Africa lacks freedom of expression because its stories are told by others
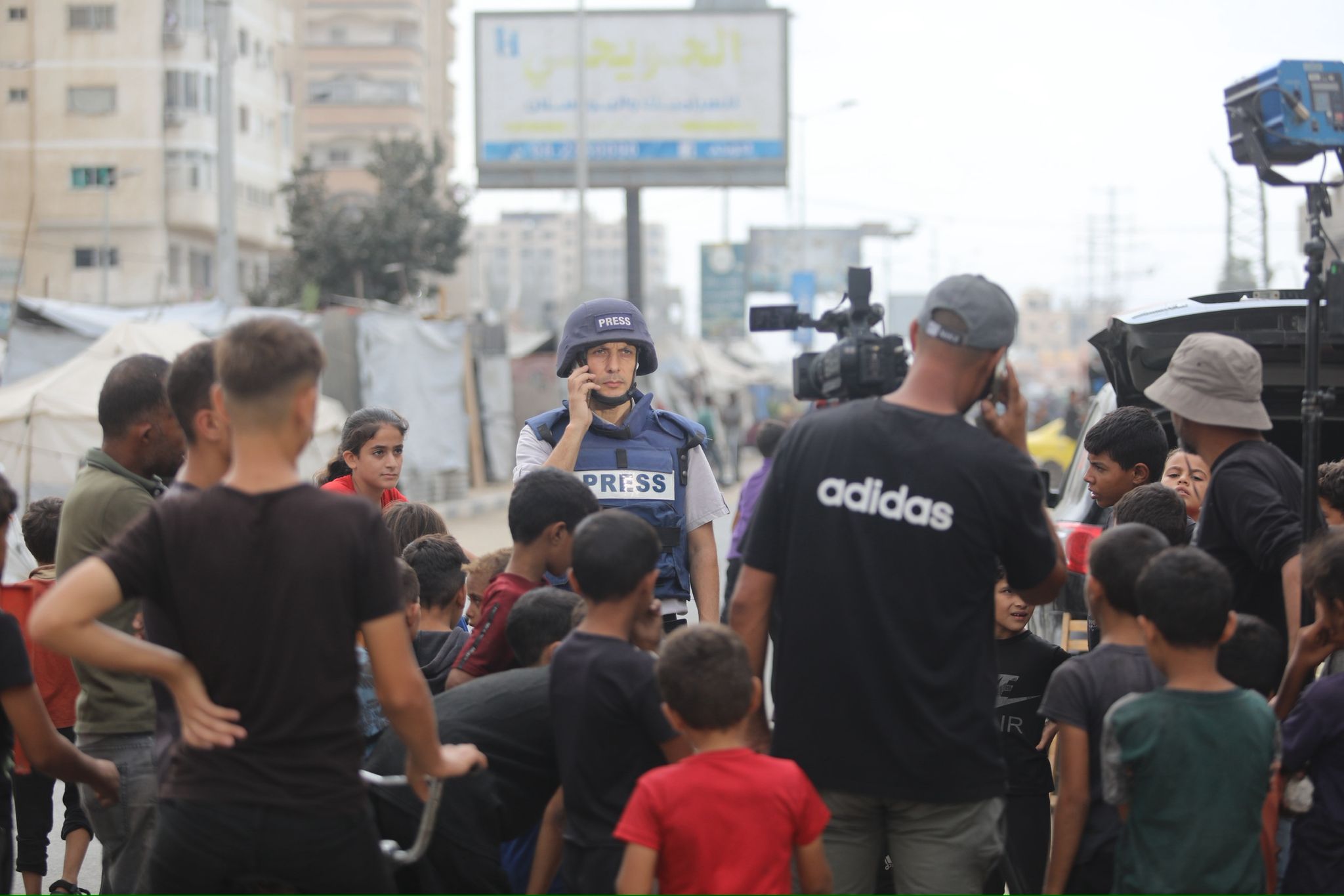
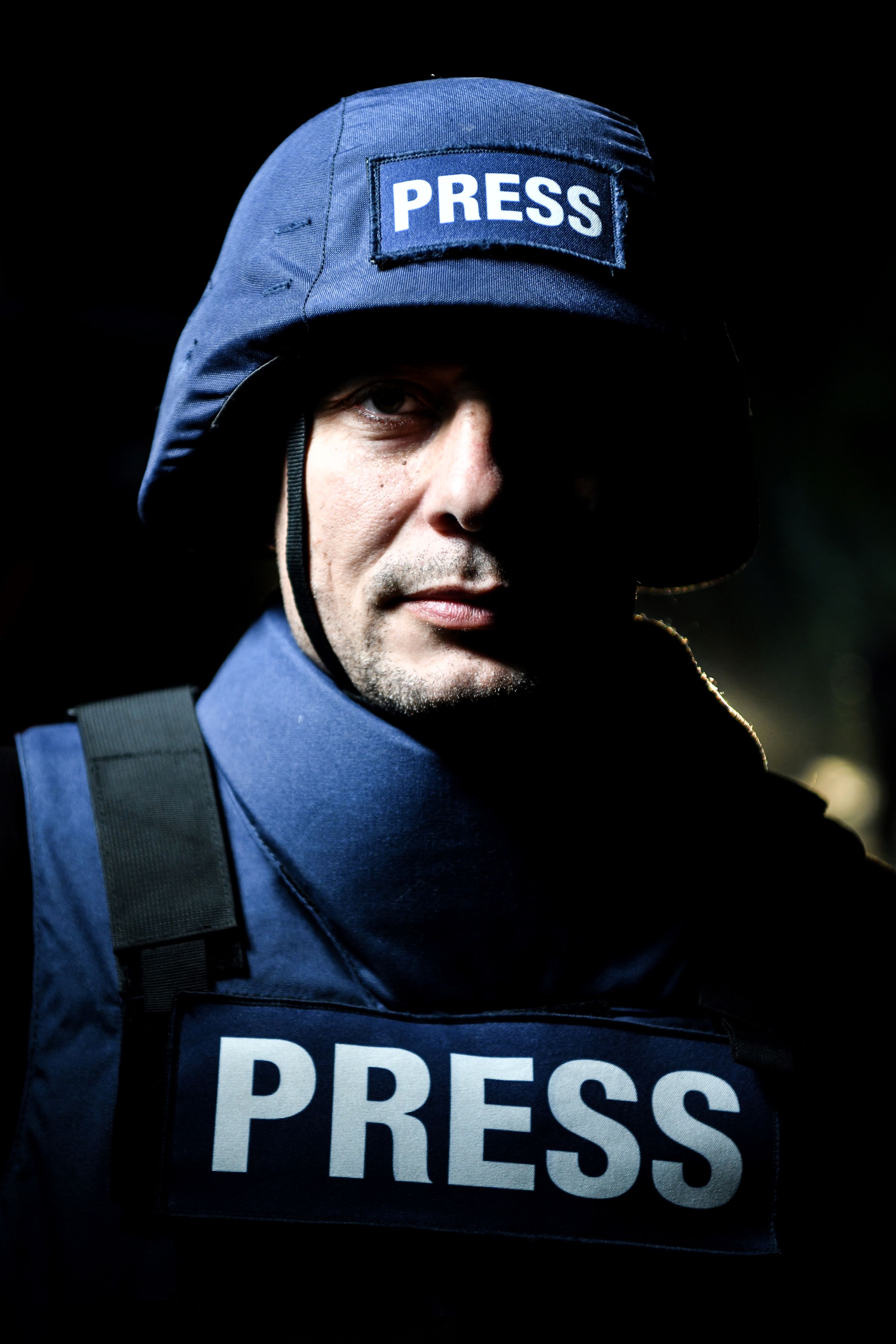
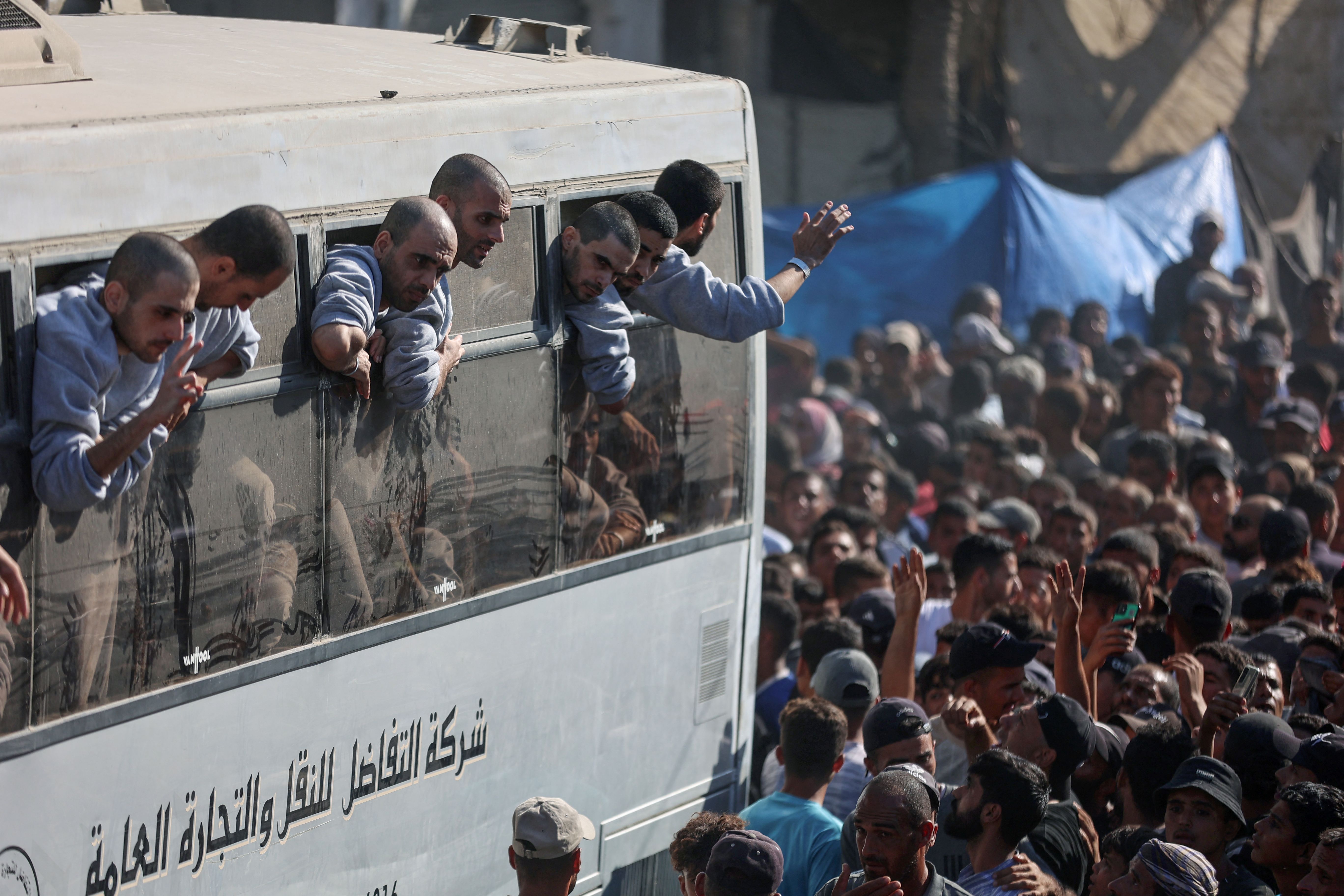
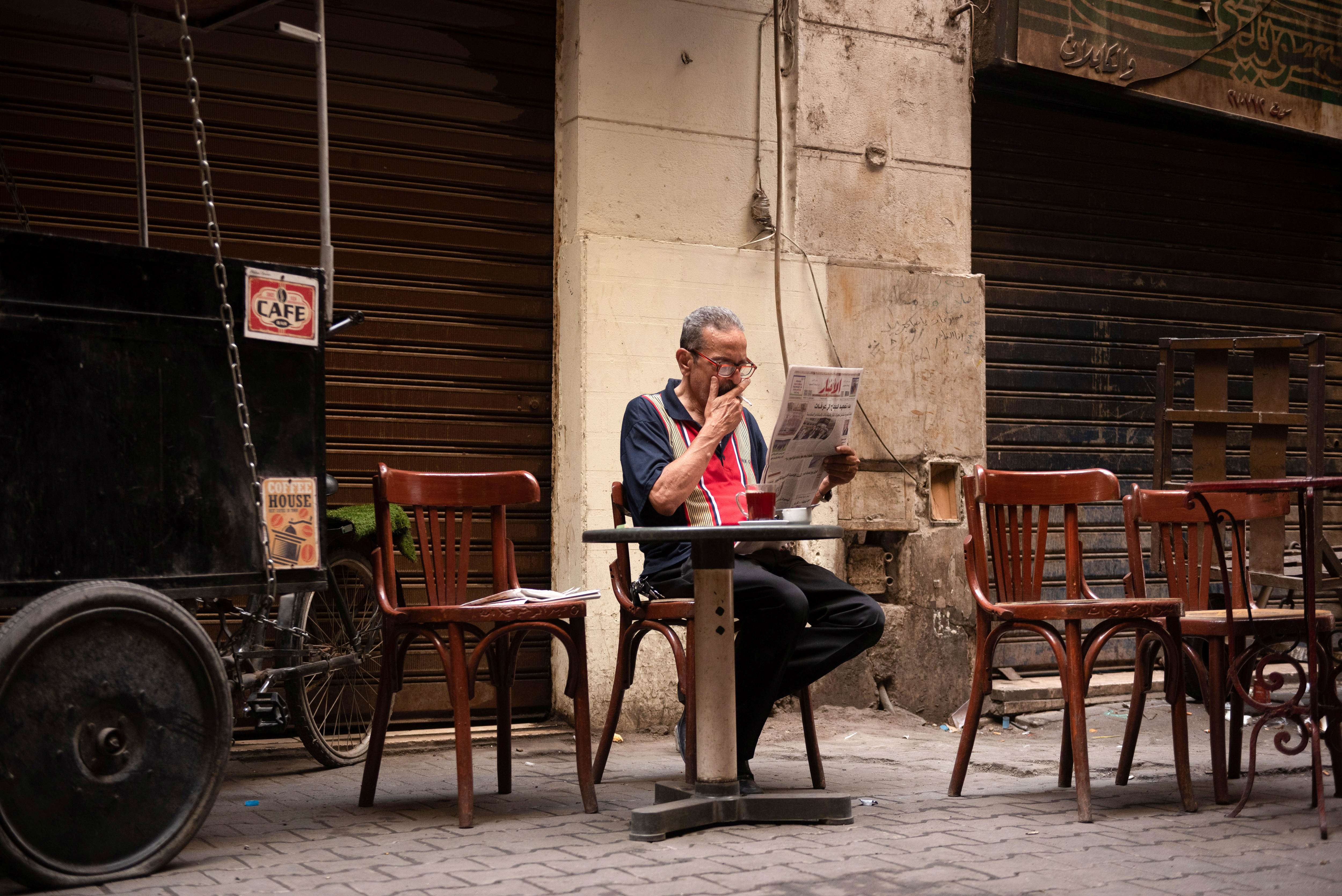
Days after the fighting between the Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF) and paramilitaries from the Rapid Support Forces (RSF) began in Khartoum, Port Sudan, a city on the Red Sea in the east of Sudan, began to swell with Sudanese and foreigners hoping to escape the conflict-struck country. As is often the case when a catastrophic event which affects citizens from various countries occurs, foreign correspondents from some of the biggest and best-known international media outlets began to arrive in Port Sudan to report not only on the evacuations but also on the conflict in the country.
But the thousands of dollars spent on their trips to Sudan may well have resulted in stories or reports that may have been distorted or incorrect, or even analysis and argument that may appear racist.
Frequently, foreign correspondents who cover conflicts in Africa miss the real story mostly for two reasons: first and foremost because a number of them only spend a few hours in the places they report; the other reason is that some have preconceived ideas about the places and people they report about.
About a decade ago, during my self-sponsored trip to the Nigerian northeastern city of Maiduguri which happens to be the birthplace of Boko Haram, I lodged in the same hotel as two foreign correspondents from well-known international media outlets based in the United States and took the opportunity to have a few conversations with them. A great deal of money had been spent to fly them from their organisations' bureaus elsewhere in the continent to Maiduguri, a city they were visiting for the first time and where they planned to stay no more than 24 hours.
I wondered how they were going to report the story after conducting interviews with internally displaced persons in a particular settlement for only a few hours when I had spent a week in the same area and had barely gotten to the root of the problems they were facing.
From my experience, having spent years reporting on the Boko Haram uprising in Nigeria and the humanitarian disaster caused by the conflict, I know for certain that the impact of the insurgency affects the people in the northeast region in ways that are cruel but not often similar. But many foreign correspondents, in their analysis, get this aspect wrong either because they haven't spent enough time in the region to be well-enough informed or they are simply biased - or a combination of the two.
What we often see when we read reports in international media about conflicts in Africa are misleading generalisations
What we often see when we read reports in international media about conflicts in Africa are misleading generalisations by foreign correspondents who either do not understand local complexities or are simply following the "standard" narrative about the continent. The average reader in the Americas, for example, could mistake the war in eastern Congo for the conflict in the Central African Republic simply because both countries are defined by the usual impoverished, starving and deadly stereotypes.
The current conflict in Sudan is just the latest example of how the world continues to read about Africa's challenges from correspondents who only made very brief visits. What is more galling is how some have made their reporting of the war more about the role of foreign mercenaries as opposed to focusing on the dire humanitarian issues that the conflict has created and the challenges that the Sudanese people are facing. It appears as if the war in Sudan has merely created an opportunity to report about the Wagner Group, which some reports claim is arming the RSF, rather than the conflict bitself.
In all of this, local Sudanese journalists who should be well placed to tell the stories about the conflict in their country rarely come into the picture. A few have written feature stories that have only barely touched on the issues on the ground because they have been briefed to limit their word count and are most likely issued with a narrative to follow. The little amount of money offered to them, compared to what foreign correspondents would get, even limits their ability to pursue in-depth reporting.
Because the media in Africa lacks the resources to ensure that the news is widely covered, many Africans themselves depend on the news from international media outlets to know what is going on around them. Even the local media, many of which copy and paste from the foreign outlets, rely on information from overseas to serve their own readers.
The continent's media houses - including the most successful ones - simply cannot match their foreign counterparts, especially newswires like AP and AFP, when it comes to recruiting reporters and sending them to various locations to cover the news.
The result is that the news reports and analysis that Africans consume are not often stories told by African journalists to their own audience.
What Africa needs to read are stories told by African reporters for African readers, but that is always going to be difficult to achieve because the funding to do so regularly is not readily available.
The consequence of poor funding is that the most skilled African journalists are forced to pitch tent with foreign outlets, which continue to request stories that fit into their narratives or which edit their reports to suit their template, continuing the trend of biased reporting even when Africans are the authors.
Africa's wealthiest people and institutions should also pay attention to its media by offering reporting grants to African journalists
The best solution to this is for African media outlets, which suffer from a shortage of skills and training, to close the funding gap.
In addition to helping African journalists to better report about issues around climate, development and inclusive economies, which are areas the international media often pays attention to when writing about Africa, donors should focus their funding on training journalists to tell the untold stories about conflicts so that when they occur, Africans can report them in ways that are correct and offer the best perspective.
Africa's wealthiest people and institutions should also pay attention to its media by offering reporting grants to African journalists to produce stories about the continent's most pressing issues. It shouldn't only look overseas for help in this regard. After all, it is in the economic and political interests of all Africans for the world to see and understand the continent as it really is, rather than as it may be imagined by Westerners.
Platforms like Google should make it easier for African publishers to earn money through digital advertising by providing them with tools that can enable them to sell more ad space to advertisers across the globe.
Finally, there is a need for more collaboration between news organisations at the industry and the reporters’ level. Media outlets in Africa should feel free to share their news content with one another rather than having journalists always sourcing reports from international news websites whose contents are usually created for foreign audiences.
At the moment, it seems Africa lacks freedom of expression because the continent can't easily find ways to tell its own stories. But it can change that by having its media organisations collaborate with each other and getting Africa's most generous individuals and organisations to support the media.
Philip Obaji Jr is an investigative journalist based in Nigeria
The views expressed in this article are the author’s own and do not necessarily reflect Al Jazeera Journalism Review’s editorial stance