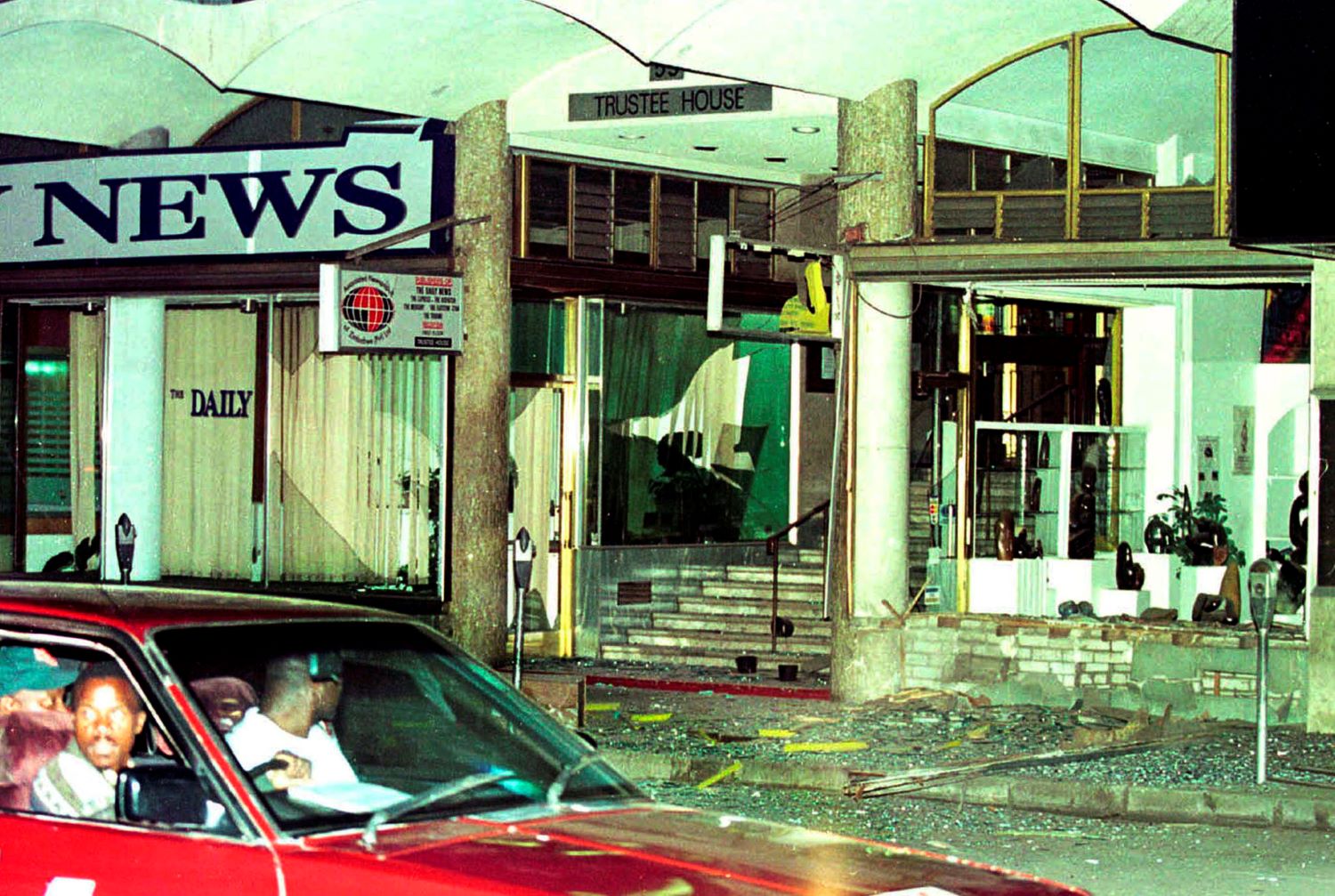
Twenty-two years after the bombing of a newspaper printing plant in January 2001, the perpetrators are still at large - and a state-sanctioned assault on a free press continues
Just one day after the Minister of Information, Jonathan Moyo, proclaimed it was only a matter of time before Zimbabweans put a stop to what he called the newspaper's “madness”, a printing press owned by the Daily News was bombed on January 28, 2001.
On the night of the January blast, several attackers forced their way into the premises. Inside, they held the security crew hostage before planting explosives, blowing up part of the building and its machinery.
Fortunately, no one was injured, but the incident confirmed a growing resentment towards privately-owned media. The perpetrators knew what they were doing. According to Davison Maruziva, the paper’s deputy editor, who spoke to the BBC after the explosion: “They were experts and they went straight to the unit that was operating and placed their explosives.''
The next day, the news made international headlines, as the police combed the crime scene for any possible clues, however, to this day, police remain baffled as to who carried out the bombing.
It was not the first time the newspaper - the only non-state-controlled paper at the time - had been targeted. Just a few months earlier, in 2000, a bomb had gone off in a shop next door to the Daily News downtown-Harare headquarters.
Indeed, a series of events leading to the blast 22 years ago could perhaps point towards the yet unknown saboteurs, or at least their intentions. Earlier on, before the January explosion, some 500 ruling ZANU-PF party supporters had marched on the publication’s offices, protesting its coverage of the death of DR Congo's President Laurent Kabila.
Resolution to ‘ban’ the paper
The picketing was a precursor for something far more brutal to come. Those familiar with local politics knew that the march was meant to intimidate the staff.

Chenjerai Hunzvi, the militant late leader of war veterans, a loyal collective used to garner support for the ruling party, also said they had resolved to “ban” the paper, mainly for its determination to speak truth to power, something that was alien within the state media. Except for the telling comments by Moyo and Hunzvi, no other leads, or suspects have been identified and the perpetrators still roam free, somewhere.
These related incidents, supported by a report by the Committee to Protect Journalists (CPJ), released soon after the attack, demonstrated that there was a resistance towards the newspaper’s growing influence, fanned by the ruling elite and its ungovernable followers. “These violent attacks appear to be part of a deeply disturbing campaign against the Daily News and its staff, which have suffered frequent and ongoing harassment at the hands of police and top-ranking officials of the ruling ZANU-PF,” said CPJ in a statement.
To politicians, the popularity of the private media, particularly the Daily News presented a new direct threat to their propaganda machinery. With a new media player gaining acceptance, the Herald - the major propaganda mouthpiece - was now becoming irrelevant, its readership being slowly eroded by the Daily News, which was appealing to a wider readership.
An alternative media would present new ideas and choices to the electorate, now desperate for change following years of dominance by a single party since 1980. With elections scheduled in 2002, the party risked losing its popularity, so it was necessary to “ban” this new threat by any means.
'Twin evils'
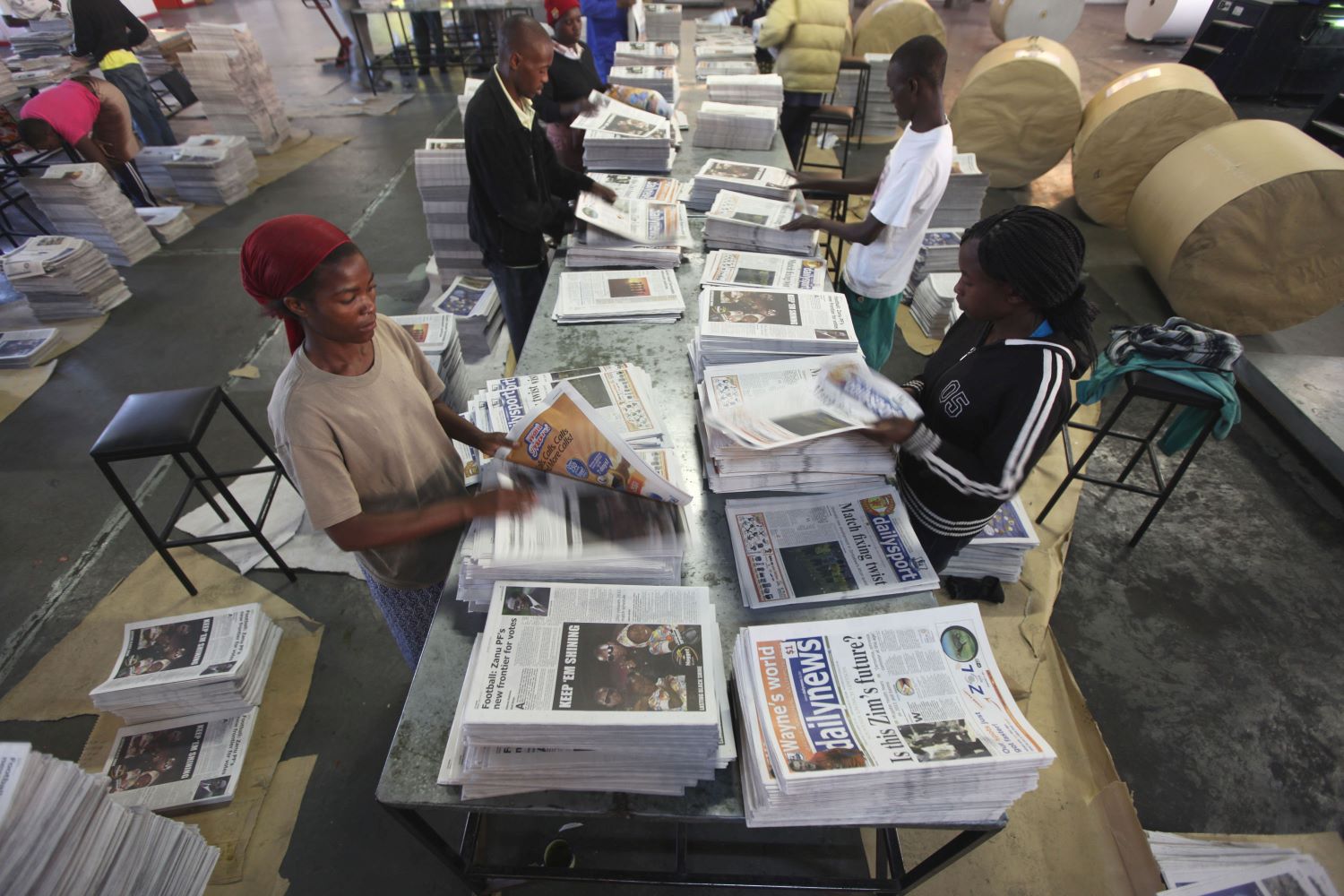
The launch of the Daily News in 1999 brought novelty to the nation after a long period of being starved of a credible, independent daily. With its tagline, “telling it like it is”, the publication promised to offer balanced, alternative news.
The staff complement included some of the most renowned journalistic brains in the county, led by the award-winning Geoffrey Nyarota as editor. Within a year, the tabloid had swiftly gained a sizable readership at the expense of the state-controlled newspapers, where Moyo had direct influence over editorial policy. Its daily circulation reached 105,000 copies, while the Herald’s reportedly fell by 50 percent. The Daily News’ main strength was in speaking truth to power and this attracted sizable enemies, mainly from the state.

The paper’s introduction coincided with the formation of a strong new political party, the Movement for Democratic Change (MDC) in 1999, a move which some saw as a growth in opposition strength.
The entrance of a strong opposition party, just like an alternative press, signalled a direct threat to the one-party state. In 2000, Moyo, previously a rabid critic of the ruling party and its leadership, was appointed into cabinet. After his appointment, he suddenly launched a sustained attack on independent media, the opposition and its entire leadership, while Robert Mugabe accused the Daily News of being a “mouthpiece” for the MDC.
During Moyo’s 2000-2005 tenure as minister, he crafted and promoted repressive laws, such as the Access to Information and Protection of Privacy Act (AIPPA) (2002) and the Public Order and Security Act (2002), which directly attacked freedom of speech and association.
AIPPA, for instance, required journalists and media houses to be licensed to operate in the country. When the Daily News was shut down in 2003 for failing to register with the Zimbabwe Media Commission (ZMC), he was quoted saying: “The Daily News is a victim of the rule of law which it had been preaching since 1999.”

To this day, Moyo denies ever participating in the suppression of press freedom, however, the late William Saidi, news editor of the Daily News at that time, believed AIPPA was used to destroy the paper. “The Daily News had overtaken the government's newspaper, The Herald, in circulation and was accused of influencing the elections in 2002, so as some form of punishment, the government decided they would ban The Daily News,” he told the BBC.
Although Mugabe was re-elected in the 2002 plebiscite, foreign observers dismissed his victory which was marred by widespread violence and intimidation.
‘Running dogs of Imperialism’
In a recent online interview with the Zimbabwean programme, In Conversation with Trevor, Geoffrey Nyarota, founding editor of the Daily News, revealed that the organisation was always a target for the state.
“They viewed us as being agents of the foreign powers who wanted to implement change of government in Zimbabwe,” he said.
Nyarota added that he had unearthed some leads in the two decade-long unresolved bombing saga that he intends to reveal in his forthcoming book. It remains to be seen, however, whether the government or police will show any interest in pursuing the case and finally bringing some closure to all those affected by it.
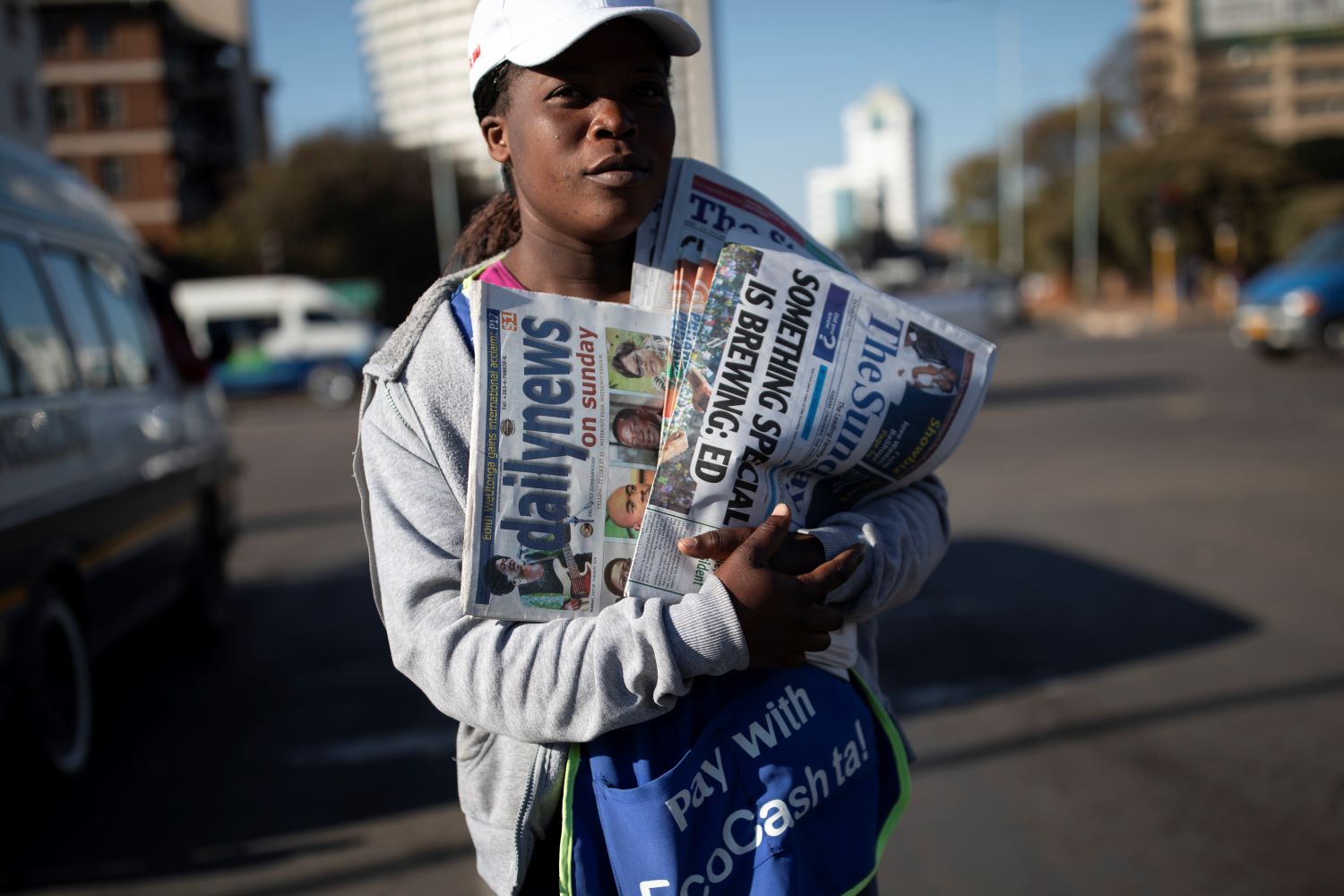

The bombing had far wider-reaching effects on the media industry in Zimbabwe than just one newspaper. The incident accelerated censorship and intolerance towards the journalism profession, fronted by Moyo, using the existing repressive laws.
Nyarota was later repeatedly arrested and was reportedly an assassination target. Going by his actions, Moyo sought to dismantle the private media at all costs. Besides attacking independent media as “running dogs of imperialism”, Moyo was a catalyst in the deportation of Andrew Meldrum, a London-based Guardian newspaper in 2003, after he was deemed “undesirable”.
Today, Zimbabwe is preparing once again for its 2023 elections. Although Moyo now resides in exile following the 2017 coup when he sided with the unpopular Robert Mugabe, the onslaught against the independent media that he initiated in 2000 does not. It continues unabated with police assaults on news rooms, harassment of journalists and the government's new Cybersecurity and Data Protection Bill, which poses a whole new kind of threat to journalism.
Now, just like in 2001, there is no let-up for either the opposition party or independent media, both still chastised as “twin evils”. Until Nyarota’s book hits the bookstores, the nation will have to keep guessing about the events of January 28, 2001.