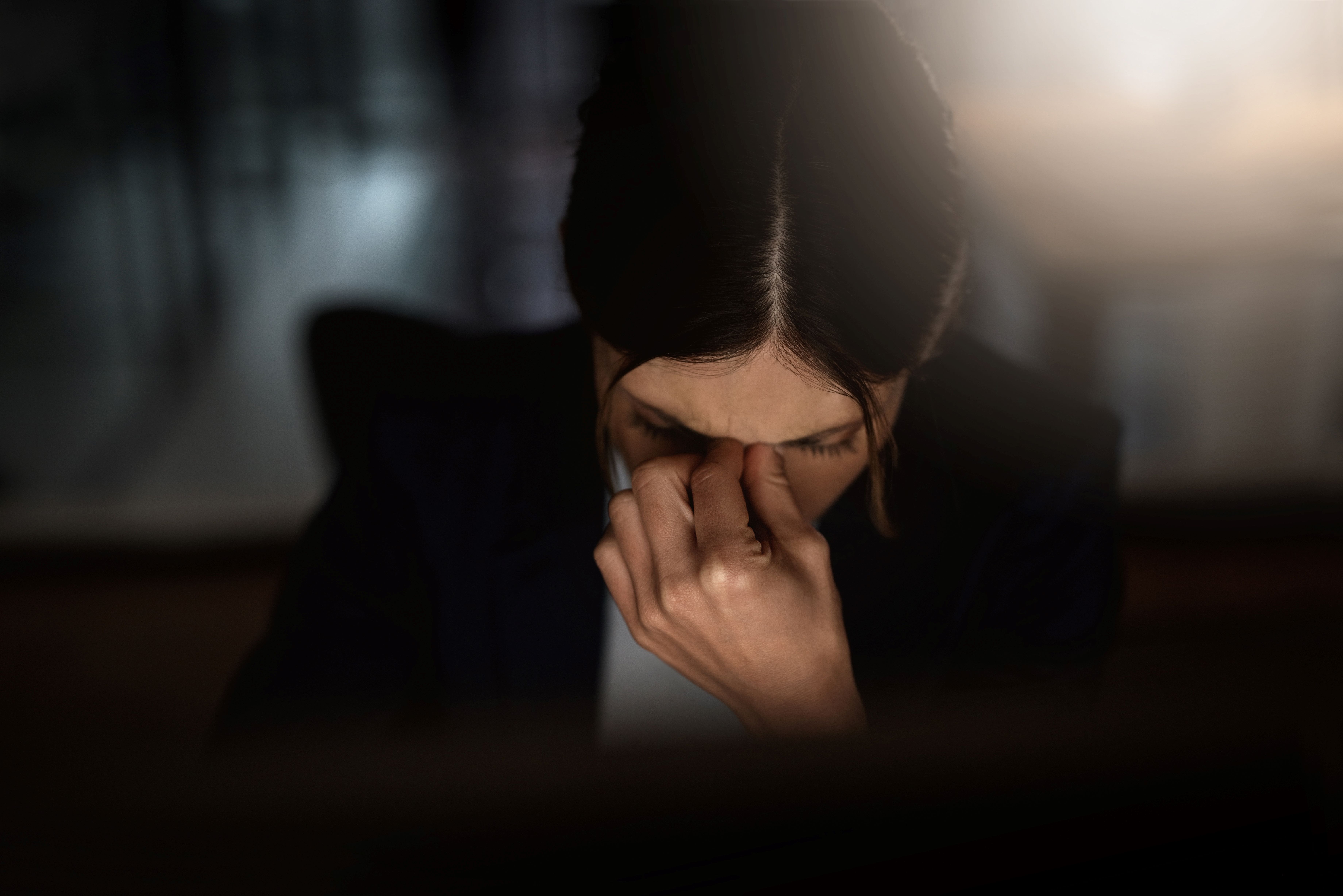
Female journalists suffer sexual harassment - and worse - on a daily basis in newsrooms in Nigeria. But for most, it’s a case of ‘put up and shut up’ or lose your job
Just days after Pamela* joined a prominent radio station in Abuja, Nigeria's capital city, last August, her immediate boss, the station's programme's director, called her to his office. "I just finished presenting a programme in the evening when he entered the studio and ordered me to his office," she says.
When Pamela arrived at her boss's office half an hour later, she found him seated on his chair with a bottle of whiskey on his desk. Then came an embarrassing invitation from her boss the 26-year-old journalist says she never saw coming.
"He looked straight at me and told me to come sit on his lap," she says. "I told him straight away that I couldn't do that."
Pamela said her boss kept insisting but she turned him down each time he demanded she sit on his lap. "When he saw that I wasn't ready to play along, he got up from his chair, put his hands around my waist and tried to hug me but I pushed him away and walked out of the office."
Pamela's boss never attempted to sexually assault her again after that incident but his attitude towards her changed afterwards. "He never said hello to me again and never approved any request I made to him that had to do with the programme I anchor."
Pamela isn't alone when it comes female journalists facing sexual harassment from their superiors or colleagues at work.

In Lagos, Angela*, a 29-year-old reporter for a newspaper that publishes daily, had barely settled into her new job when her editor began to sexually harass her. On a daily basis, she said, her married boss would call her and praise her body shape and request that they both spend time alone in a hotel for a couple of days at least.
"He has been harassing me right from the first day I began work," said Angela, who was hired as a reporter at the start of November 2022. "Sometimes, he'll call me to his office and begin to touch me inappropriately, including grabbing my buttocks."
Angela continues to work at the organisation only because finding a job in Nigeria, where the unemployment rate nears 40 percent, is not easy. "I have to find a way to adapt to the situation because if I quit my job, I'll have no other means of survival," she says.
But holding on to her job means Angela continues to face sexual harassment from her editor who she says is bent on having a relationship with her. "I've told him I'm not interested in him but he just wouldn't stop bothering me," she says. "I hate going to the office because there's a chance I'll be sexually harassed when I get there."
Not far away from where Angela works is the office of another of Nigeria's leading newspapers, where 39-year-old Fidelia* work on weekdays as a reporter. Just like Angela, she reports to an editor who is sexually attracted to her. But unlike Angela, she finds herself in a newsroom where her male colleagues - just like her editor - also often harass her sexually, even in public.
Male colleagues make unpleasant comments about Fidelia's breasts and buttocks whenever she shows up at the newsroom in the morning, according to her. Some, Fidelia says, often walk up to her and ask if they can touch her "soft" body. Others, like her editor, have touched her on her breasts and buttocks without her consent.
"Sadly, there's a culture of sexual harassment where I work," Fidelia says. "You can't report incidents of sexual harassment to anyone because it's a male dominated organisation and so many men are involved in harassing women."
Like Angela, Fidelia joined her newspaper in November after months without a job. While she hates working in an environment where sexual harassment targeted at female employees is rife, Fidelia can't quit because getting a new job at a time when many news organisations are cutting their work force is so difficult in a country where inflation is rising and about 60 percent of the population (133 million people) are multidimensionally poor, according to Nigeria's National Bureau of Statistics.
"Everyone in the family looks up to me for financial support, so it's very important that I keep my job," says Fidelia, who is the only employed child in a family of three girls whose parents died about a decade ago. "If I quit, my siblings would suffer."
Pamela, Angela and Fidelia are just three of a large number of female journalists who suffer sexual harassment in newsrooms but are so scared of speaking out publicly because they fear it could have a negative impact on their jobs, and the trauma they could experience if they come forward could be further devastating.
But the three women want to see changes in newsrooms that would make life better for female journalists.
"There must be very tough policies in place to put an end to sexual harassment in media organisations," says Pamela, whose workplace, according to the journalist, has no dedicated anti-sexual harassment policy. "If such a framework is in place, it will encourage many of us who've suffered sexual harassment to come forward without any fear of retribution."
Pamela wants "responsible" male journalists to get involved in the fight against sexual harassment in newsrooms as well.
"There are male journalists with good characters who hate to see women being sexually harassed by their colleagues but are unwilling to speak publicly against it because they don't want to hurt the culprit who may be their friend," Pamela says. "That has got to change, and I believe having anti-sexual harassment policies [in news organisations] would also encourage some men to speak against sexual harassment."
Similarly, Angela wants an anti-sexual harassment policy to be a priority for media organisations and wants having such a document to be made compulsory for all media organisations. "If we want to see results, the government should shutdown any media platform that does not have a policy against sexual harassment in its office," she said.
In addition, Angela wants any anti-sexual harassment policy to be protective of the accuser whether or not she's able to prove her case. "If I'm not sure I'll be able to keep my job after reporting the person who harassed or assaulted me, then there's no need coming forward," she said.

Some incidents of sexual harassment, according to Angela, may be difficult to prove "especially when there are no witnesses" but she insists a woman shouldn't be forced out of her job because she couldn't convince anyone that she was sexually assaulted. "Any policy against sexual harassment must ensure that I can keep my job even when I'm unable to win my case against the culprit."
For Fidelia, having more women in newsrooms would also reduce the scale of sexual harassment at media organisations. "When there are many women in the newsroom, men would feel uncomfortable harassing women verbally or physically," she says.
Many newsrooms, according to Fidelia, who worked at two previous news organisations before landing her current job, are dominated by male reporters and supervisors who are very comfortable targeting the very few women they work with. She believes there's a gender bias when it comes to hiring staff at newsrooms and until that is tackled, addressing sexual harassment may be difficult.
"First of all, men have to change the perception that the newsroom is a place best suited for male journalists and that women don't make very excellent reporters," said Fidelia, who also points to the high rate of men holding executive positions in news organisations in Nigeria. "If they don't think female journalists are good enough for the job and don't hire more women, then we'll continue to see newsrooms with very few women who'll keep being targeted by some irresponsible male colleagues."
Like Pamela and Angela, Fidelia wants to see new policies put in place to protect women in media organisations across board.
"Perhaps these changes should start with the government coming up with a policy that ensures that news organisations don't create bias when hiring staff and contractors," says Fidelia. "The more women in the newsroom, the less likely a woman becomes a victim of sexual assault."
*Names have been changed to protect identities