Social media and complex AI newsroom tools are combining to produce a toxic environment in which dangerous misinformation is flourishing
Two decades ago, science researchers and journalists would receive hard copies of professional journals and browse through them regularly to keep up with developments and the latest science news.
These days, anyone interested in science can find articles online using search engines and social media. The result has been a worrying rise in misinformation, which can so easily be disseminated via click-bait “news” stories on a multitude of platforms.
Last November, the annual science conference organised by the Falling Walls Science Foundation in Berlin, Germany, took place. The conference, which is organised each year on the anniversary of the fall of the Berlin Wall, is attended by researchers and scientists from around the world.
The three-day programme for 2022 included inspiring keynotes, discussions and a lot more on topics related to science, its communities and the opportunities connected to science and society. But this time the conference expanded its scope beyond just science and also addressed the issue of misinformation and journalism, with particular focus on how misinformation can impact science reporting in just the same way it does any regular news issue. Participants from 80 countries were present and acknowledged the fact that misformation can create huge challenges/barriers for science journalism.
The internet has changed the way we consume media. Some of us still read the morning paper at the breakfast table, but more receive the majority of their information from the internet. Many more people consume news online through social media or online news sites than in print form, especially younger readers. Meanwhile, mainstream news organisations which do remain popular for print and broadcast news are becoming more and more partisan as traditional, independent funding sources dry up.
In the current era, misinformation undermines collective sense making and collective action. Therefore, we cannot solve problems of public health, social inequity, or climate change without also addressing the growing problem of misinformation.
The new trend for AI tools in newsrooms also poses a danger. “I do indeed see a danger for scientific communication to society through new generative AI procedures, such as ChatGPT by OpenAI or the now discontinued Galactica model by Meta,” says Dr Bittkowski Meik from Science Media Center Germany, who was part of the discussion about the misinformation and disinformation and its impact on science at the summit in November.
“Specifically, the danger is that these models, or their near successors, will allow the creation of almost arbitrarily extensive make-believe worlds of scientific ‘bullsh*t’ (which looks like science but has no relation to scientific truths) with falling marginal costs.
“This allows for more complex and credible disinformation campaigns that can point to a completely fabricated landscape of ‘science’. This would make it almost impossible for lay people to distinguish real from fake science. It would also be much more taxing for journalists to expose disinformation,” Dr Meik adds.
A research paper, ‘Misinformation in and about science’, published in The Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), a peer reviewed journal of the National Academy of Sciences (NAS), highlights that during a crisis, science can often be forced into the media spotlight.

The paper explains how misinformation is dangerous for science and takes the recent example of COVID-19 to illustrate.
“There is no credible evidence that SARS-CoV-2 responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic has a bioengineered origin, but a series of pre-prints has pushed false narratives along these lines. One such paper, posted to bioRxiv, was quickly refuted by bioinformaticians and formally withdrawn - but in the interim, the paper received extensive media attention.
“If preprint servers try to vet the material, authors find other outlets. A two-page note - not even a research paper - claimed that SARS-CoV-2 is an escaped bioweapon and was posted to the academic social media platform ResearchGate. Though quickly deleted from the site, this document took off, particularly within conspiracy circles. A deeply flawed paper making similar arguments was posted online,” the authors write.
The news media has written a lot about fake news and other forms of misinformation, but scholars are still trying to understand it - for example, how it travels and why some people believe it and even seek it out.
Denise-Marie Ordway, managing editor of Journalist's Resource at the Harvard Kennedy School, wrote an article for Harvard Business Review explaining what researchers know to date about the amount of misinformation people consume, why they believe it and the best ways to fight it but the problem is not going to end anytime soon.
Caroline Lindekamp, associated with correctiv, a German nonprofit investigative journalism newsroom, is in charge of the interdisciplinary research project, noFake. She stated during the Falling Walls Summit that disinformation is the biggest threat to science.
“The most problematic issue that we are facing today is disinformation because it is deliberately manipulated information that is spread by various channels and is often linked to conspiracy theories and is usually intended or used to set a particular agenda.”
As another participant at the summit added: “Misinformation can be very difficult to correct and may have lasting effects even after it is discredited. One reason for this persistence is the manner in which people make causal inferences based on available information about a given event or outcome. As a result, false information may continue to influence beliefs and attitudes even after being debunked if it is not replaced by an alternate causal explanation.”
We must find a solution to the problem of misinformation in science news before it is too late.
Safina Nabi is a freelance journalist covering South Asia
The views expressed in this article are the author’s own and do not necessarily reflect Al Jazeera Journalism Review’s editorial stance
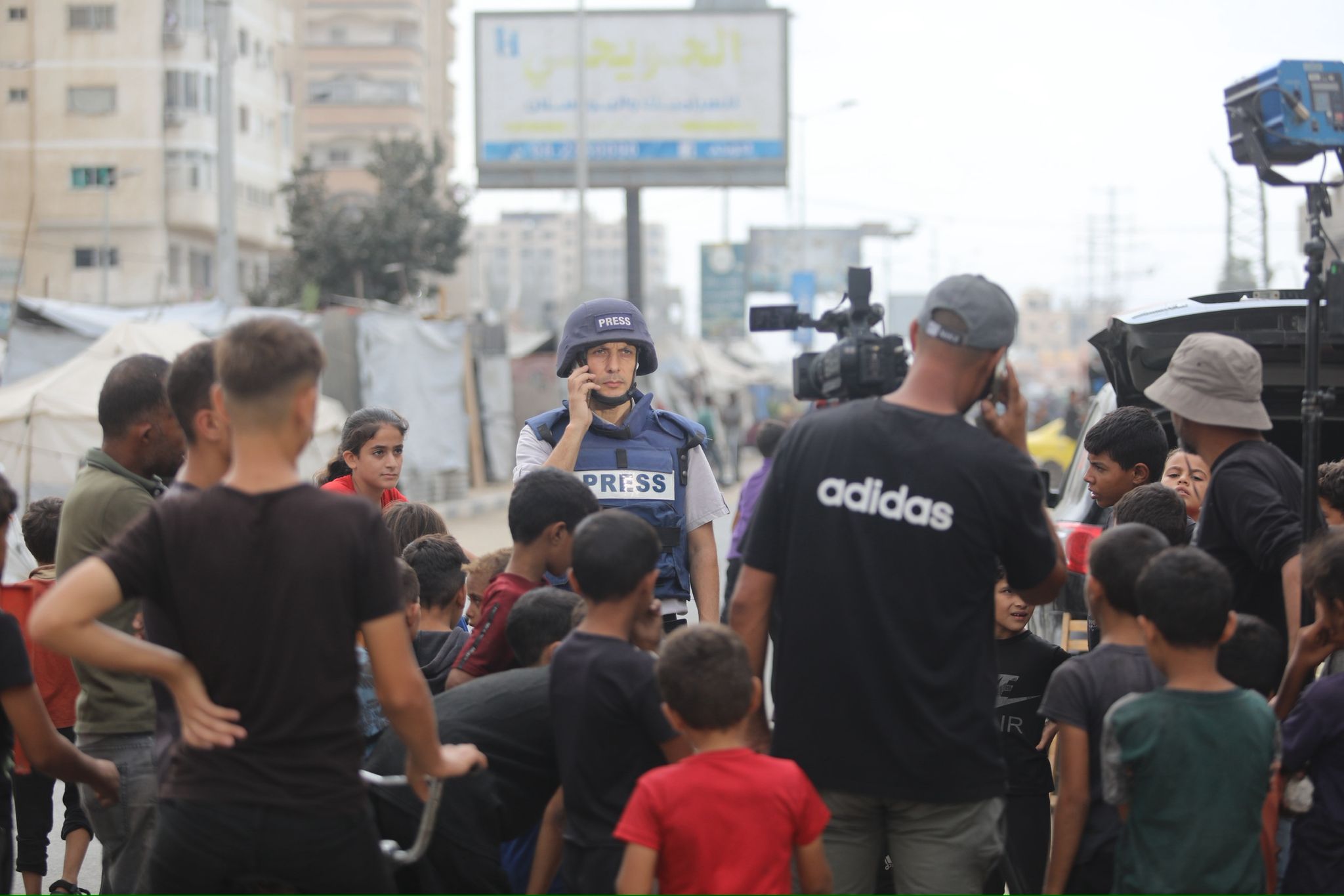
























![Palestinian journalists attempt to connect to the internet using their phones in Rafah on the southern Gaza Strip. [Said Khatib/AFP]](/sites/default/files/ajr/2025/34962UB-highres-1705225575%20Large.jpeg)