Working as a journalist is not easy for people with disabilities in Cameroon - many of whom are forced to work as volunteers for years to ‘prove’ themselves able to do the job
It takes a lot to practise journalism in Cameroon. Precarious work environments, hardline media laws, criminalising journalists for doing their jobs, arrests and kidnappings are rife and place a chokehold on the work of journalists. All journalists are affected by these issues, but none more so than those living with disabilities.
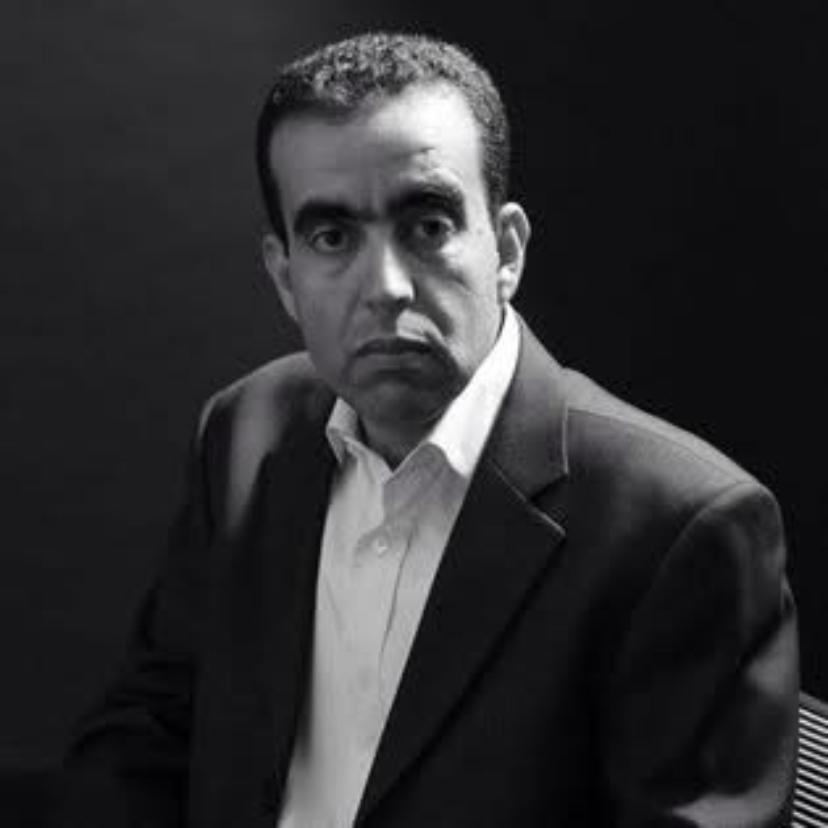
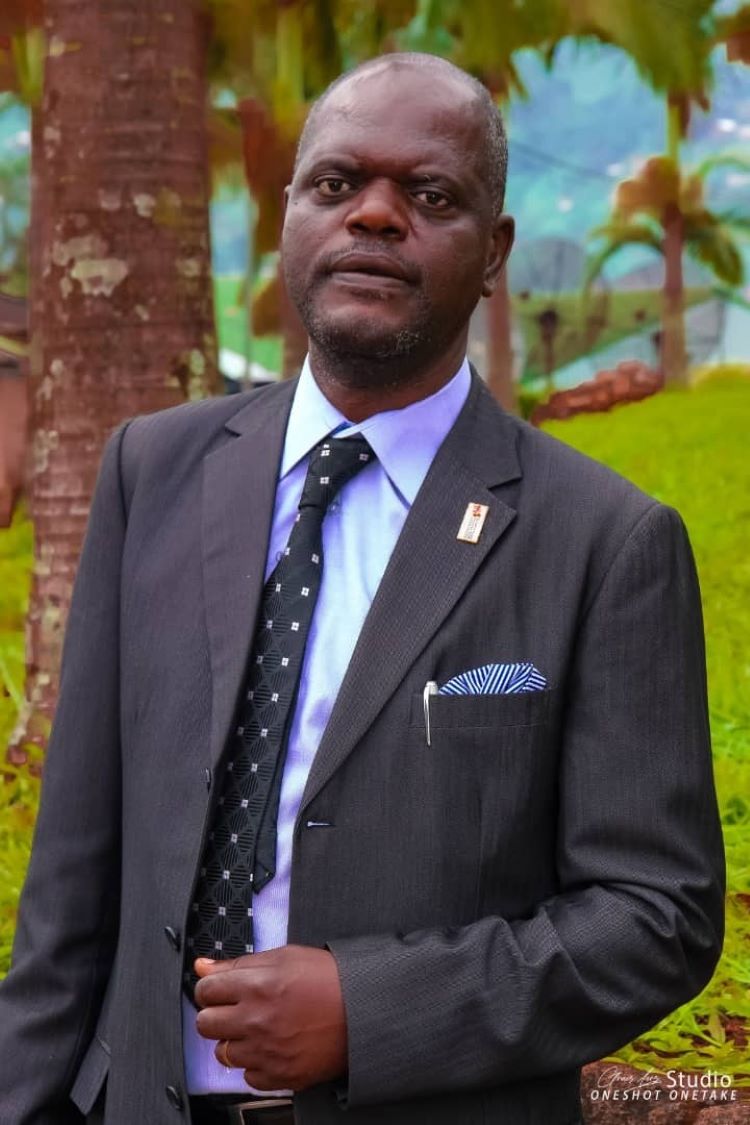
Bonkung Handerson, a journalist with a speech impairment, says finding a job as a journalist was very difficult. “Everyone liked my writing but employing me full-time wasn’t easy [owing to my disability],” he says. “They didn’t say it outright but I could tell they were wondering if I could sustain a job position. To prove the point, I decided to volunteer my services to the media house - Cameroon Baptist Convention Communications Ministry for about three years.
“Given my expertise, I rose from writer to desk editor and then managing editor - still as a volunteer on a monthly stipend that hardly allowed me to make ends meet. Then I found my current employer - the Cameroon Baptist Convention (CBC) Health Services - which hired me in 2000 to start up their Communications Unit.” The department has since grown to include eight communications staff, where Handerson is Editor-in-Chief.
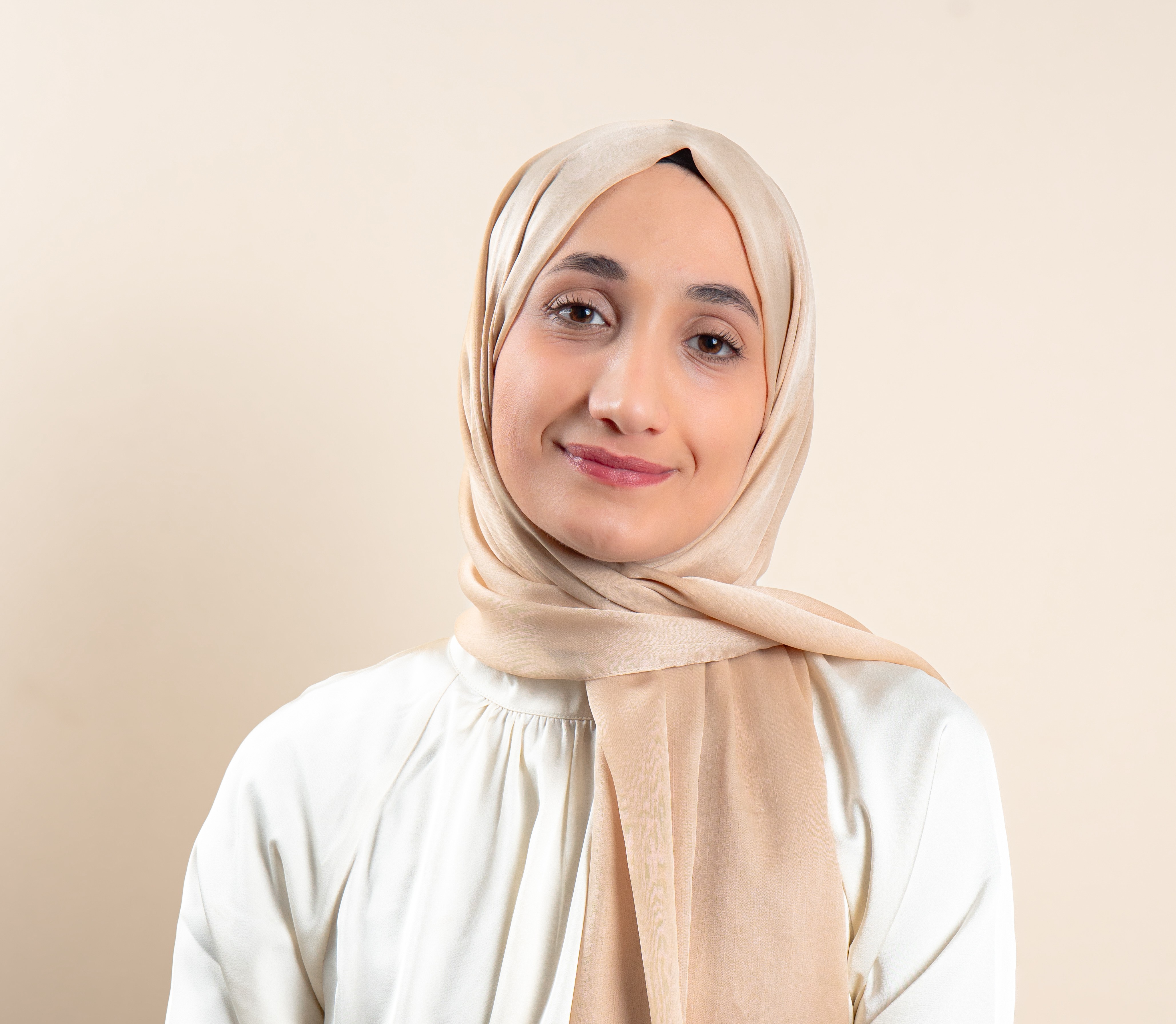
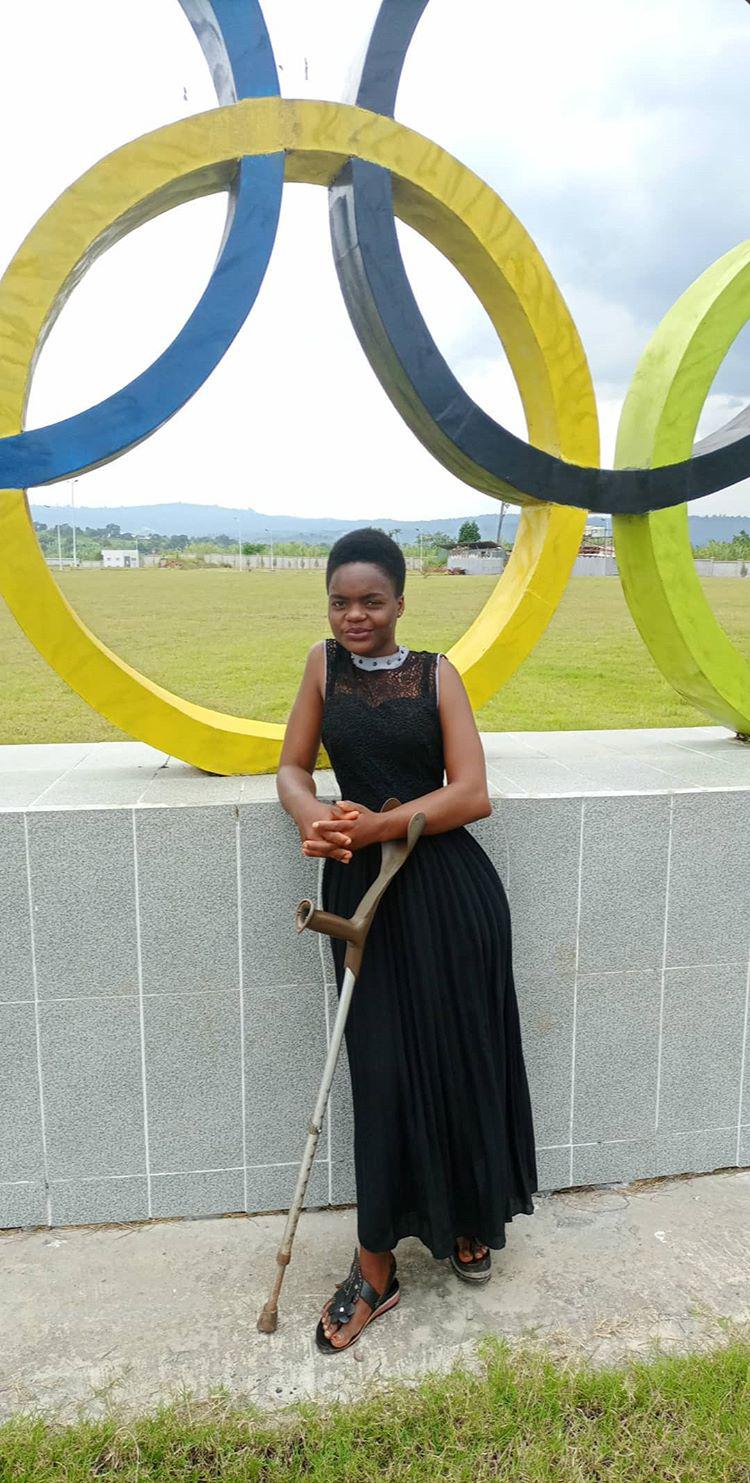
Chansiline Nanze, a sports journalist with a mobility impairment, had a similar experience of getting a job. "Journalism to me was a dream profession but after my training in 2017, picking up a job wasn’t easy,” she says. “It’s difficult to have a job in Cameroon these days."
Unwilling to let her dream career slip away, Nanze decided to work as a volunteer in order to prove she could deliver as well as to hone her skills.
“I had to start as a volunteer with the state media organisation CRTV (Cameroon Radio Television) for two years before I was recruited. Then I had to go through the normal recruitment procedure everyone goes through. I wasn’t given any exceptions or favours.

“I served as a volunteer just because I needed to gain experience so that if in the end I was not recruited, I might be able to find a job elsewhere,” she adds.
According to the United Nations’ disability “twin-track” inclusion strategy, disability is a cross-cutting issue and should be considered in all walks of life. Sadly, the needs of journalists with disabilities in the media industry in Cameroon are rarely, if ever, considered. Even if they do manage to find jobs, journalists with disabilities quickly start facing challenges at work.
‘Our buildings were constructed in the 80s’
“My major challenge is accessibility,” says Nanze. “The work environment is not disability friendly at all. Our buildings were constructed in the 80s when disability awareness and the need for a universal design in construction were not commonplace in Cameroon. To get to our newsroom, you have to climb the stairway to the second floor. Imagine climbing two floors to the newsroom and that is what I have to do every day. That’s quite challenging,” she says.
“Another challenge is adapting to the speed at which news breaks. When there is a major story happening somewhere far from the workplace, since my mobility is reduced, I may only get to the scene late.
“Covering sports is another difficult aspect of my work. Sports is extremely fast-moving; imagine at the end of a football game you have to rush for a post-match press conference, or to the mix zones, with my reduced mobility it becomes challenging. It’s worse when the stadium is not disability friendly.
“I went to the last game Cameroon played against Botswana at the Prince Moulay El Hassan Stadium in Morocco during the 2022 Women’s Africa Cup of Nations. That sports facility was not disability friendly. To get to the media tribune, mix zones and press conference room was a whole long trajectory, so I had to go round and round. Nonetheless, I’ve found a way now. I always rush down a few minutes before the blast of the final whistle to get to either the mixed zone or the press conference room in time.”
Handerson says he faces challenges daily which are both internal and external. "As a journalist with a speech impairment, I find it difficult but not impossible to respond spontaneously to emergencies. I need to write to express myself in every instance."
During his interview with Al Jazeera Journalism Review, Handerson used his personal computer to respond to our questions - a process which took more than half an hour.
He adds that people frequently express that they cannot understand how someone that doesn’t speak can be a journalist. Getting a taxi or travelling by public transport to make a deadline is another everyday challenge for Handerson.
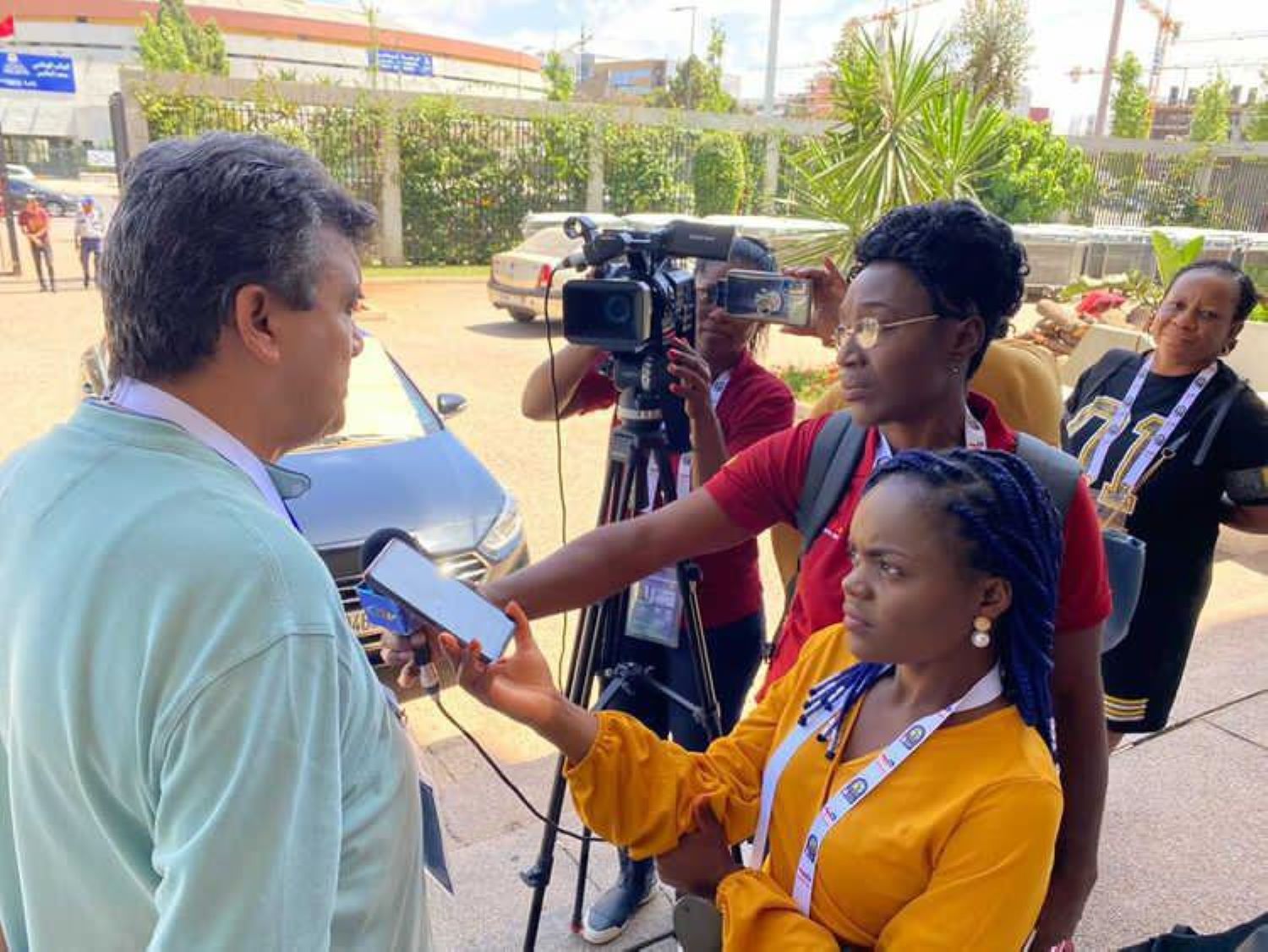

He also found arranging interviews for news stories very difficult during the early days of his career.
“Initially, I had difficulty gaining acceptance from my news sources. However, this perception changed over time when they realised how credible my writings were. From that moment, I can’t remember when I’ve been turned down from doing my job because of my disability. Rather, I receive invitations sometimes to cover events from previous interviewees”.
Unlike Handerson, Nanze says interviewees accept her requests but are usually surprised when they meet her face to face. "They are surprised when they match my voice to the one they hear on the radio. At times they're shocked that I'm a person with a disability."
Inflexibility over training
The challenges journalists with disabilities face on the job can to an extent be managed individually but when it comes to training, they are deep-rooted, says Handerson.
"My training was another ball game. I acquired my disability at a time when issues of disability were still a taboo subject in my country with little or no consideration given to persons with disabilities. Government officials outright rejected my application to sit for public examinations because of my disability. I was refused extra time to sit my GCE (General Certificate Exam) Advanced Level because my disability also affected my hands and drastically slowed down my writing speed. This greatly affected my grades.
“With all these, a person with a disability at that time just had to struggle on his own. Thank God, I finally secured a scholarship to receive my training abroad in editorial management,” he says.
Making societies inclusive for all is imperative
According to the Media Diversity Institute, journalism is about people and if journalists with disabilities are ignored in the newsroom, that will translate into many important stories going unheard.
As for Nanze, the way to ensure journalists with disabilities in the newsroom are not ignored is by making their working environment much more accessible. Another inclusion strategy could be the direct recruitment of journalists with disabilities by the government upon graduation or to reduce the length of time they must serve as a volunteer, she adds.
"Often, it is the journalist that has to buy his or her work tools. I, for one, with mobility impairment, can function like any other person. But colleagues with visual or auditory impairments - who need adapted and assistive devices to ease their work - come to my mind. It becomes difficult because that equipment is very expensive.
“So, I think if these equipment or devices are provided by media houses, it will enhance the performance of journalists with disabilities. What is essential is to make the newsroom inclusive,” she says.

Handerson believes it will take understanding on the part of society for newsrooms where journalists with disabilities can thrive become more inclusive.
“My experience is that persons with disabilities make good journalists,” he says. “Society must understand this fact and give them a chance to do their jobs. Journalists with disabilities are giants who have overcome self-pity and are very hard working. I’m a typical example of someone who has overcome self-pity and is excelling as a journalist with a disability. At the Communications Unit where I work as Editor-In-Chief, my colleagues rather depend on me to pitch the spirit that reigns in the newsroom,” he says.
Jolenta Rose, a broadcast journalist and amputee, says journalists with disabilities should have equal access to reporting and employers should learn to inquire about their capabilities - rather than their disabilities - before assigning them. “Sometimes bosses sideline me because they feel I can’t do certain jobs which is not supposed to be the case. It’s high time colleagues and employers respect us as humans and stop the open discrimination towards us.”
From Nanze’s, Rose’s and Handerson’s stories, it is clear that journalists with disabilities can thrive if attitudinal and structural barriers are broken.
For this to happen, it takes enlightenment and the media should be at the forefront - not only in raising awareness but in integrating journalists with disabilities. As the Media Diversity Institute puts it: “When you open the door for journalists with disabilities, you open the door to a more inclusive and accurate reporting that reflects diversity”.