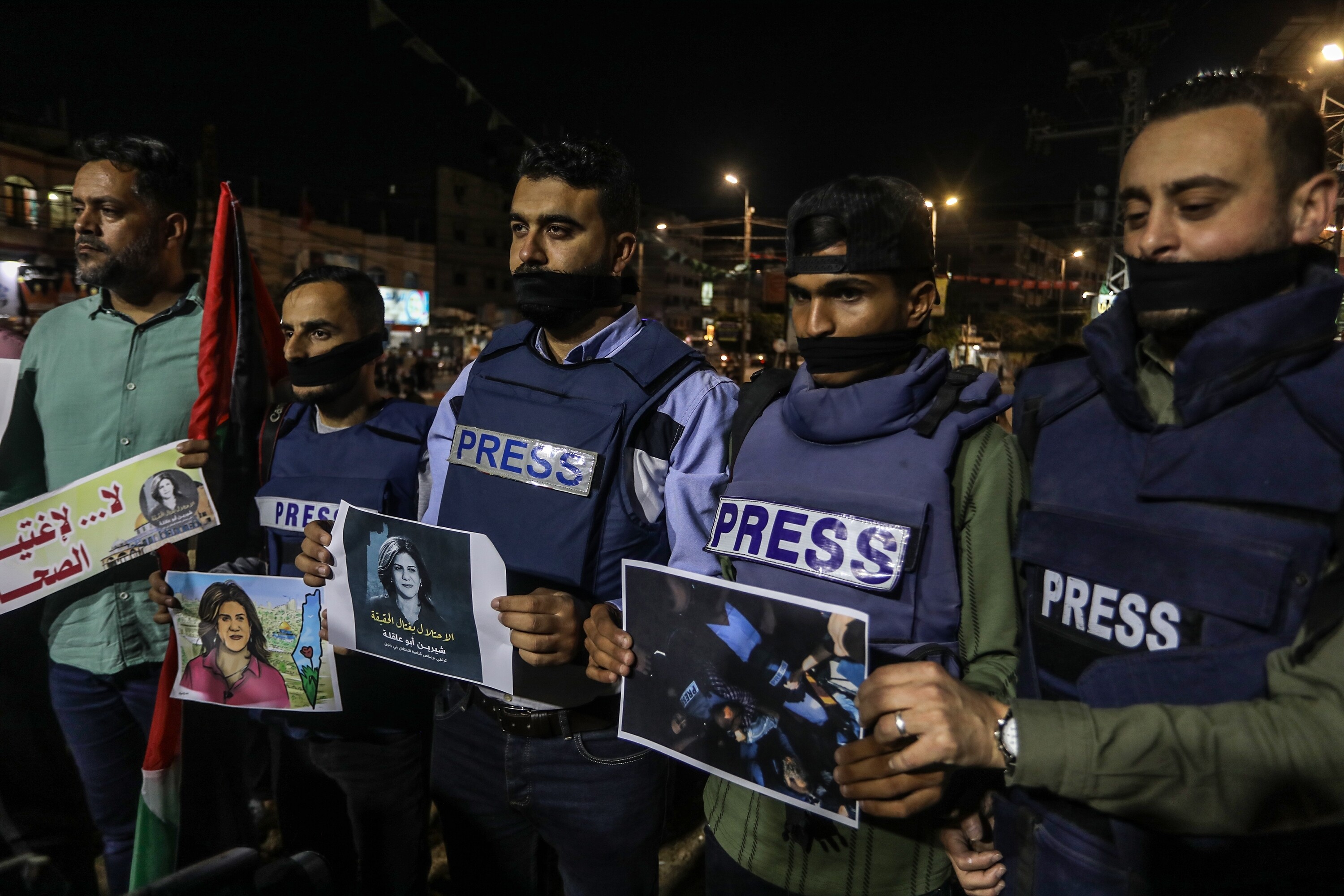
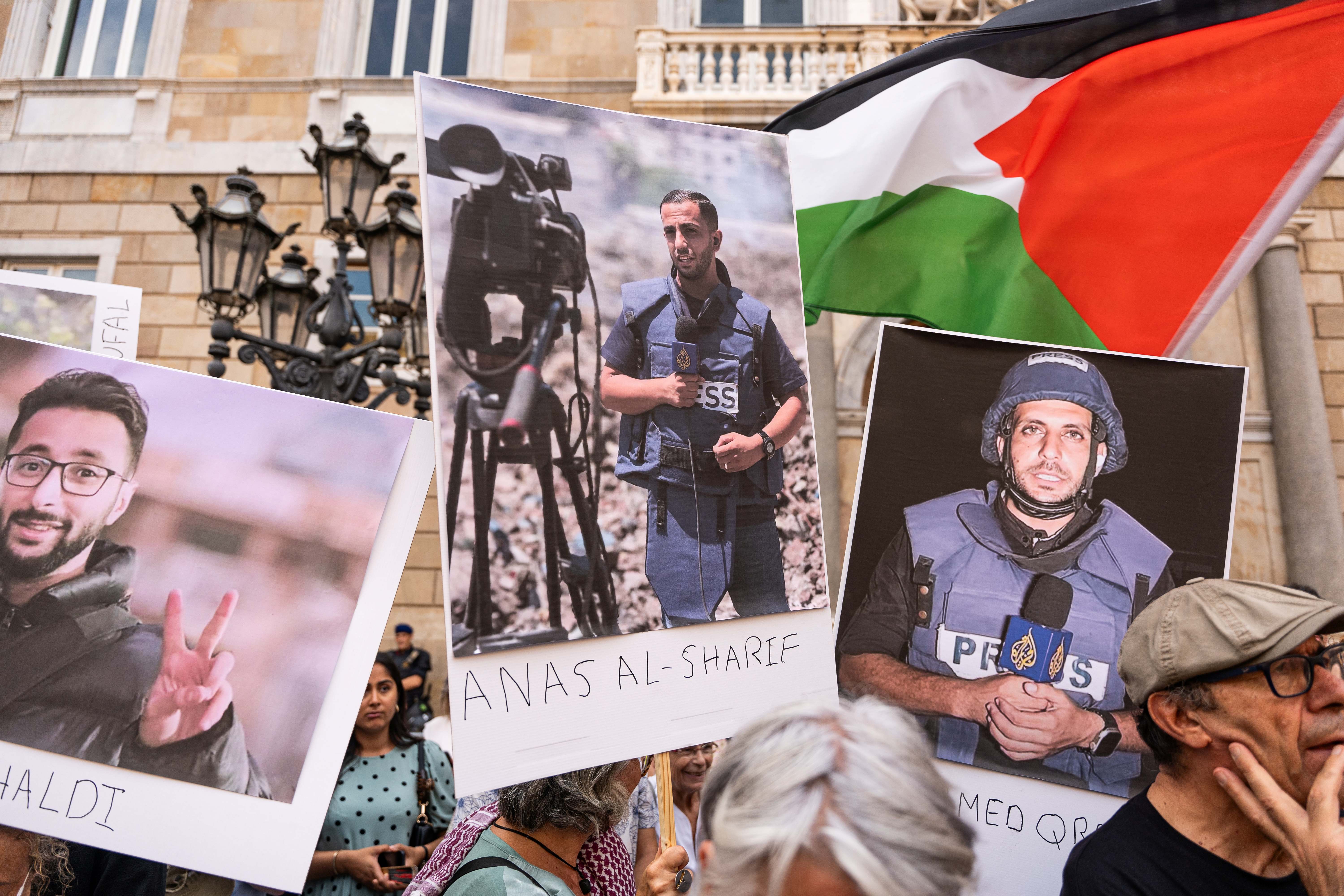
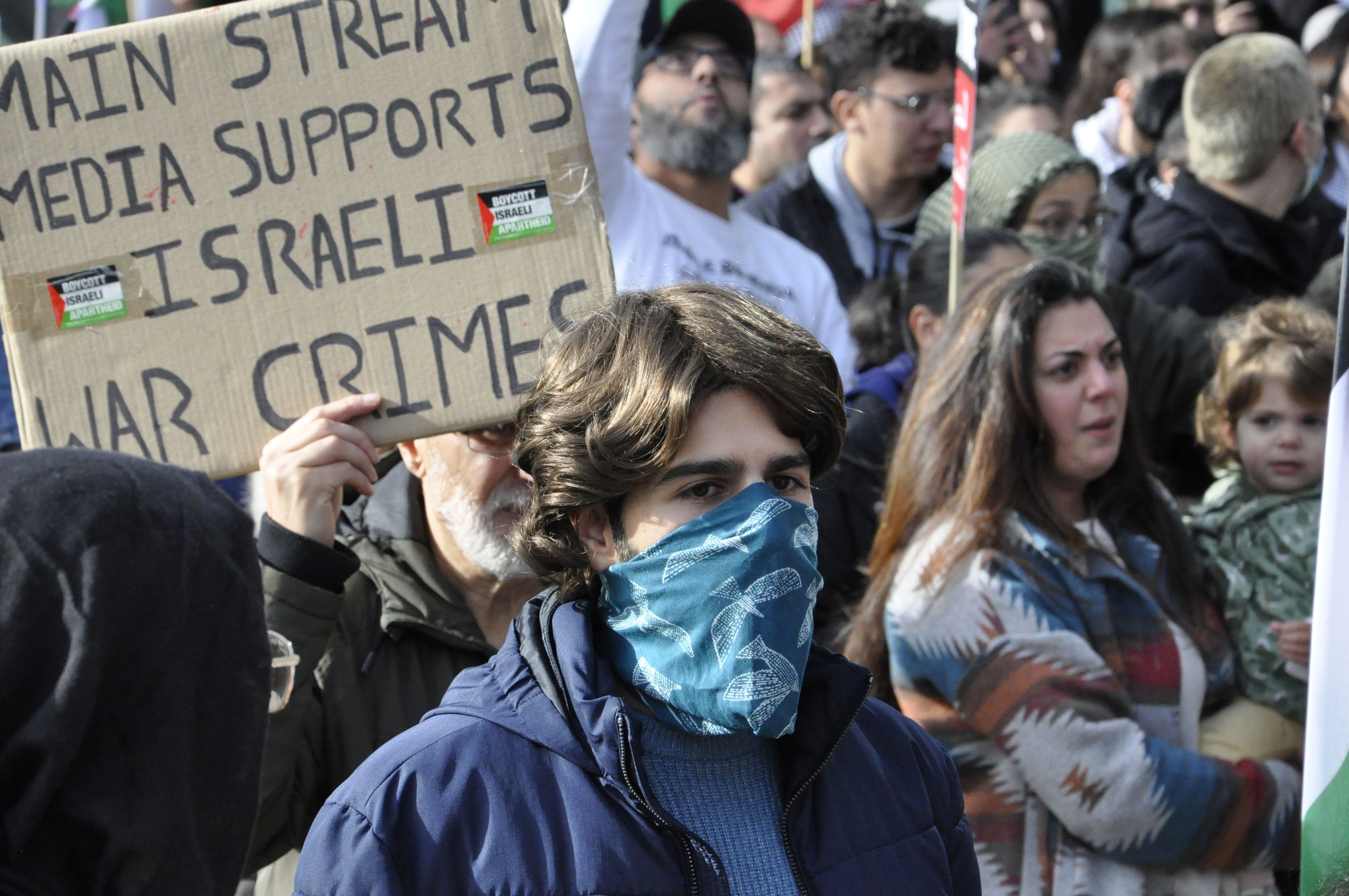
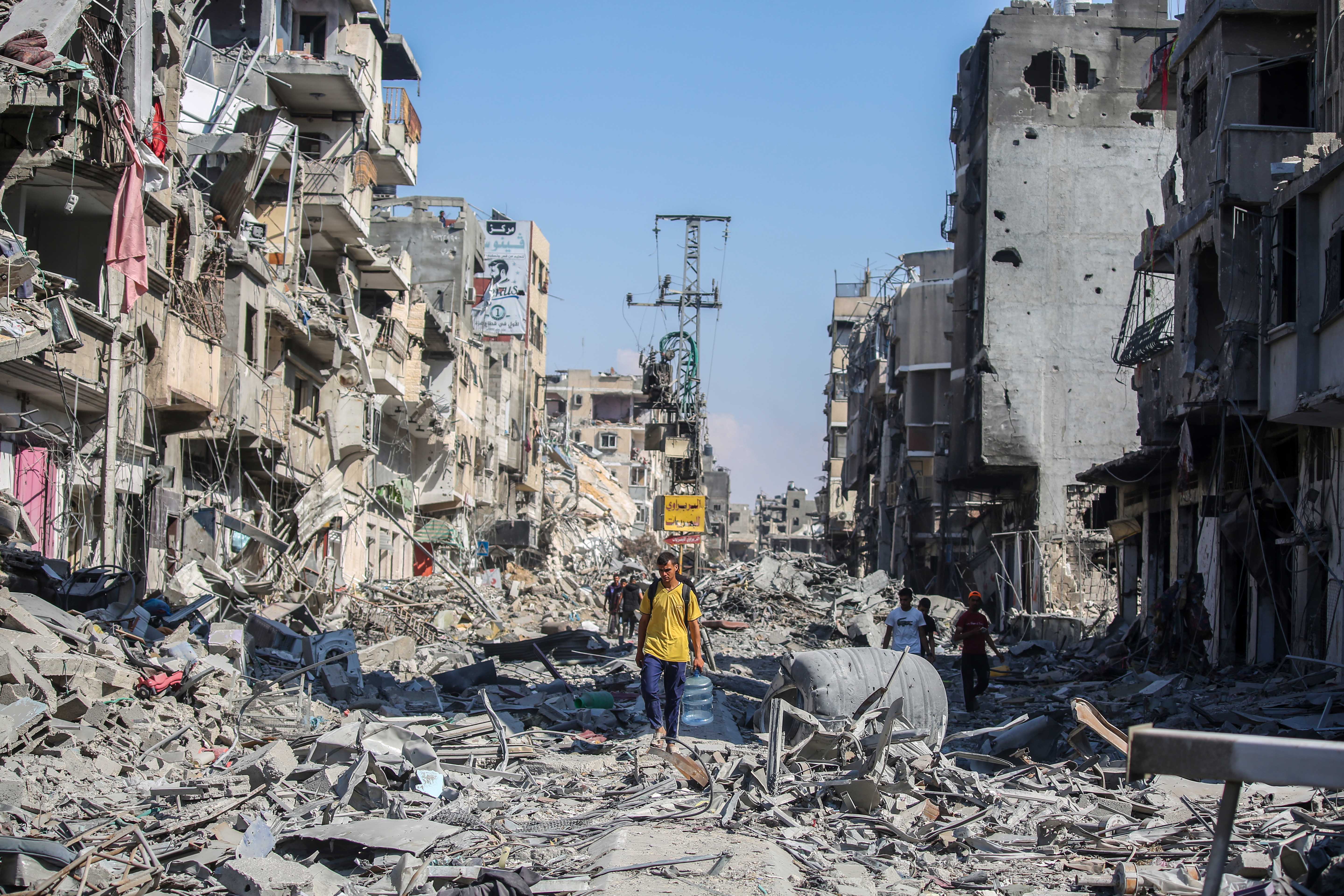
Over the years, many journalists have fallen victim to recurrent Israeli occupying forces' attacks on the Gaza Strip. It has become apparent that the Israeli occupying forces specifically target media teams, deliberately destroying media buildings with their staff and infrastructure in an attempt to prevent the dissemination of their violations against the Palestinian people.
This series of practices culminated in the deaths of 71 (as of December 12) journalists and the injuries of dozens more, in addition to the complete or partial destruction of 50 media institutions, during the Israeli aggression on the Gaza Strip on October 7. These figures, according to the Palestinian Journalists' Syndicate, raise questions about the stance of international humanitarian law on Israel's violations.

The law protecting journalists prohibits acts such as killing, maiming, torturing, or taking them hostage. During military operations, journalists must not be subjected to harsh or dehumanizing treatment.
How Does the Israeli Occupation Obscure the Truth?
"The occupation directly targets us as journalists, whether by live bullets or missiles. A journalist in the field reports the news without knowing if he will remain alive or become a martyr and thus become the news himself," began Mohammed Subh, a Palestinian journalist in the Gaza Strip, discussing the Israeli violations faced by journalists.
Subh narrates the challenges he and his colleagues face while covering the Israeli aggression in Gaza. These include internet blackouts and constant power outages that hinder journalists from working quickly, as well as preventing them from performing their duties and reporting on the events on the field.

The Israeli occupation also targets the families of journalists, forcing journalists to prioritise the safety of their families over covering events. Journalists fear being targeted while travelling in vehicles or when they are at the direct scene of incidents. There's also a shortage of offices, cameras, journalistic equipment, broadcasting vans and news transportation vehicles, many of which have been targeted, according to Subh.
Commenting on this, Saif Al-Jundi, a professor of law specialising in human rights issues, believes that the deliberate direct targeting of journalists by Israeli occupying forces constitutes "killing the truth" and represents a war crime under the statutes of the International Criminal Court—the foundational Rome Statute of 1998. He states that assaults on journalists aren't taken in a singular context merely as crimes, but they fall under a more severe category of violations according to these referred rules. Al-Jundi further adds, "The Arab world today is experiencing a justified crisis with the concept of international law due to the Israeli occupation's impunity and not being held accountable—or even held responsible—for war crimes committed against civilians, including children, women and the elderly."
He also adds, "This is also due to the lack of effective measures against crimes committed against journalists. The ramifications of this crisis will have a broader horizon post-humanitarian catastrophe in the Gaza Strip.”
Does International Humanitarian Law Protect Journalists?
International humanitarian law, applicable in situations of war and armed conflicts, contains only two references to those working in the fields of journalism and media. Firstly, Article 4 of the Third Geneva Convention covers individuals accompanying the armed forces without being an actual part of them, such as civilians on board military aircraft, war correspondents, and other similar individuals. Secondly, there is Article 79 of the First Additional Protocol, which mentions measures to provide protection and allow access to an identification card issued by the government of the state in which the journalist is a national, where they reside, or where the news agency employing them is located, certifying their status as a journalist.
The military should not target locations or equipment that are used by journalists to cover the conflict. If military necessity dictates attacking areas where journalists maybe present, occupying troops must give sufficient warning to enable journalists to evacuation.
Journalist researcher Hussein Charaira, in his discussion with Al Jazeera Journalism Review, states that "journalists are essentially afforded the general protection granted to civilians under the Fourth Geneva Convention of 1949 and the two additional protocols annexed to it from 1977. These conventions represent the most effective general means for the protection of journalists working in danger zones.".
Concerning journalists undertaking risky tasks during armed conflicts or in tension areas, they are considered civilians according to Article 79 of the First Protocol of 1977. Based on that, they are entitled to international legal protection against any aggression they might face. This protection is contingent upon them not engaging in activities that might jeopardise their status as civilians or journalists, explains Charaira.
Charaira further elaborates that a journalist should be discerning in "assessing the importance of the information near a tank and far from it, understanding its added value and the purpose behind it. Some journalists get embroiled in details insignificant to the public but crucial from an intelligence perspective, thereby placing themselves in the crosshairs of military operations.".
Security Council Resolution 2222 affirms the necessity to protect journalists, media professionals, and associated personnel engaged in dangerous professional missions in areas of armed conflict who shall be considered civilians. The resolution also recalls that media equipment and installations constitute civilian objects, and in this regard, they shall not be the object of attack or reprisals.
Protecting civilian media facilities and places, preventing the inhumane or harsh treatment of journalists upon arrest, and preventing the confiscation or destruction of journalistic equipment and documents.
What Rules-of-War Apply to Palestinian Journalists?
What are the rules of war that the Israeli occupation applies to journalists in Gaza? A journalist posed a question to the American President, Biden, while aboard the presidential plane en route from Tel Aviv to Washington, D.C. The journalist inquired whether Israel was adhering to the laws of war during its attack on the Gaza Strip. Biden simply responded, "It was nice talking to you," according to a White House statement.
So, what are the rules of war that Israel should abide by, and do they specify the protection of journalists? Professor of Public International Law, Dr. Imran Muhafeza, stated in a conversation with Al Jazeera Journalism Review that "The law that protect journalists include the prohibition of killing, maiming, torturing, or taking them hostage. Journalists should not be subjected to treated in a harsh or dehuminising manner during military operations. ."
Dr. Muhafeza added, "Furthermore, the military should not target locations or equipment that are used by journalists to cover the conflict. If military necessity dictates attacking areas where journalists maybe present, occupying troops must give sufficient warning to enable journalists to evacuation.."

The rules of International Humanitarian Law that protect journalists, according to journalist-researcher Hussein Charaira, include "protecting civilian media facilities and places, preventing the inhumane or harsh treatment of journalists upon arrest, and preventing the confiscation or destruction of journalistic equipment and documents."
Regarding the Fourth Geneva Convention of 1949, it is concerned with the protection of civilians during international conflicts. It includes a provision, as in all four Geneva Conventions, for protection in non-international armed conflicts.
It also protects civilians under occupation and civilian properties, including homes, schools, and establishments, as well as hospitals and places of worship. This convention protects journalists only as civilians, since the definition of a civilian applies to journalists. A civilian is defined as an individual who does not fit the definition of a combatant.
Despite the journalists' role becoming significantly more challenging and dangerous in wars as they operate under fire, International Humanitarian Law has overlooked providing special protection for them as individuals performing risky duties while covering armed conflicts and wars. They are granted the general legal protection that encompasses civilians, considering them civilians and not military targets.