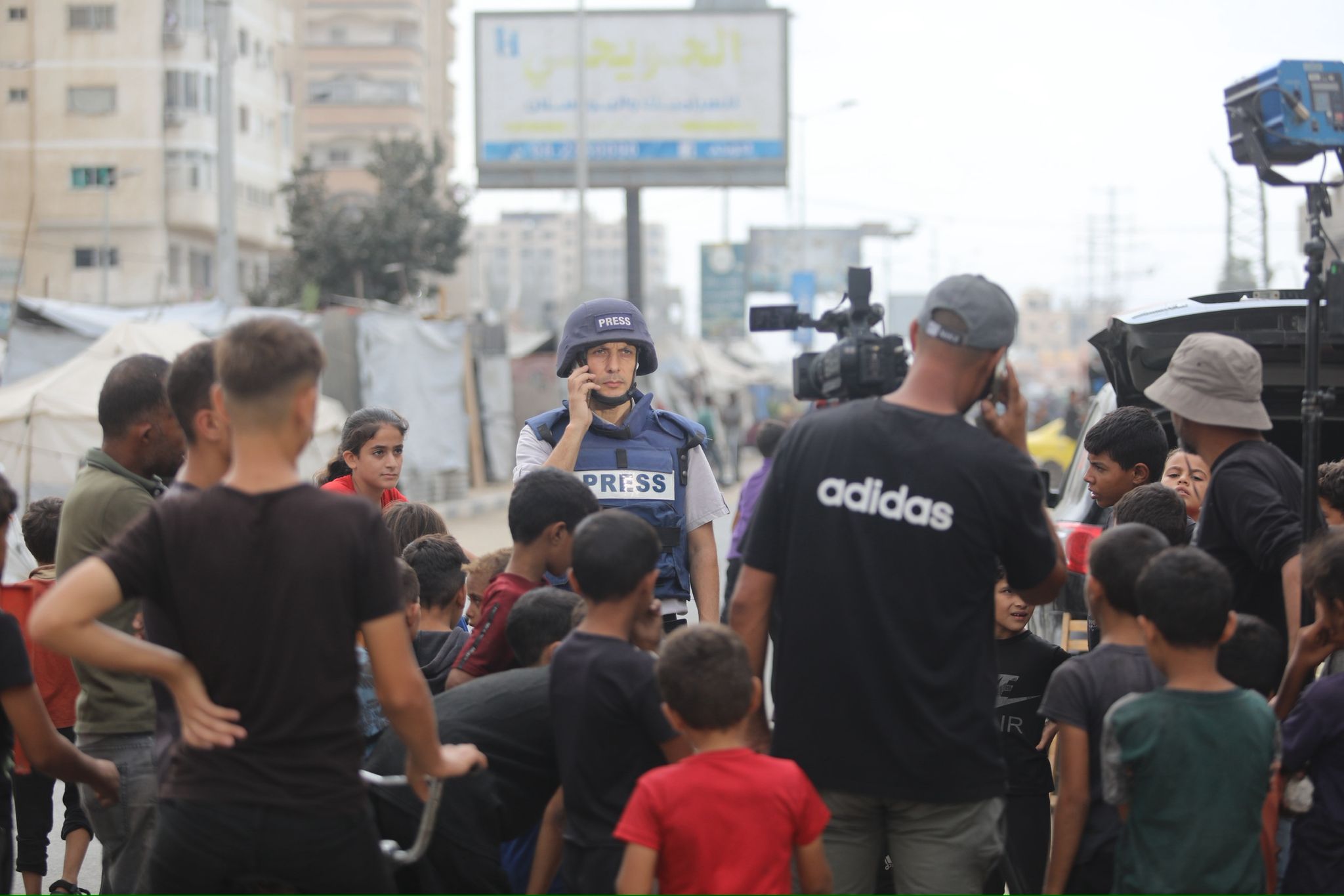
Recent advances in AI are mind-blowing. But good journalism requires certain skills which, for now at least, only humans can master
Like many professions, journalism is facing a relentless advance in AI technology that some fear could be about to overtake human skills, even those that involve creativity and expression.
For journalists, it is somewhat natural to feel a sense of trepidation. However, history has shown us that technological revolutions always create opportunities. Technological advancements might reduce the need for some previous jobs but they do not necessarily eliminate them. The key to survival is the ability to adapt.
Read more:
What is ChatGPT and why is it important for journalists?
AI in the newsroom - how it could work
How to prompt ChatGPT effectively
Understanding the pitfalls of AI in the news room
What happened when I asked ChatGPT to write my article
The printing press did not eliminate scribes, nor did the radio extinguish newspapers. Television, with its revolution in visual news, did not spell the end of the radio and the internet revolution has not killed off any of these earlier forms of media. Indeed, in many countries today, community radio stations remain the most popular form of news consumption.
Each new advance certainly requires learning, adapting and evolving -and this new technological tide is no different. Let’s take a look at some of the human aspects of journalism that will remain crucial and how we can make the most of the changes that are coming our way with the AI revolution.

The power of empathy
At present, no AI, no matter how sophisticated, can replicate the human ability to empathise with other humans. Nor does it have the ability that journalists do to convey what touches and moves them as they connect with and tell the stories of their subjects.
This human connection allows journalists to understand, respect and authentically convey experiences to their readers and broadcast audiences.
Our empathy and sense of understanding are what enable us to tell stories that resonate on a deeply human level
Empathy is a lens through which we view the world. Our human experience of pain, sorrow, fear, happiness and hope allows us to step into the shoes of our subjects and convey what we see through our stories. Our empathy and sense of understanding are what enable us to tell stories that resonate on a deeply human level. Empathy is also the drive that steers us towards a certain story and makes us insist on telling it.
Journalists like Nicholas Kristof who won several awards including the Pulitzer Prize, has been recognised for his empathetic storytelling that sheds light on global human rights issues and social injustice, from human trafficking to gender inequality and poverty. No advanced AI can replicate this human connection. It's the difference between a dry text and a story that touches hearts and changes minds.

Context and critical thinking
A journalist’s role is not merely to report on a list of information but to analyse, fact-check, and interpret them. This critical thinking is further strengthened with the ability to contextualise the situation and linking separate events to produce analysis of logical outcome of events. These human aspects enable us to question, to probe, and to present nuanced perspectives, and to produce in-depth coverage and analysis of the situation we are reporting on. While AI can process a vast amount of data at an unprecedented speed and it can help us flag potential misinformation, it lacks the human capacity for analysis, contextualising and reasoning.
In an era of information overload, AI-generated content, a new drive towards populism and algorithm-triggered viral news, the ability to discern truth from misinformation and disinformation, to sift through the noise and find meaningful information, is more crucial than ever. The human ability for critical thinking is what allows us to question the flood of information, challenge assumptions and present balanced, nuanced perspectives. It's what separates journalists from mere AI-generated content that is trained on all sorts of information, including the flood of misinformation on the internet and the algorithm driven by the repetition of false information.
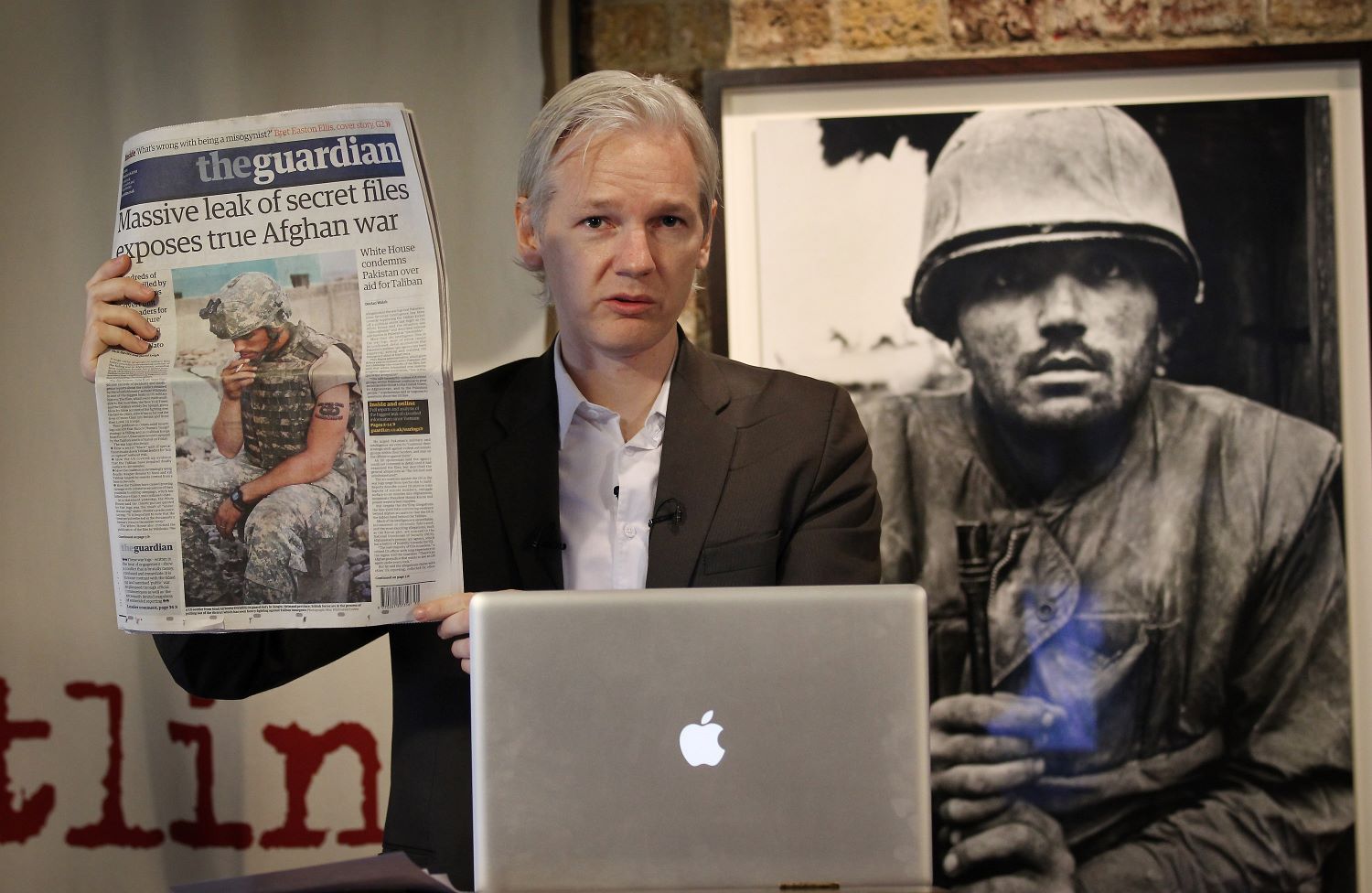

Reporting with integrity
The journalistic code of ethics is the cornerstone of our profession; principles such as truthfulness, fairness, accuracy, impartiality, accountability, fact-based objectivity, respect and protection of sources are the standards that guide our work. Ethics are an inherently human value that earn us the trust of our audience and credibility as professionals.
AI, on the other hand, can be programmed to operate within certain rules, but it lacks the ability to make moral judgments and decisions in sensitive situations. Take the examples of the Pentagon Papers leaks by Daniel Ellsberg, the Wikileaks diplomatic cables leak by Julian Assange and Edward Snowden's leak on NSA spying and data gathering. Independent media made a challenging but ethical decision to publish the revelations from classified documents to hold the US government accountable for its war crimes and to promote transparency. At present, an AI would not be able to understand the context and complexities of such situations, nor would it be able to make an ethical judgement and consider factors like potential harm, public interest and the right to privacy.
No advanced AI can replicate human connection. It's the difference between a dry text and a story that touches hearts and changes minds
We must admit though, that trust gaps exist and vary from one media outlet to another and from one journalist to another. Journalists are held accountable for their work by the public - and the law. They are trained to be accurate and to verify the truthfulness of the information they obtain and they are expected to correct errors and face consequences for any ethical misconduct. If or when an AI generates mistaken or misleading content, it does not learn from its mistakes nor take responsibility for its errors or harm it causes.
As journalists, we can recognise our biases and strive to produce fair reporting when we come across misinformation or misrepresentations of disadvantaged communities. AI can be trained to avoid biases; however, if it is trained using biased data reflecting existing misinformation, disinformation, misrepresentation, and underrepresentation in the real world, AI-generated content will perpetuate these injustices and biases in its output.

An ability to adapt?
The news media landscape is constantly changing and, as journalists, we have been adapting to the technological revolutions from the printing press to the internet. New situations require quick change in the profession like live and war coverage and journalists quickly acquire new skills to deliver the needed reporting.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, journalists had to quickly gain the most up-to-date medical knowledge and learn how to stay safe in order to report daily about the crisis. Our ability to navigate in the face of change has also made our profession more versatile and relevant. The AI revolution is no different; it is a chance for us to learn how to utilise a time-saving tool. AI can help journalists sift through vast amounts of information, detect fake news and content, find sources and contacts and prepare the groundwork for upcoming reports.
The art of storytelling
Journalism is essentially a form of storytelling; it’s about transforming factual information and testimonies into narratives that inform, resonate and inspire. Human contact and emotional understanding allow us to connect with the people whose stories we want to tell. Journalists build relationships with their sources over time and, as a result, gain access to information that we may not otherwise have obtained, something an AI will not be able to do in its current form. An AI may generate content or a report imitating the style of certain famous people, but will still lack the ability to tell a story in a nuanced way with emotional resonance.
Furthermore, the human expression of their five senses has a tremendous importance in storytelling. When we describe a warzone through the smell of blood or stench of corpses, or when we see happiness in people jubilant in celebrations, we share something only humans can understand. Storytelling is a gained skill of the imagination that transforms information into understanding and news into knowledge. Digital journalism expert Paul Bradshaw describes AI tools like ChatGPT “as unreliable narrators, with their priority being plausible, rather than true, stories”.
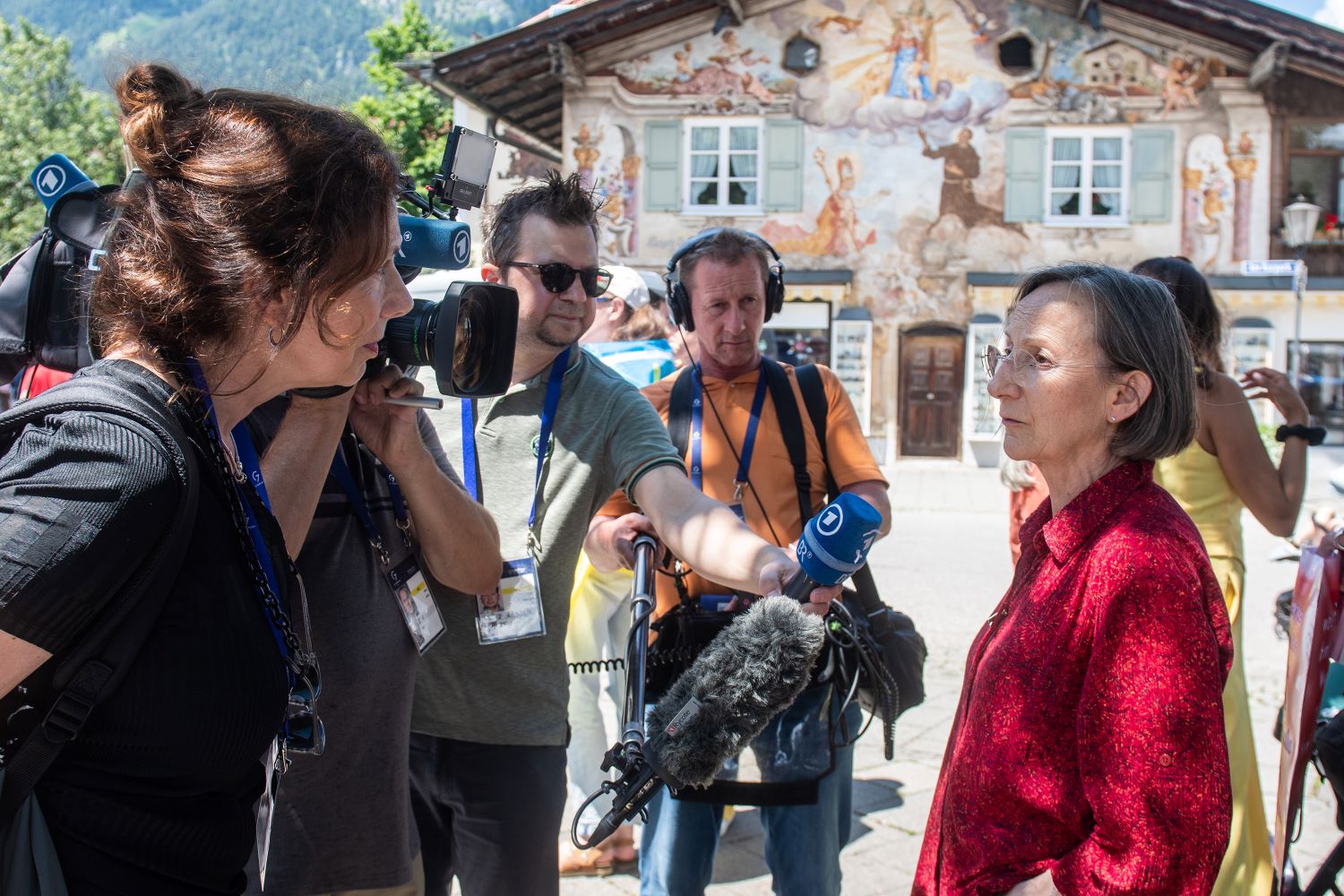

Intuition and interviews
While conducting in-depth interviews, journalists often need to ask follow-up questions. They read body language to decide on the pace of the interview and adjust their questions and approach according to the responses. There is an added layer to intuition and the ability to understand the subject; it’s the understanding of culturally infused body language. This ability to “read the air” as we call it in Japanese - or “feel the pulse” in Arabic - is a human intuition and a valuable asset in human communications. A sophisticated AI may be programmed to literally read the human pulse and analyse comfort or discomfort, but intuition is not something it can be capable of.
The real race today is among humans; those who adapt quickly and learn how to utilise AI tools will experience smooth passage to the next stage
As we navigate the AI revolution, our human qualities will remain essential for journalism. AI is [so far] incapable of feeling, taking responsibility, making ethical decisions, contextualising, scrutinising, reading body language or and storytelling - all skills that are at the core of journalism as a profession.
The real race today is among humans; those who adapt quickly and learn how to utilise many useful AI tools within their profession will experience smooth passage to the next stage. Journalists have proven to be among the first to change and adapt, and they will especially need an AI assistant to help identify the ever-increasing misinformation and fake news.
Governments and international organisations have yet to set rules for the ethical use of AI-generated content, so it is up to us journalists to face this latest new tide with ethical integrity and critical thinking, while upholding the values of accountability, truthfulness and fairness as we step into the new media landscape.










































