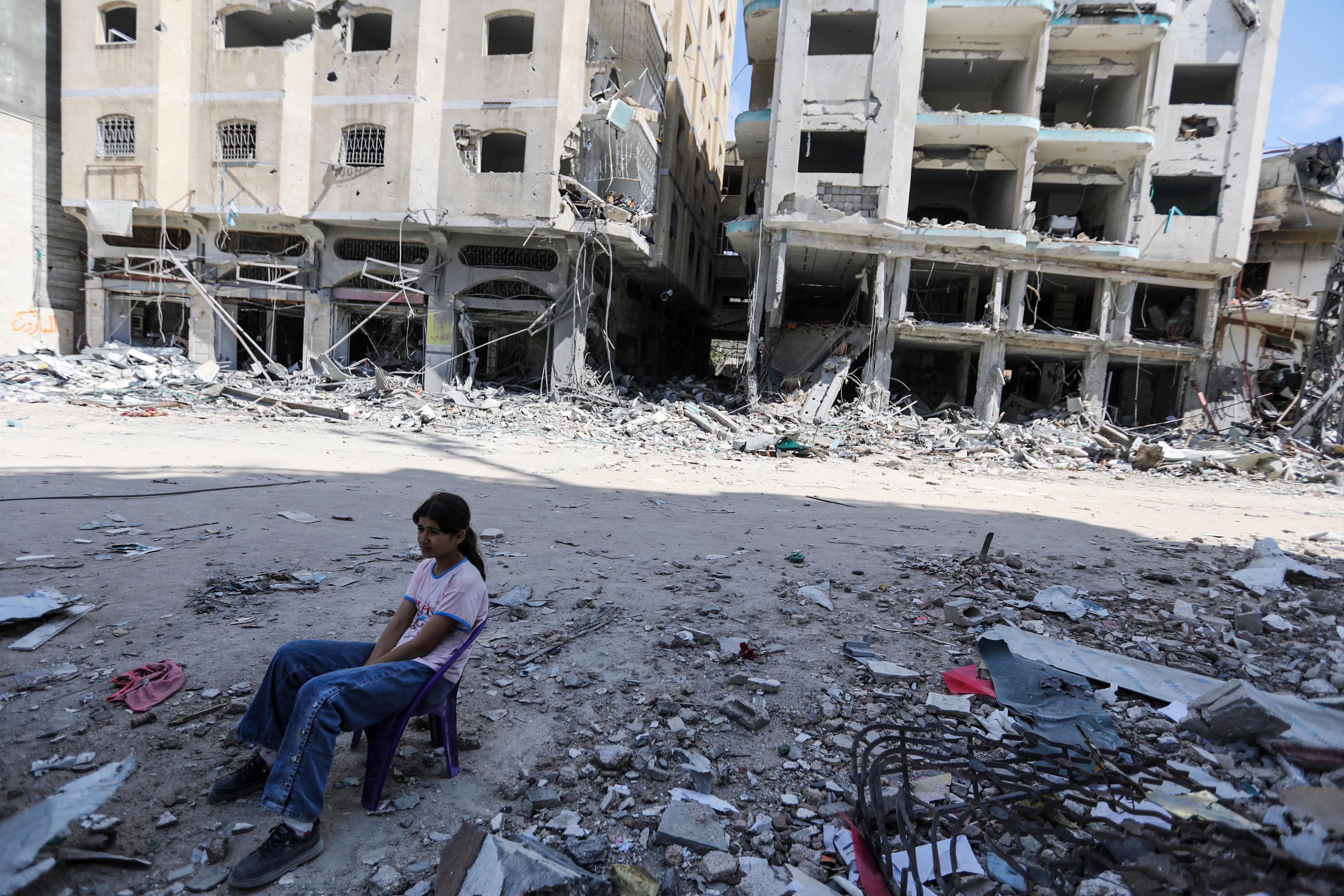
OSINT is increasingly important for journalists in a digital world. We take a look at ethics, safety on the internet and how to spot a ‘deepfake’
Open Source Investigation carries important ethical concerns, as well as legal compliance. Information might be publicly available but personal data may be subject to data privacy regulations to varying degrees.
Always do the following when using open source investigative techniques:
- Consider carefully the origin and the intent of your sources.
- Make sure that all your searches are targeted and that you are collecting only the information that is relevant to your investigation.
- Data is sensitive: Make sure that you are collecting only public data and data that is freely available online. Make sure the data you collect is safely and securely stored so as to not breach data privacy rules.
- Use a VPN: Do not forget to protect your identity. Using a Virtual Private Network or VPN can help mask your location and make your internet browsing more secure. Investigators can come into contact with a large amount of graphic footage.
Read more:
Open-Source Investigations, Part 1: Using open-source intelligence in journalism
Open-Source Investigations, Part 2: What is open-source investigation?
Open-Source Investigations, Part 3: Planning and carrying out an open-source investigation
Open-Source Investigations, Part 4: Tracking ships, planes and weapons
Open-Source Investigations, Part 5: Analysing satellite imagery
Al Jazeera Media Institute Open-Source Investigation Handbook
Al Jazeera eLearning Course: Open-Source Investigations
How to reduce the risk of secondary trauma?
Secondary trauma refers to a range of trauma-related stress reactions and symptoms that may result from exposure to graphic details of another individual’s traumatic experience. As content from open source investigations is often very graphic, knowing yourself, and knowing what images affect you the most, is important to consider.
Another factor in preventing secondary trauma is understanding your personal connection to the work you are investigating. In 2020, a study conducted at Berkeley, School of Law, USA identified six general practices as helping to mitigate secondary trauma: Processing graphic content; limiting exposure to graphic content; drawing boundaries between personal life and investigations; bringing positivity into investigations; learning from more experienced investigators; and employing a combination of techniques.

Dealing with deepfakes
Prepare, Don’t panic: Deepfakes and synthetic media
By Jacobo Castellanos, Witness
Malicious deepfakes and synthetic media are - as yet - not widespread outside of non-consensual sexual imagery. However, with the rapid development of new technologies, it is expected that in the coming years these will be evermore photorealistic and pervasive, further blurring the lines between what is real and what is not.
For digital investigators and fact-checkers, the challenge of identifying synthetic media is growing. Already we are at a point where depending on our own eyes for detection is unreliable. There are some tips that can help spot them - for example, looking for visible glitches - but these are just current slips in the forgery process that will disappear over time (you can try to detect deepfakes yourself with this MIT Media Lab test).
The use of detection tools also provides no guarantees. If the technique used to generate the synthetic media is unknown, the results will tend to be unreliable as they would with low-resolution or compressed media generally found online. A recent experience of a suspected deepfake in Myanmar shows that relying on publicly available detectors without further knowledge about how to interpret the results may lead to inaccurate assessments. What’s more, recent attempts at developing deepfakes detection tools have not come up with models that were effective enough on known techniques or sufficiently applicable to new techniques.
Even if robust tools are developed, they may not be made available widely, particularly outside specific mainstream platforms and media companies. It is likely that media and civil society organisations in the Global South will be left out, and it is important to advocate for mechanisms that enable them to have greater access to detection facilities. WITNESS is arguing for increased equity in access to detection tools, investment in the skills and capacity of global civil society and local newsrooms, and for the development of “escalation mechanisms” that can provide timely analysis on critical suspected deepfakes.
As a way to tackle misinformation from AI-generated or manipulated media, there is a growing movement pointing towards the need for disclosure when synthetic media has been created or shared (see for example the EU Code of Practice on Disinformation or Partnership on AI’s upcoming Synthetic Media Code of Conduct). “Disclosure” can take the form of labelling, or of other less visible techniques such as inserting forensic traces that are machine-readable, or metadata that contains information about its provenance.
Any one of these techniques could facilitate the process of identifying synthetic media, but without proper consideration they could lead to further harm - for instance, labelling could lead to suppressing certain forms of free expression, particularly in art, parody or satire (see WITNESS’s Just Joking! report for an analysis of these grey areas). Even well-intentioned efforts to provide tamper-evident provenance metadata for authentication, such as the work led by the Content Authenticity Initiative or the Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity (C2PA), could create risks of surveillance and exclusion for people who do not want to add extra data to their photos and videos, or cannot attribute the photos to themselves for fear of what governments and companies may do with this information (see the WITNESS led Harms, Misuse and Abuse Assessment of the C2PA).
Whether it be through detection tools, media literacy or disclosure mechanisms such as labelling, forensic traces or provenance-rich metadata, WITNESS is generally concerned that this work on ‘solutions’ does not adequately include the voices and needs of people harmed by existing problems of media manipulation, state violence, gender-based violence and misinformation/disinformation in the Global South and in marginalised communities in the Global North.
As these technologies evolve, the challenge for digital investigators and fact-checkers, as for journalists, human rights defenders and technology companies and synthetic media creators, will be to develop a better understanding of how to detect synthetic media and deepfakes in a way that is effective and accessible to those that need it most, while mindful of the unintended consequences, as well as potential misuses of these frameworks and tools.

Archive your data
Archiving for Accountability
By Carolyn Thompson, The Sudanese Archive
Since December 2018, the Sudanese Archive - a joint partnership run through Gisa and Mnemonic - has been gathering digital documentation, archiving it, and verifying it, with the goal of using it to contribute to investigations, court cases and other accountability mechanisms. The project includes several components. First, a monitoring team collects material by scouring the Internet daily for evidence of human rights violations. This can include photos and videos filmed by documenters on the ground in Sudan and posted on Twitter, Facebook, Tiktok, and other open platforms. Also, materials are gathered from partners and contacts directly and shared with the Sudanese Archive team. These photos and videos can include many pieces of the story; they document a human rights violation in action, or the scene before or after, and sometimes they include testimony from a victim of a crime. They can also include public statements or medical records, or other pieces of information that can help us understand what really happened.
At first, we gathered links in a spreadsheet to track the protest violence, but we quickly realised many of those links would break when content was removed by the person who posted it for their safety, or by the platforms because of its graphic nature. All those important photos and videos proving what happened were getting lost. We tried downloading on our own computers, but there needed to be a centralised space to hold the content and keep it safe. That’s why we began partnering with Mnemonic, which runs the Syrian and Yemeni Archives. Through Mnemonic’s archiving process, all those pieces of digital documentation are permanently saved, and in a way that includes chain of custody components, such as timestamping and hashing, to ensure the documentation can one day be used in a court process.
Once the material is archived, our investigative team sorts the content and identifies crucial pieces to be verified. The verification process involves determining the source of the video, the location where it was filmed, the time of day and date on which the incident happened, and any other relevant context. Once many videos have been verified from the same event, our team can begin piecing together the truth of what occurred on that day. We use a standardised data tagging process to ensure every researcher is using the same tools and drawing the same conclusions, and we share those methods with our readers - an important piece of accountability is transparency in this process.
Our most recent investigation is a large dataset called the Coup Files, which aims to verify documentation of violent incidents at any protests that have occurred in opposition to the 2021 coup. In this dataset, our teams tag each investigated piece of documentation with identifiers that help us conclude who was the perpetrator of the violence. This includes tags focused on identifiable weapons, uniforms, vehicles and other indicators of those perpetrator groups. As well, we identify any protest characteristics that could help us prove there were indicators of excessive force or unlawful use of crowd control techniques.

That can be examples such as videos of tear gas canisters thrown directly into a dense crowd of people, or photos of live bullets at a protest involving the presence of students and children. We publish incident reports focused on the protest days, grouping together violent incidents or the presence of security forces that we can confirm using this open source documentation. We also publish the data, set on a map, to help human rights advocates find the information they need - including by sorting for verified documentation of specific types of incidents or possible perpetrators.
Already, our work has contributed to court cases within Sudan, and to international lawyers and sanctions teams. As well, numerous journalists have cited our investigations or worked with us to publish their own. While legal accountability processes are a significant part of our focus, we also prioritise the importance of ensuring we remain visible and consistent so that the perpetrators of these crimes know they are being watched, and those standing up for their rights know they are seen.