What does the future hold for journalism in the ‘third drone age’? A lot of manipulated news, most likely
Future wars will be fought by robots, sent to distant lands to hunt and kill. Where there were once boots on the ground, there will be swarms of unmanned drones overhead. But where there were once boots, there were eyes and ears too. The eyes, ears and cameras of the war correspondent will be absent from a computerised conflict, fought from a distant operation centre, thousands of miles away.
The dawning of the “third drone age” and the prospect of autonomous warfare will have profound implications for civilians living in combat zones, and those innocents killed or injured by military miscalculation. It also has a corrosive effect on transparency and democracy itself, the covert consequences of conflict kept from the enquiring minds of liberal societies left comfortably and cosy in the dark.
When US President Biden withdrew troops from Afghanistan in 2021 and announced his preference for “over-the-horizon” capabilities, he knew it would play well with the American people. No more risk to US military personnel, no more long protracted, expensive ground engagements, no more tearful family farewells, and no more concern for “others” living half a world away.
The idea of a sky full of killer robots may sound like fantasy science fiction, but we know that Iranian-made so-called kamikaze drones are already being used in the Ukraine conflict. As Russian troops withdrew in numbers from Kherson, reports emerged of multiple drones circling the skies of Ukrainian cities before locking on to their targets and exploding on impact with devastating effect.
Such weapons are being developed and commissioned by armed forces around the world including the UK. In September 2022, the British Army held a demonstration of “multiple nano-Unmanned Aerial Systems (nUAS)” to test the capability of a swarm to be operated by one individual. Commanding officer Colonel Arthur Dawe said the technology would help by adding “precision strike capability… making us more lethal at range, which will protect our very valuable forces and people”.
The hierarchy of accountability is somewhat fuzzy when there is no hand wielding a weapon, and algorithms are at the controls
Advances in technology during the post-9/11 era saw an increased use of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), or drones, as the “go-to” weapons of choice in the Global War on Terror. There is little doubt that such machines offered the US administration clear advantages in accessing remote areas, surveilling potential targets for lengthy periods, and most importantly not requiring an American pilot in the cockpit.
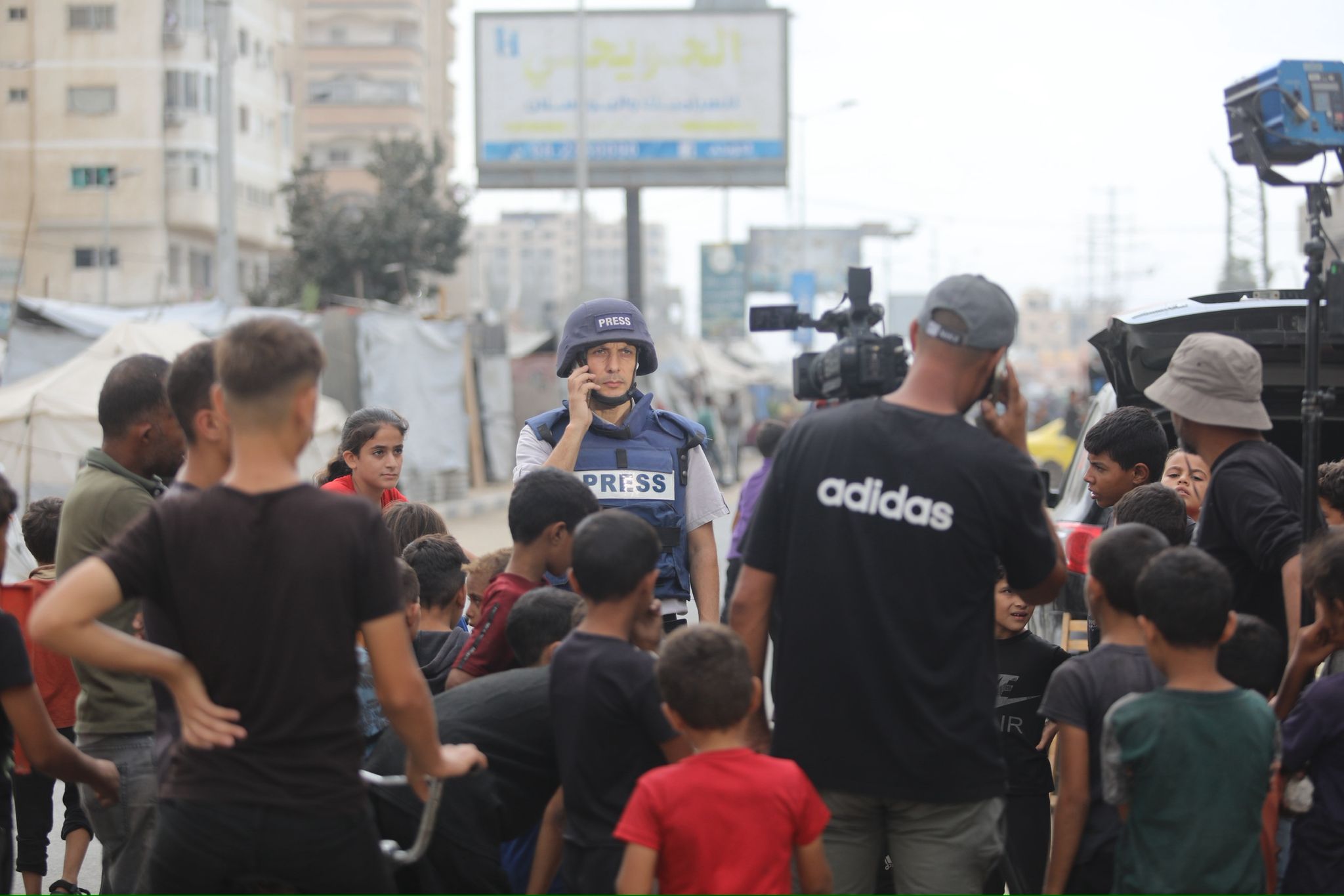
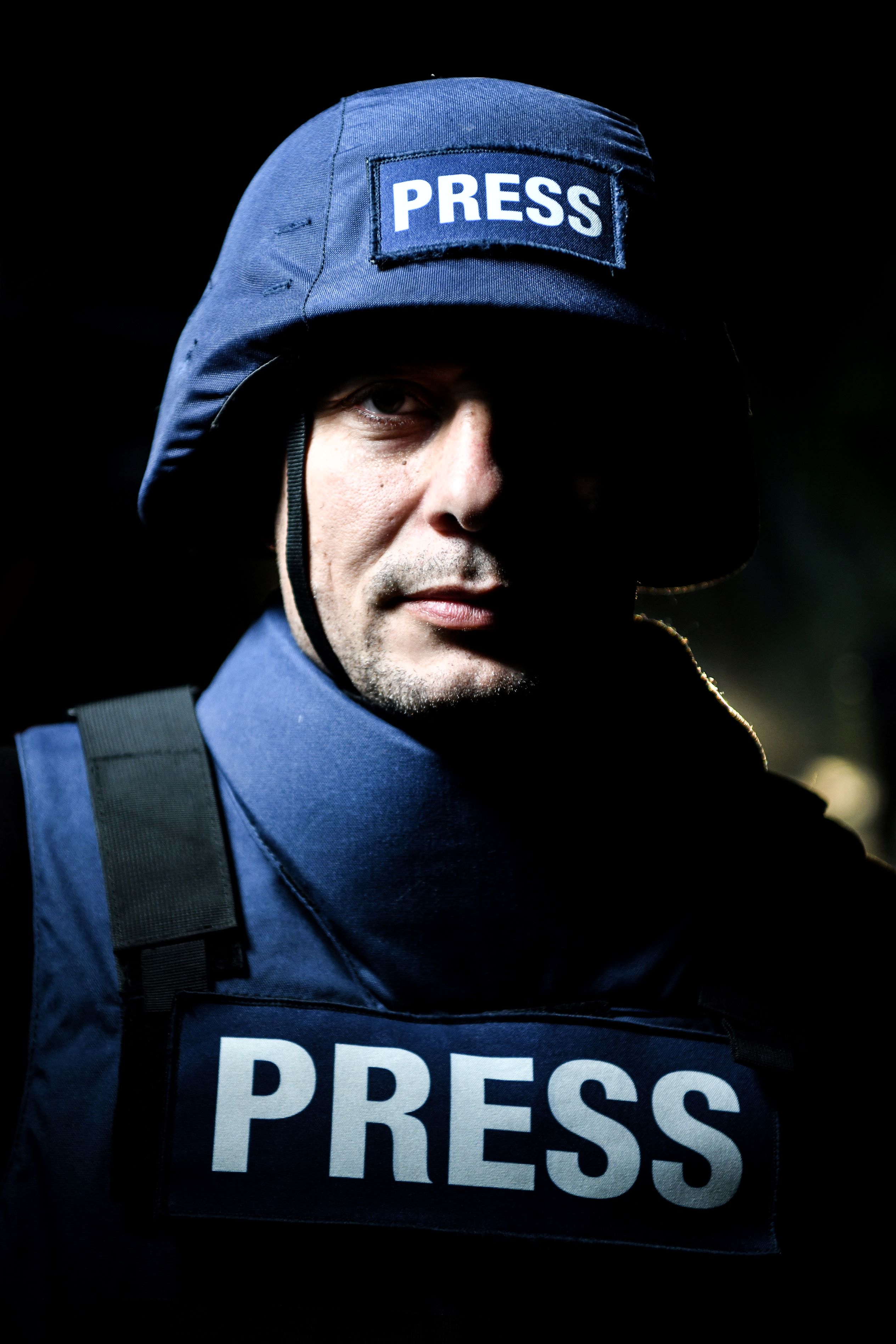
Fighting war from a distance has obvious benefits. But it comes at a cost. First, to those innocent civilians living within the arena of robotic warfare. For them, there is no choice, no distance, no technological alternative to the suffering that inevitably comes to the victims of war. But there is another cost, not so immediately clear; a cost to transparency and democracy itself. War correspondents embedded with troops, or working independently, play a critical role in bearing witness to the battle, up close and personal to the bloody realities of combat. But there will no longer be a place for them.
In victory or defeat, the role of the war correspondent stands to support democracy in providing the people back home with accounts of the injuries inflicted in their name. They witness the impact on bombarded communities, document civilian casualties and report violations of international law. They draw the world’s attention to the brutal realities of conflict and have been pivotal in changing the direction of wars of the past.
The best example is perhaps the Vietnam war, known as the “first televised war” which was broadcast on TV networks across the United States from the mid 1960s. The ability to reach into the homes of the people with images of that war was critical in moving hearts and minds and adding pressure on the US administration to end its involvement.
Newspaper images of the Mai Lai Massacre, press coverage of the Tet Offensive and news reports of the increasing number of US army body bags returning home added fuel to the protest movement. The media hit the US public full in the face “on colour screens” with the horrific consequences of war, and they were able to do so because they were there. They had access to the battlefield, they saw the devastation with their own eyes and they documented it with their cameras.
Thirty years later, under George HW Bush, the US entered the first Gulf War. Advances in military technology and political lessons learned from media coverage of Vietnam meant it would be a very different kind of war. The development of “stealth bombers, cruise missiles and laser-guided ‘smart” bombs’” meant that the US and its allies were able to conduct the war against the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait, without a significant ground invasion. It also meant that the war was witnessed in a very different way. Instead of graphic pictures of the dead and injured, lying mangled and lifeless in the bloody, dusty aftermath of an attack, the US military released cockpit imagery of laser guided missiles hitting their targets. But these were not images captured by impartial truth-seekers. These were carefully manipulated messages of military precision without the messy ramifications of civilian casualties splashed across newspapers and beamed into living rooms. This was the first war at a comfortable distance.
The invisibility of the covert drone programme has rendered Western societies deaf, dumb and blind against the tyranny their governments are inflicting on others
There were some reporters present on the ground, but they were hamstrung by a new “pool” system controlled by the US military with severely limited access. Stanley Cloud, the Washington Bureau Chief for Time Magazine said: “We’re getting only the information the Pentagon wants us to get. This is an intolerable effort by the government to manage and control the press.”
The sense of distance from the impact of the coalition’s bombardment of Iraq inspired French philosopher and sociologist, Jean Baudrillard to write his triptych of essays, “The Gulf War Did Not Take Place”. In it he described the unreality and detachment of that war. He referred to the cockpit imagery through which the pilot viewed his targeted victim as “electronic interference that creates a sort of barricade behind which he becomes invisible”.
Since the first Gulf War, technology has removed the pilot even further. As much as there is a detachment from the killing, there is also now detachment from accountability when the inevitable mistakes are made. We have seen countless US drone attacks gone wrong: “The wedding that became a funeral” in Yemen, the Datta Khel drone attack that killed 40 innocent civilians at a tribal meeting in Pakistan and the strike in Kabul in 2021 that killed 10 members of one family, including seven children, just as the US was withdrawing from Afghanistan. The hierarchy of accountability is somewhat fuzzy when there is no hand wielding a weapon, and algorithms are at the controls.
The many documented incidents of civilian casualties have cast a long shadow over the much-touted precision of drones. Secretary General of Amnesty International, and former UN Special Rapporteur on Extrajudicial and Arbitrary Execution, Agnes Callamard has called the “precision” labelling of drones a “myth”, saying they were “ten times more likely to cause civilian casualties than conventional air attacks”.
Documenting civilian casualties in remote areas where there is no military ground presence and no international media has proven less than straightforward. It has required huge determination on the part of organisations like the Bureau of Investigative Journalism, and local NGOs like Mwatana for Human Rights in Yemen. Speaking at a Drone Wars webinar in November 2022, lawyer and accountability specialist Bonyan Gamal expressed the difficulties in seeking accountability for the Yemeni victims of US drone strikes. She said that since 2002, no reparations have been paid and their efforts to obtain redress for the victims has been met by a wall of silence from the US government.
We must wake up, demand transparency and support a free and independent press to cover each and every conflict, even distant robotic ones
The invisibility of the covert drone programme has rendered Western societies deaf, dumb and blind against the tyranny their governments are inflicting on others. Do UK voters know that British-made autonomous Brimstone missiles have been sold to Saudi Arabia and have been used in the war in Yemen? Probably not. No headlines and no colour pictures mean no victims, no outrage, no protests, no pressure to change course. Mobilising western publics around the plight of ‘others’ requires the victims first to be seen and then to be humanised as lives worth grieving and defending.
Both Amnesty International and Human Rights Watch were borne out of the power of the media to expose human rights abuses. Amnesty International originated from a 1961 article in the Observer, written by lawyer Peter Benenson about two Portuguese students jailed for “raising a toast to freedom”. Human Rights Watch, meanwhile, developed out of a campaign to monitor government compliance to the 1975 Helsinki Accords in Eastern Europe and the Soviet Union. “Helsinki Watch” began in 1978 to expose violations of the agreements through media coverage, and eventually evolved into the global organisation we know today.
The proliferation of drones and autonomous weapons continues apace while debates about ethics and tighter UN regulation struggle to keep up, and any hope of agreement is trampled under the heavy boots of geopolitics. Western liberal societies are sleep-walking into a dystopian future, in which human rights violations go untold and the civilian victims of war are left unseen and voiceless. They must wake up, invoke the spirit of the Vietnam protest movement, demand transparency and support a free and independent press to cover each and every conflict, even distant robotic ones.
And as governments and militaries around the world forge ahead with remote forms of warfare, sending their killer robots over the horizon, those of us who care to hold them to account must find a way to be there waiting for them.
Pauline Canham is a freelance journalist who volunteers for the justice campaign group, 3DC
The views expressed in this article are the author’s own and do not necessarily reflect Al Jazeera Journalism Review’s editorial stance























![Palestinian journalists attempt to connect to the internet using their phones in Rafah on the southern Gaza Strip. [Said Khatib/AFP]](/sites/default/files/ajr/2025/34962UB-highres-1705225575%20Large.jpeg)